Let’s discuss the SCCM Console Slowness Issues and How to Fix SQL Query Timeout Configuration Manager. This post addresses issues that may occur after migrating from SCCM/ConfigMgr SQL 2012 to SQL 2014 or 2016.
This issue could be prevalent for SCCM/ConfigMgr Admins once SQL servers are migrated to 2014 or 2016 versions. This is the first time I have a guest blogger, Kannan C S, sharing his experience. SCCM Console Slowness Issues How to Fix SQL Query Timeout Configuration Manager ConfigMgr?
He is an expert in SCCM/ConfigMgr and has several years of experience in SCCM and system center. I will let Kannan C S explain his experience in detail.
Hi All, I’m Kannan C S, and I work as a Sr. Infra Architect at a leading IT company with 15 years of IT experience. I have been with Configuration Manager [Designing, Implementation, Migration, and Support], System Center Orchestrator [Designing and Implementation], and Windows Server support. You can refer to my blog here.

- SCCM WSUS Cleanup FIX SCCM Scan Timeout Errors
- Free SCCM Training 37 Hours of Latest Technical Content Lab Setup
- Top 50 Latest SCCM Interview Questions and Answers
- Top 50 Latest Intune Interview Questions And Answers
Table of Contents
SCCM Console Slowness Issues and How to Fix SQL Query Timeout Configuration Manager
This blog post will briefly overview the best practices SCCM/ConfigMgr admins must follow before and after the SQL Server 2014 or 2016 migrations. This also covers guidelines on troubleshooting issues such as SQL query timeout and SCCM/ConfigMgr console slowness.
Microsoft recommends the compatibility level below for SQL Server when SCCM DB runs with this SQL instance.
| SQL Server Version | Support compatibility level values | Recommended compatibility level for ConfigMgr/SCCM |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Server 2016 | 130,120,110,100 | 130 |
| SQL Server 2014 | 120,110,100 | 110 |
The following plan affecting trace flags is available in Microsoft SQL Server 2014 when SCCM CB is running with this instance of SQL.
| Trace Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| 9481 | Use when running SQL Server 2014 with the default database compatibility level 120. Trace flag 9481 forces the query optimizer to use version 70 (the SQL Server 2012 version) of the cardinality estimator when creating the query plan. |
| 2312 | Use when running SQL Server 2014 with database compatibility level 110, which is the compatibility level for SQL Server 2012. Trace flag 2312 forces the query optimizer to use version 120 (the SQL Server 2014 version) of the cardinality estimator when creating the query plan. |
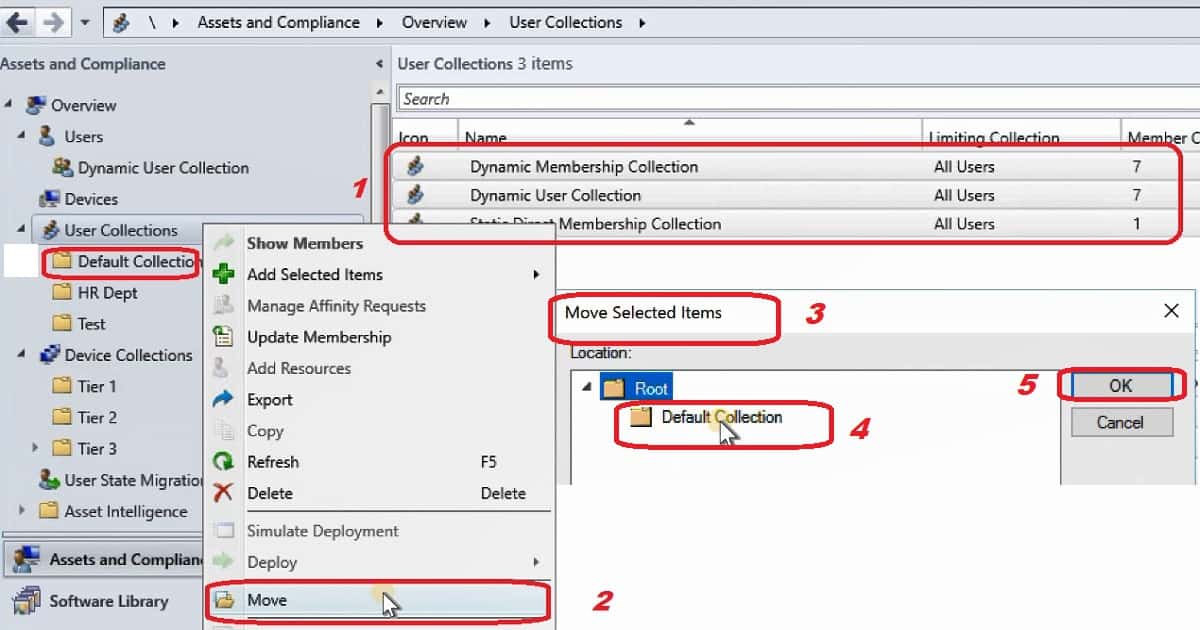
Getting Started – SCCM Console Slowness Issues and How to Fix SQL Query Timeout Configuration Manager
In the SQL 2014 XML plan, a new attribute in StmtSimple called CardinalityEstimationModelVersion exists. When the value is 120, the new cardinality estimator is used. If the value is 70, the old cardinality estimator is used.
Note that if my database compatibility level was for an earlier level, I see the following.
<StmtSimple StatementCompId=”1″ StatementEstRows=”1597640″ StatementId=”1″ StatementOptmLevel=”FULL” CardinalityEstimationModelVersion=”70″ StatementSubTreeCost=”21.0895″ StatementText=”SELECT c.[charge_no],
 m.[lastname],
 m.[firstname]
FROM [dbo].[charge] AS c
INNER JOIN [dbo].[member] AS m ON
 c.[member_no] + ‘ ‘ = m.[member_no] 
OPTION (RECOMPILE)” StatementType=”SELECT” QueryHash=”0xF698FF11488A3A3D” QueryPlanHash=”0x41F421A8F51D61CE” RetrievedFromCache=”false”>
After migrating SQL 2012 to SQL 2014 or 2016, run the following query to identify the SQL CE compatibility level in use for the SCCM/ConfigMgr database.
SELECT name, compatibility_level FROM sys.databases
See the following example of a specific-query test run at the SQL 2012 CE level:
Note: ANN00012 is an example of Deployment ID; it will vary based on your environment.
select all SMS_DeploymentSummary.ApplicationName,SMS_DeploymentSummary.AssignmentID,SMS_DeploymentSummary.CI_ID,SMS_DeploymentSummary.CollectionID,SMS_DeploymentSummary.CollectionName,SMS_DeploymentSummary.CreationTime,SMS_DeploymentSummary.DeploymentID,SMS_DeploymentSummary.DeploymentIntent,SMS_DeploymentSummary.DeploymentTime,SMS_DeploymentSummary.DesiredConfigType,SMS_DeploymentSummary.EnforcementDeadline,SMS_DeploymentSummary.FeatureType,SMS_DeploymentSummary.ModelName,SMS_DeploymentSummary.ModificationTime,SMS_DeploymentSummary.NumberErrors,SMS_DeploymentSummary.NumberInProgress,SMS_DeploymentSummary.NumberOther,SMS_DeploymentSummary.NumberSuccess,SMS_DeploymentSummary.NumberTargeted,SMS_DeploymentSummary.NumberUnknown,SMS_DeploymentSummary.ObjectTypeID,SMS_DeploymentSummary.PackageID,SMS_DeploymentSummary.PolicyModelID,SMS_DeploymentSummary.ProgramName,SMS_DeploymentSummary.SecuredObjectId,SMS_DeploymentSummary.SoftwareName,SMS_DeploymentSummary.SummarizationTime,SMS_DeploymentSummary.SummaryType from fn_DeploymentSummary(1033) AS SMS_DeploymentSummary where SMS_DeploymentSummary.DeploymentID = 'ANN00012' option (querytraceon 9481)Solution:-
SCCM Console Slowness Issues How to Fix SQL Query Timeout Configuration Manager ConfigMgr? If the above query returns a faster result, then no change is required in your environment. Before making any changes to the DB, take a backup!!
If the above test indicates that performance gains can be achieved, use the following command in SQL Server Management Studio to set the ConfigMgr/SCCM database running on SQL Server 2014 to the SQL Server 2012 CE compatibility level.
ALTER DATABASE <CM_DB> SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL = 110; GO
Use the following to set an SCCM/ConfigMgr database running on SQL Server 2016 to the SQL Server 2016 CE compatibility level.
ALTER DATABASE <CM_DB> SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL = 130; GO
Replace <CM_DB> with your ConfigMgr/SCCM site database name in the two examples above.
Important
However, when a database is upgraded from an earlier version of SQL Server, it retains its existing compatibility level if it is at the minimum allowed for that instance of SQL Server.
Upgrading SQL Server with a database at a compatibility level lower than the allowed level automatically sets the database to the lowest compatibility level allowed by SQL.
Conclusion
One of the performance improvements in SQL Server 2014 is the redesign of cardinality estimation. The cardinality estimation (CE) component is called the cardinality estimator.
It is the essential component of the SQL query processor for query plan generation. Cardinality estimates are predictions of the final row count and row counts of intermediate results (such as joins, filtering, and aggregation).
These estimates directly impact plan choices such as join order, join type, etc. Before SQL Server 2014, the cardinality estimator was primarily based on SQL Server 7.0 codebase.
SQL Server 2014 introduces a new design, and the new cardinality estimator is based on research on modern workloads and learning from experience.
Resources
We are on WhatsApp now. To get the latest step-by-step guides, news, and updates, Join our Channel. Click here. HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
Anoop C Nair is Microsoft MVP! He is a Device Management Admin with more than 20 years of experience (calculation done in 2021) in IT. He is a Blogger, Speaker, and Local User Group HTMD Community leader. His main focus is on Device Management technologies like SCCM 2012, Current Branch, and Intune. He writes about ConfigMgr, Windows 11, Windows 10, Azure AD, Microsoft Intune, Windows 365, AVD, etc.



What Deployment ID should I use for running this query?