Let’s see how to perform SCCM WSUS Cleanup and FIX SCCM Scan Timeout Errors. I think this post will help you FIX the SCCM WSUS cleanup or maintenance issues. It will also help the admins who manage the SCCM infrastructure. I’m sharing my implementation experience with this post on several other blogs about the same topic.
There are different WSUS cleanup options available. As the first step, I would try the SCCM console setting to clean up WSUS. This post will also show how to set up the WSUS Cleanup Task from the SCCM console. I have been inspired by the blogs mentioned in the references section of this post.
How to Setup WSUS Cleanup Task from SCCM console Configuration Manager ConfigMgr MEMCM? There is a practice to run the WSUS clean-up task from the WSUS console. Is that the best practice from the SCCM perspective when WSUS is used as part of SUP?
However, cleaning up WSUS is an important activity for SCCM admins to do to maintain a healthy SUP and SCCM environment. There are two options for setting up WSUS cleanup maintenance scheduled tasks from the SCCM console.
Table of Contents
SCCM WSUS Cleanup FIX SCCM Scan Timeout Errors – The First Option is to Set up WSUS Cleanup Maintenance Activity from the SCCM Console
In SCCM CB, there is an option to schedule the WSUS cleanup while setting up the SUP site system role. This option is part of the SUP setup wizard on the WSUS Maintenance page.
- Navigate to \Administration\Overview\Site Configuration\Sites
- Or you can configure it from Software Update Point Component Properties from Configure site components -> Software Update Point.
I have enabled all three options to perform WSUS clean-up. This is a good initiative; you don’t need to run the WSUS clean-up wizard from the WSUS console. This was against the best SCCM practices of SCCM.
The SCCM best practice is NOT to open the WSUS console and make any changes from it when using SUP.
- Decline expired updates in WSUS according to supersedence rules
- Add non-clustered indexes to the WSUS database
- Remove Obsolete updates from the WSUS database
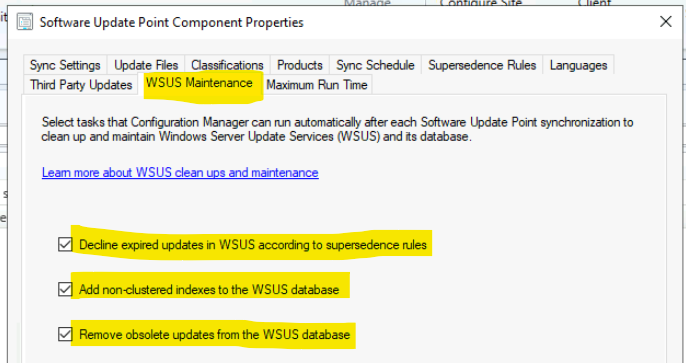
WSUS Cleanup SuperSedence Rules
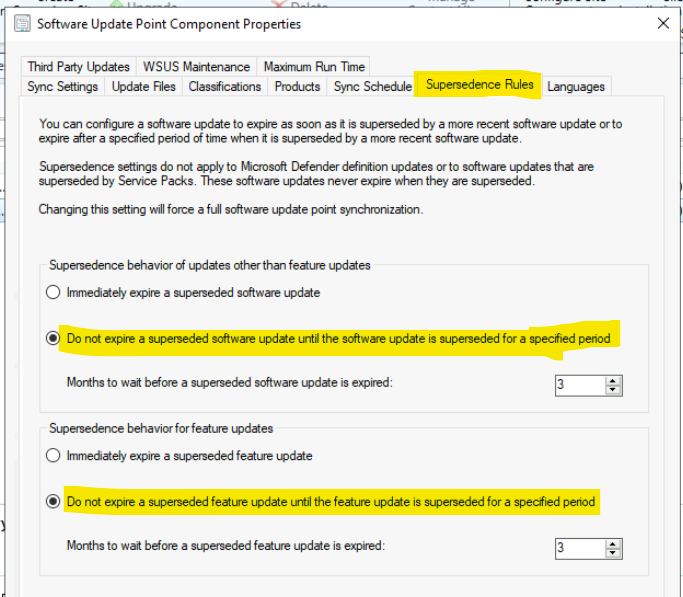
The second option to schedule the WSUS cleanup for your SCCM environment is under settings – Configure Site Components – Software Update Point (SUP) Component properties – Supersedence Rules TAB.
This option is useful when you forget to enable the WSUS Cleanup task during the SUP installation on your SCCM CB server.
When you select to run the WSUS clean-up task from the SCCM console, it will run at the next software update synchronization.
The expired software updates are set to a status of decline on the WSUS server. The Windows Update Agent on computers will no longer scan these software updates.
Below are the two options under the Supersedence behaviour of updates other than feature updates. The screenshot has the details that I recommend for various reasons.
- Immediately expire a superseded software update.
- Do not expire a superseded software update until the software update is replaced for a specific period.
- Months to wait before a superseded software update expires: 3 months.
Supersedence behaviour for feature update options is available in the second section (for feature updates) of the settings under the Supersedence tab of the WSUS Cleanup configuration.
- Immediately expire a superseded Feature update.
- Do not expire a superseded Feature update until the software update is replaced for a specific period.
- Months to wait before a superseded software update expires: 3 months.
Will the WSUS Cleanup Task from the SCCM Console be Applicable for Multiple SUPs and Secondary Site SUPs?
I have not tested this for secondary site SUPs and multiple SUPs on the same site with Windows Internal Database. But I think it’s the same when you have numerous secondary site SUPs and multiple SUPS on the same site.
If the WSUS cleanup task configured in the SCCM CB console is not working as expected, it’s better to raise a support case with Microsoft or run the WSUS clean-up wizard from the WSUS console.
Why Perform WSUS DB Maintenance or Cleanup
The following are the high-level activities of Software Update clients that lead to scanning timeout errors. To fix scan timeout errors in your workplace environment, you must regularly perform WSUS DB maintenance or cleanup.
- The catalogue file updates the metadata information whenever the SUP syncs with Microsoft.
- The catalogue file size also increased every time post the SUP sync with Microsoft.
- The catalog file has all updated (Active, Superseded, Expired) patch information based on Microsoft product selection in the environment.
- Due to the above steps, clients often fail to complete the scan due to timeout errors or cannot load the catalog file.
For better performance for SUS DB with active patch information, we need to perform WSUS maintenance activity at a monthly interval. SCCM WSUS Maintenance cleanup tasks will help you to understand better.
Better Understand SCCM Icons – Software Update
In SCCM, various icons convey important information, especially regarding software updates. The table below helps you to show the different Icon, Patch statuses and descriptions.
| Icon | Patch Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Active | These Green icons indicate ACTIVE/ available updates ready for deployment | |
| Expired | The black X icons represent expired SCCM software updates. You can also identify expired software updates by viewing the Expired column for the software update when it displays in the SCCM console. | |
| Superseded | The yellow star icon represents a superseded SCCM software update. You can also identify superseded software updates by viewing the Superseded column for the software update when it displays in the SCCM console. | |
| Invalid | The icon with the red X represents an invalid software update. Invalid SCCM software updates are in active deployment, but for some reason, the content (software update files) is not available. | |
| Metadata | Blue icons mean Metadata-only SCCM software updates are available in the SCCM console for reporting. You cannot deploy or download metadata-only software updates because a software update file is not associated with the software updates metadata. |
Steps Involved in SCCM WSUS Maintenance Tasks
Three (3) steps are involved in these SCCM WSUS Maintenance tasks. These three tasks are explained in the below sections of the post with more details.
- Re-index the WSUS DB
- Cleanup Obsolete Updates
- Decline superseded updates
Important:
- Do not sync your SUPs during this SCCM WSUS Maintenance process, as you may lose some of the work you have already done if you do.
- Select the non-patched Product and Classification in the Software Update Point (SUP) configuration.
[Related Post – How to Setup WSUS Cleanup Task from SCCM console]
How to Identify & Connect the WSUS DB
When you have SCCM secondary servers or remote SUP servers, you might have installed WSUS DB on the Windows Internal Database. I don’t recommend using Windows Internal Database and SQL Express versions to install WSUS DB. WSUS DB can be installed on SQL Server or Windows Internal Database (WID).
For WSUS DB installed on SQL Server:
If WSUS DB is installed on SQL, you connect the WSUS DB using SQL management studio.
For WSUS DB Installed on Windows Internal Database (WID):
- Download and install SQL Management Studio
- Connect the SUS DB with the below options,
- If your OS is Windows Server 2012, use \\.\pipe\MICROSOFT##WID\tsql\query
- If you are not running Windows Server 2012, enter \\.\pipe\MSSQL$MICROSOFT##SSEE\sql\query
Note: Always run the SQL Management Studio with administrator privilege mode; the query will return the execution error.
Before running the SCCM WSUS maintenance task, follow the task execution in the order mentioned in the table below. Below are more details about the SQL 1, SQL 2, SQL 3, and SQL 4 tasks.
| Software Update Point | Sync Source | To find the Number of Obsolete Updates | Re-index job (Bottom to Top) | Cleanup Obsolete Updates (Bottom to Top) | Decline Superseded Updates (Top to Bottom) |
| Server 1 | Microsoft | SQL 1 | SQL 2 ( once the SQL 3 job is completed for downstream servers) | SQL 2 ( SQL 2 re-index job is completed) | SQL 4 (1st Run) |
| Server 2 | Server 1 | SQL 1 | SQL 2 ( 1st run concurrently) | SQL 3 ( 1st run concurrently) | SQL 4 (2nd Run or currently run post upstream server job completion) |
| Server 3 | Server 1 | SQL 1 | SQL 2 ( 2nd run or concurrently after 1st run) | SQL 3 ( 2nd run or concurrently after 1st run) | SQL 4 (2nd Run or currently run post upstream server job completion) |
Find the Number of Obsolete Updates from SQL Management Studio (SQL 1)
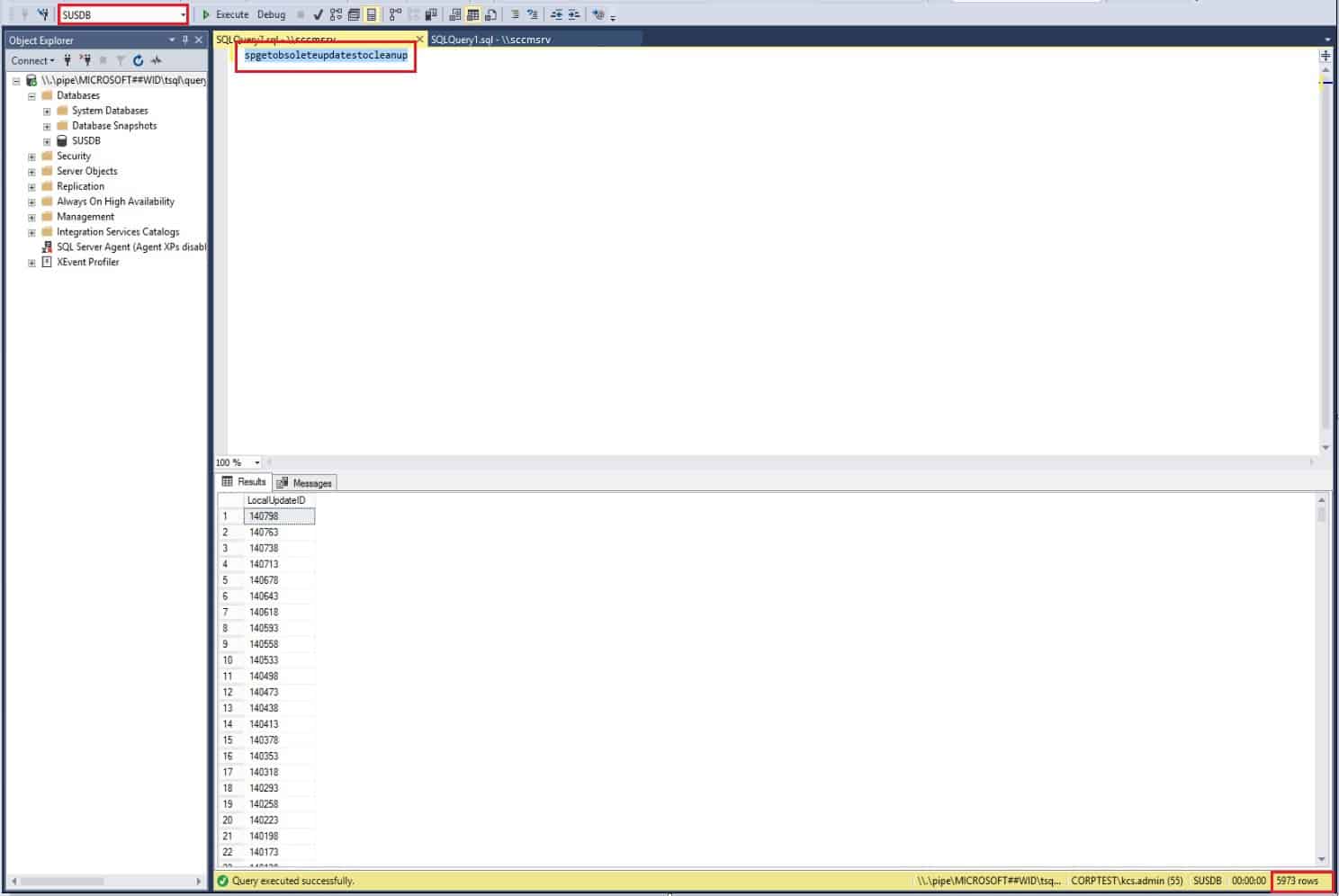
To find the number of obsolete updates present in the SCCM -managed WSUS database, execute the below query. This step is the first step toward the cleanup of SCCM WSUS Maintenance. The result will be displayed in the bottom side right corner (Marked in RED).
SQL query : spgetobsoleteupdatestocleanup
How to Re-index the SCCM WSUS DB (SQL 2)
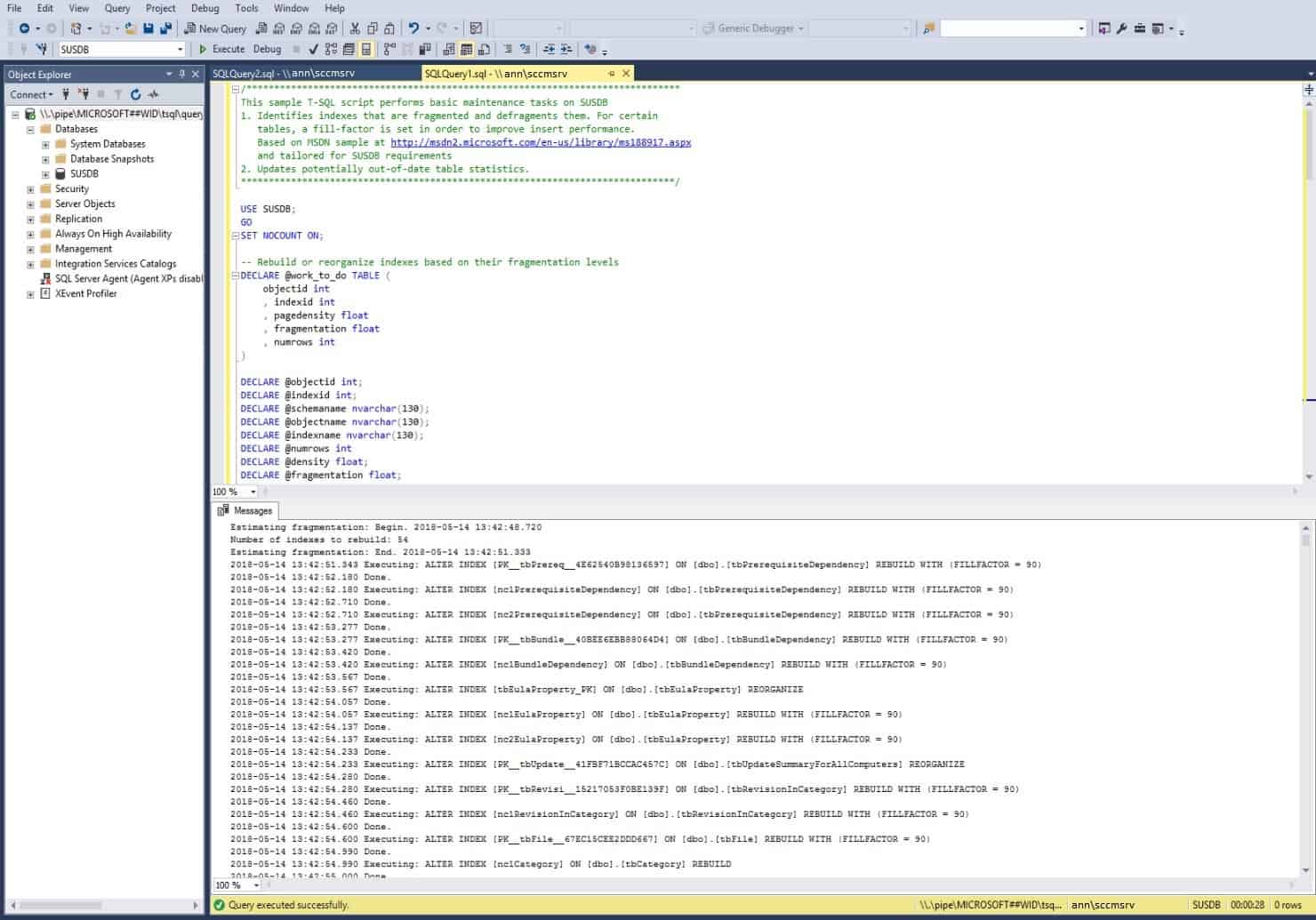
To re-index the SUS DB, copy and paste the query in the new query window and click Execute. This is the second step toward cleaning up SCCM WSUS Maintenance.
Once the Query has been Executed successfully, consider that WSUS DB has successfully re-indexed. Download the Re-index query from the following Microsoft TechNet gallery.
https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/6f8cde49-5c52-4abd-9820-f1d270ddea61 – Script Re-index the WSUS Database (archive.org)
How to Cleanup Obsolete Updates from SCCM (SQL 3)
You can use the stored procedure query (below) in the SQL Management studio and then Execute it. This step is the third step toward the cleanup of SCCM WSUS Maintenance.
Execute the stored procedure query in the SQL Management studio. Make sure you have the backup of the SQL DB. You can check out the SQL query from the GitHub repository.
[Related Post – How to Setup WSUS Cleanup Task from SCCM console]
It will delete any obsolete or OLD update from the SUS DB. It will show the deletion of rows previously shown in the SQL 1 query statement.
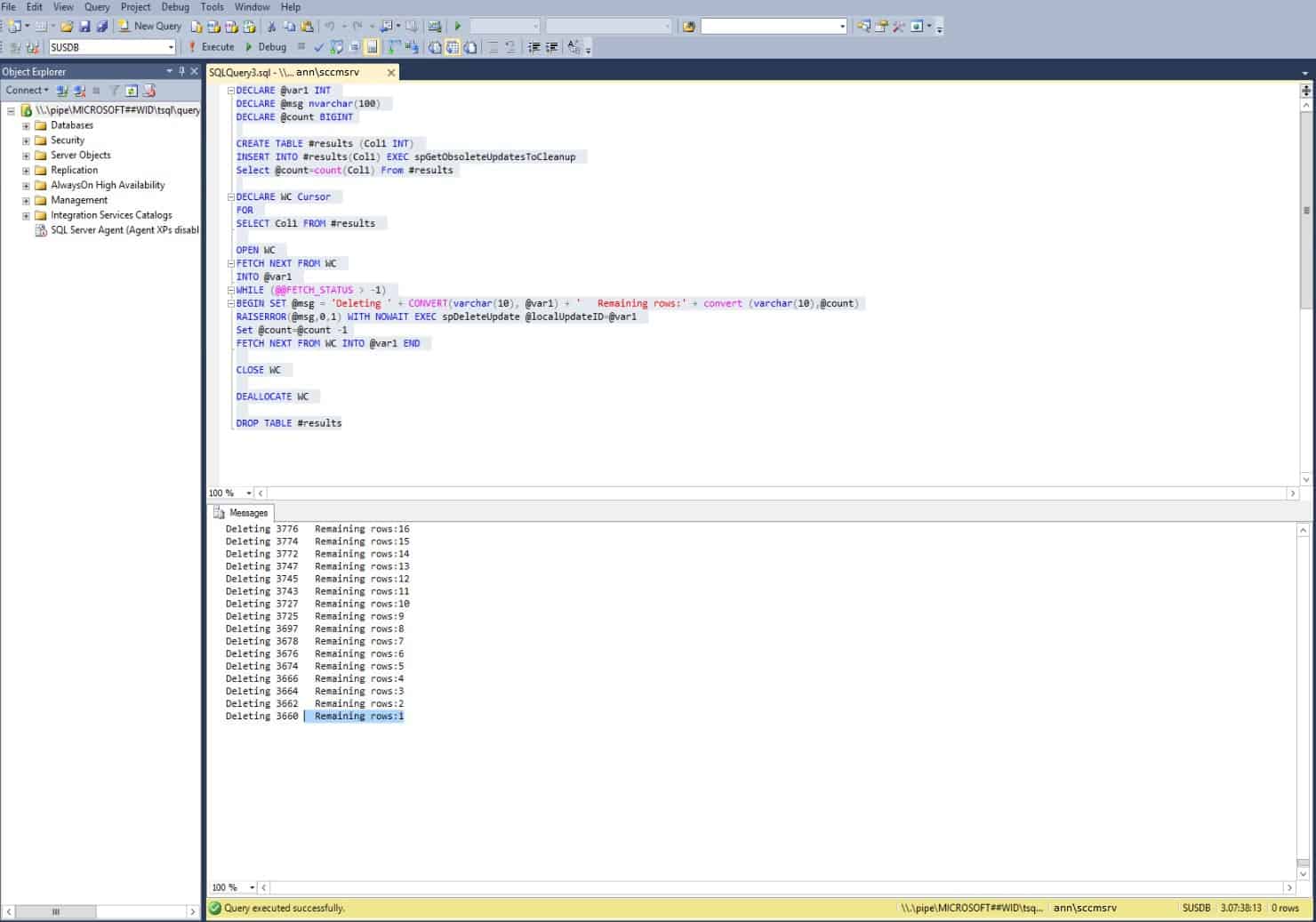
Decline Superseded Updates from SQL Management Studio (SQL 4)
Additionally, you may want to decline superseded updates in the WSUS server so it helps your clients scan more efficiently. This step is the fourth step toward the cleanup of SCCM WSUS Maintenance.
Note: The SQL 4 is not applicable for ‘Replica’ WSUS Servers.
- Download the PowerShell script from this MS URL https://msdnshared.blob.core.windows.net/media/TNBlogsFS/prod.evol.blogs.technet.com/CommunityServer.Blogs.Components.WeblogFiles/00/00/00/69/06/Decline-SupersededUpdatesWithExclusionPeriod.ps1.txt (I have made a copy of the PS1 script into Github repository)
- Open the PowerShell with administrator privilege.
- In PowerShell, navigate the downloaded folder that contains the script
- Run the command as > .\SupersededUpdates.ps1 -UpdateServer -Port -SkipDecline
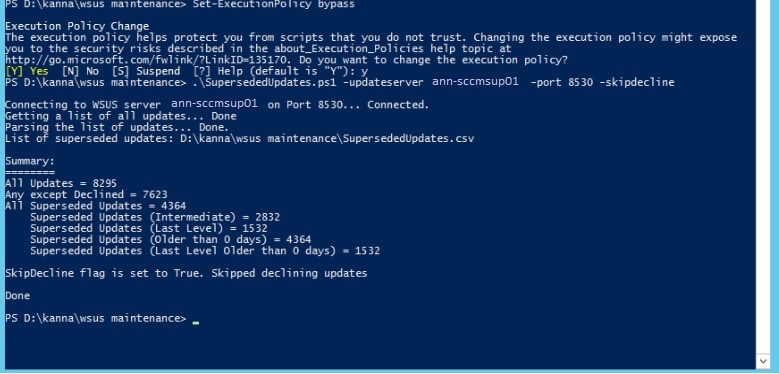
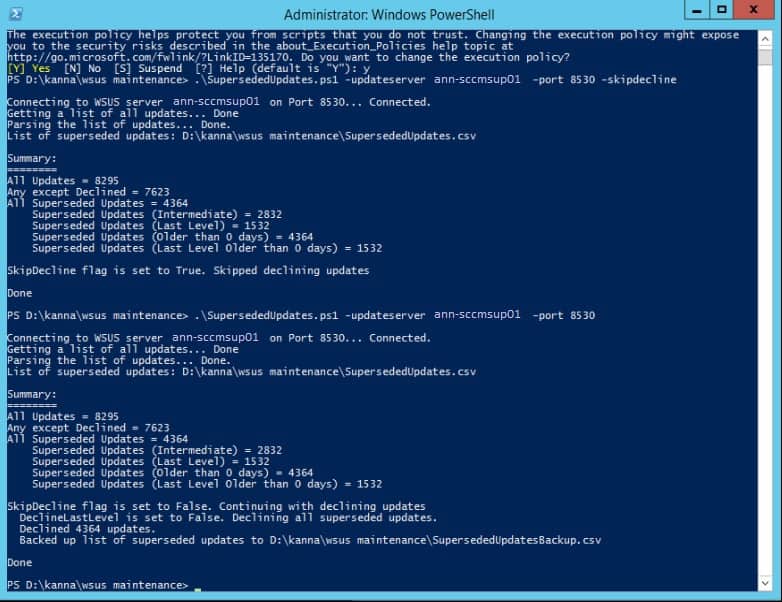
Once done, it will give you a list of superseded updates. After that, run another command as > .\SupersededUpdates.ps1 -UpdateServer -Port. It will decline the superseded updates on your Upstream server. Repeat the same steps post all secondary site task is completed.
We are on WhatsApp. To get the latest step-by-step guides and news updates, Join our Channel. Click here –HTMD WhatsApp.

Great Article! I usually use this procedure to maintain the health of WSUS with SUP.
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/configurationmgr/2016/01/26/the-complete-guide-to-microsoft-wsus-and-configuration-manager-sup-maintenance/
I think Kannan already linked the blog post you mentioned in the Resources section of the post 🙂 Anyways glad to know you liked the article !
Thanks Douglas!
Hi thanks for the great post – i have one question.
The 3. thing “Cleanup Obsolete Updates” i am running it now, and it shows:
Deleting 855493 Remaining rows:17800
Deleting 855416 Remaining rows:17799
Deleting 855415 Remaining rows:17798
Now after running approx 1,5 hour… I have timed it, and it seems to delete one row every 50-60 second, so my calculations tell me that the script will run somthing like 296 hours to complete ?? 12 days it looks like… Will et start over, if i terminate the script, or will my database be damaged ? can i stop the script, and sync my WSUS and then start the script again, or will i have to run everything now, and wait with wsus sync until eerything has finished ?
Yours
Erling B. Kjeldsen
How is your performance of the SQL box? How about the server performance? Is it ok, I don’t think a row deletion should take that long. I will let Kannan to answer your questions with details.
Hi Anoop –
I have checked, and the SQL box is only using 20% cpu, but after i have changed so that SQL can use more of the RAM (16gb) now its doing 2 deleted row pr. minute approx.. so it seems that i am down to approx 5-6 days and not 12 as first calculated – but i still might need to stop the script and do a wsus sync sometime during the next 5-6 days.
Latest progress is now that the script has been running for 3 hours and 6 minutes and we still have above 17600 rows to delete:
Deleting 846829 Remaining rows:17661
Deleting 846827 Remaining rows:17660
Deleting 846719 Remaining rows:17659
Deleting 846689 Remaining rows:17658
I don’t think if you stop in between that will damage your SQL DB
Thanks – i will keep it running for a day or two – and se how far it gets..
Hope that this will not be for nothing, when i have synced updates in a couple of days and starts the script again.. 🙂
Maybe Kannan or you can tip me whether i must run all the steps from the top again after a sync, or just run this script again at that time ?
It’s recommended to follow all the steps. Not only the script. I will let Kannan to confirm
okay thanks – i will start from the beginning if i have to interrupt the running script and do a sync.
Thanks Anoop,
Hi Erling,
Based on your updates, it will take time to clean up the Obsolete update. It is based on your product selection configured in SUP. I would recommend to re-think the product/classification which is needed, rest you could unselect the same. My environment, it will take 1 day to clean up nearly 1800 updates.
Yes, you need to perform all the steps to have better performance for SUS DB.
Good article Anoop!
I’m not much of a SQL person so others may have noticed and corrected this on their end already. The first step shows to executed “spgetobsoleteupdatescleanup” on the SUSDB. That command fails so just in case, I zoomed in on the screenshot which as the word “TO” in the command. So I believe it should be “spgetobsoleteupdatesTOcleanup”.
I’m on to the next steps in the guide 🙂
Hi Chris,
I have updated the syntax of the SQL statement. Thanks for being pointout.
It seems Microsoft has moved all the linked scripts
if the “Cleanup Obsolete Updates” is runnign slow you can run this against tha database
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/mem/configmgr/update-management/spdeleteupdate-slow-performance
Please, can you write a script that can do remove unneeded language records from WSUS table tbXML.
My tbXML is 8.5 Gb large.