Key takeaways
- The built-in Administrator account exists on all Windows devices and needs extra protection.
- Default account names are easy targets for attackers.
- Renaming the Administrator account makes password attacks harder.
- The Administrator account cannot be locked, so protecting it is very important
- This policy reduces risk with a simple configuration change.
- Intune helps apply the setting consistently on all devices.
- The policy follows CIS Level 1 security recommendations.
In this post, we are discussing, Enhancing Endpoint Security with Administrator Account Renaming Using Intune Policy. The Administrator account is available on every Windows device by default. This account has full control of the system, so it is very important to protect it. Many systems keep the default settings unchanged, which can make them easy targets for attacks.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Enhancing Endpoint Security with Administrator Account Renaming Using Intune Policy
By renaming the Administrator account, you make it harder for attackers to find the right account to attack. Many attack tools depend on the default account name. When the name is changed, these tools are less effective, and the system becomes safer.
Using Intune to apply this setting helps the organization manage all devices from one place. It ensures the same security rule is applied to every managed computer. Attackers usually try simple and common ways to enter a system. One of the first things they look for is the default Administrator account. When the account name is the same on all computers, it becomes easier for attackers to try passwords and gain access. This is why changing default settings is a basic security step.
- Intune Security Policy to Set Up Smart Screen Enhanced Phishing Protection
- How to Install Microsoft Defender Browser Protection Extension using Intune PowerShell Script
- How to Prevent Smart Screen Prompt Override for Files Policy in MS Edge Browser using M365 Admin Center
Create a Profile
You know, better security practice is to avoid using default names and settings. Small changes can make a big difference in system safety. Renaming important accounts is a simple way to reduce risk and improve protection without affecting normal work.
The Administrator account is more important than other accounts because it cannot be locked even after many wrong password attempts. This makes it a favorite target for password-guessing attacks. If the account keeps its default name, attackers know exactly which account to target.
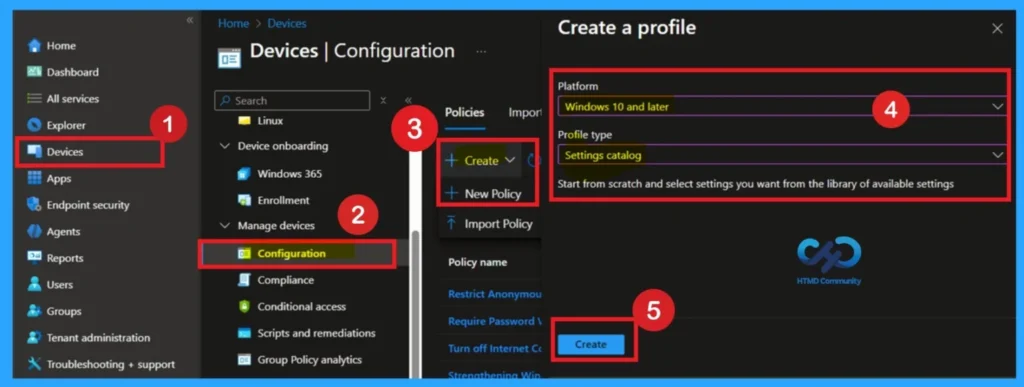
- Using simple steps, you can easily complete the policy creation. Open the Intune admin center.
- Go to Devices > Configuration > Policies> + Create > + New policy.
- After that, you will get a profile window to select the platform and profile type.
- Select Windows 10 and later as the platform and select settings catalog as the profile type. Click on the create button.
Basics
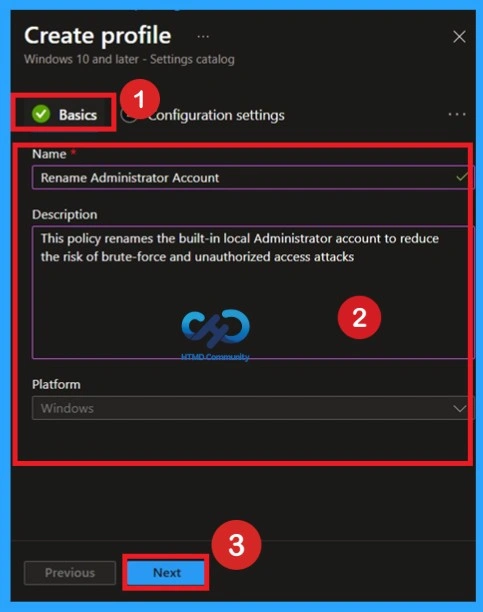
Enter the basic details such as the policy name, description, and platform, which is set to Windows by default. Use a clear name like Rename Administrator Account and add a short description explaining the purpose of the policy.
Configuration Settings
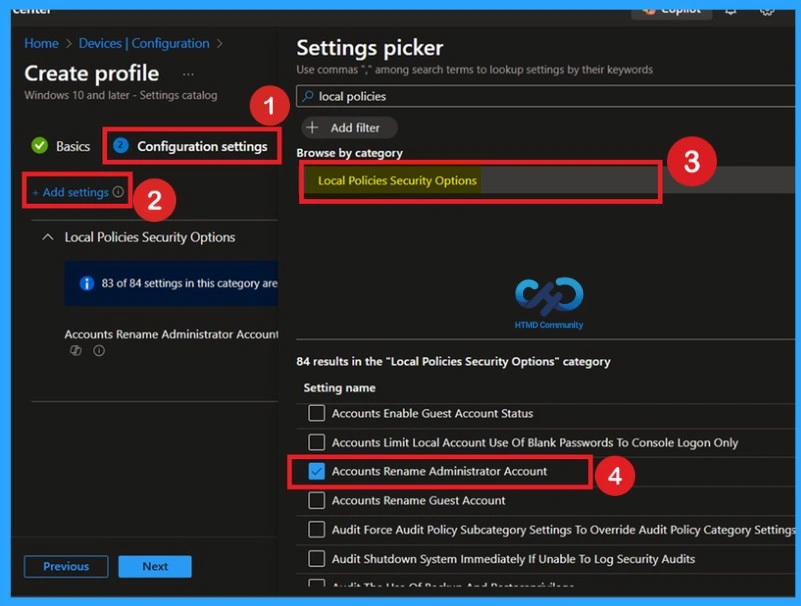
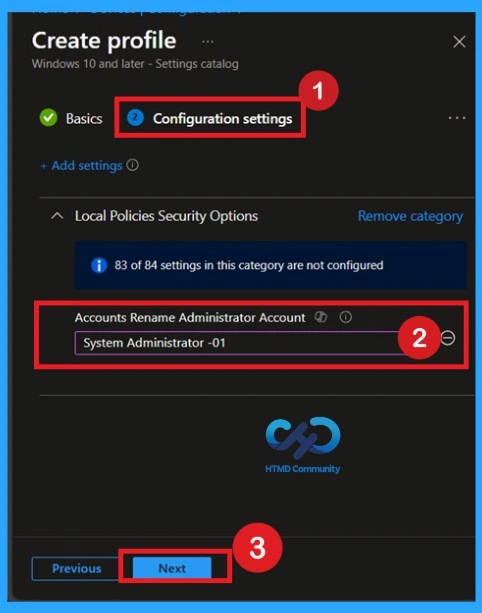
Go to the Configuration settings section and click on the Add settings option. This will open the settings picker window where different setting categories are available. Select the required setting. In the settings picker window, choose Local Policies Security Options and select Accounts: Rename administrator account. After selecting the setting, close the settings picker to return to the configuration settings page.
| Configuration Path |
|---|
| Configuration Settings> +Add Settings>Local Policies Security Options>Accounts Rename Administrator Account |
Defaulted Name for the Account
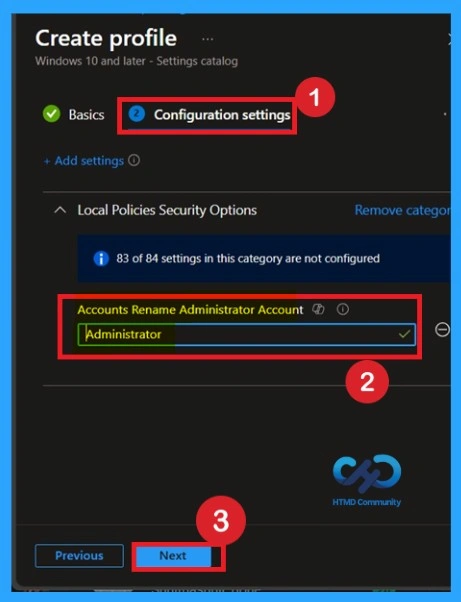
Now you can see that the policy is set by default with the account name Administrator. If you want to continue using the default administrative account name, simply click Next to proceed
Rename the Account Name
If you want to rename the administrator account, you can enter any name of your choice. In this example, the name SystemAdministrator01 is entered, as recommended in the CIS documentation. After entering the new name, click Next to continue with the configuration using the updated administrator account name.
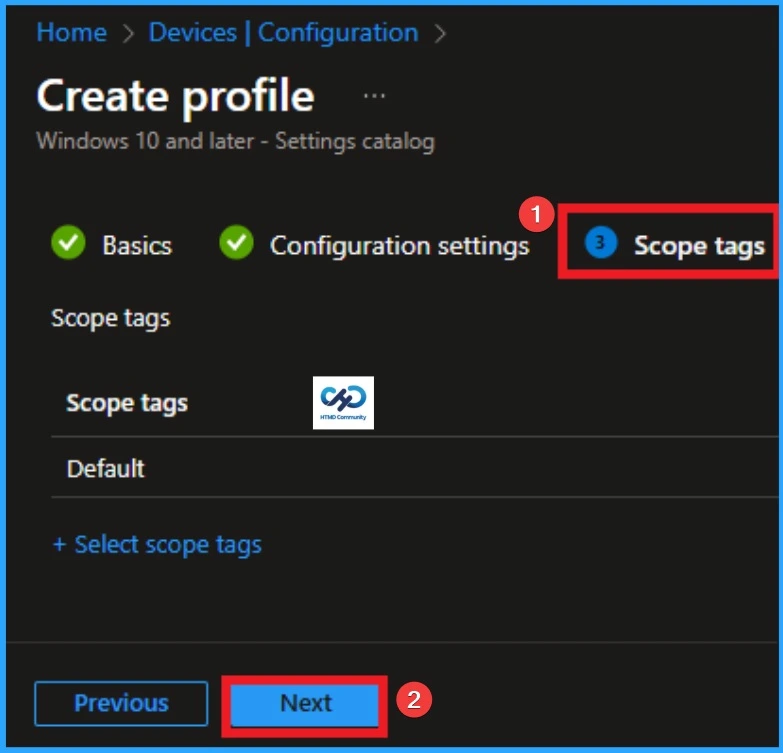
Scope Tags Importants
Now you are on the Scope tags section. Scope tags are used to assign policies to specific admin groups for better management and filtering. If needed, you can add a scope tag here. However, for this policy, I chose to skip this section.
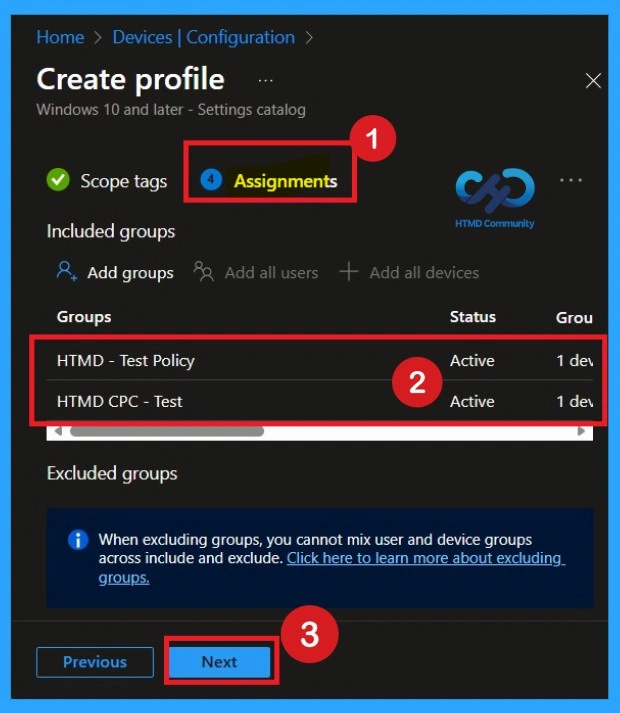
Assignment Section
Next, you’ll reach the Assignments section, which is a very important step. This is where you decide which user or device groups should receive the policy. In this case, I selected the specific group I wanted to apply the policy to. After selecting the group, click Next to continue.
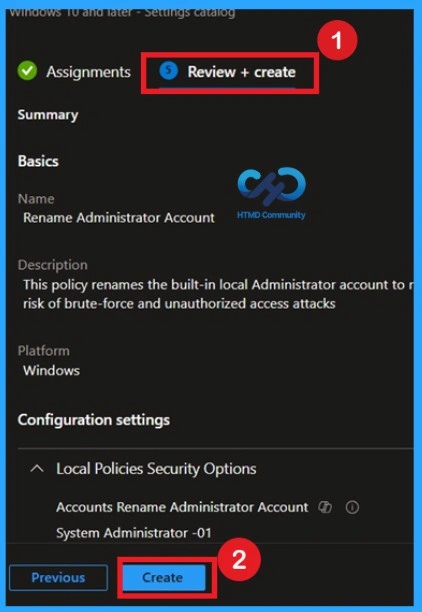
Review + Create
Review + Create is the final stage of policy creation. In this step, you will see a summary of all the details, including Basics, Configuration Settings, Assignments, and more. You can review all the information, and if anything needs to be changed, you can go back to the previous steps and edit them easily. In the Review + Create section, you will see a Create button.
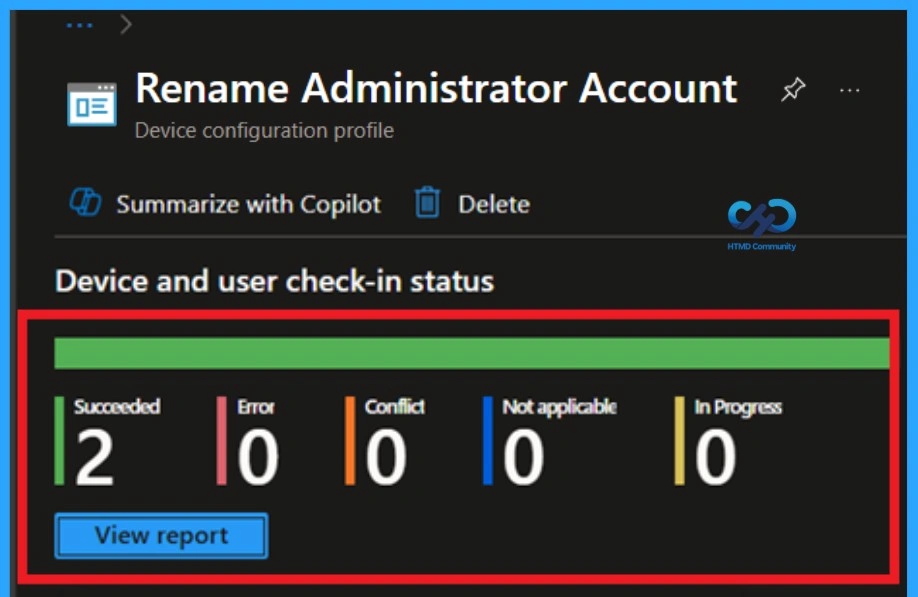
Monitoring Status
After the policy is created, the main concern is whether it has been successfully deployed. Typically, it can take up to 8 hours for the policy to apply. This is the minimum waiting period. However, you can manually sync the policy through the Company Portal which helps to apply the policy more quickly. To check if the policy has been successfully deployed.
- In the Configuration Policies list, look for the policy you created.
- Click on the policy to view its deployment status and detail
- Sign into the Microsoft Intune Admin Center.
- Navigate to Devices > Configuration Policies.
Event Viewer Details
To confirm the policy is successful or not, you can use the Event Viewer. First, open Event Viewer and navigate to Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > Device Management > Enterprise Diagnostic Provider > Admin. Look for Event IDs 813 or 814, as these typically policy-related information. You can use the Filter Current Log option in the right-hand pane to get the results easily. In the below screenshot the policy details were found under Event ID 814.
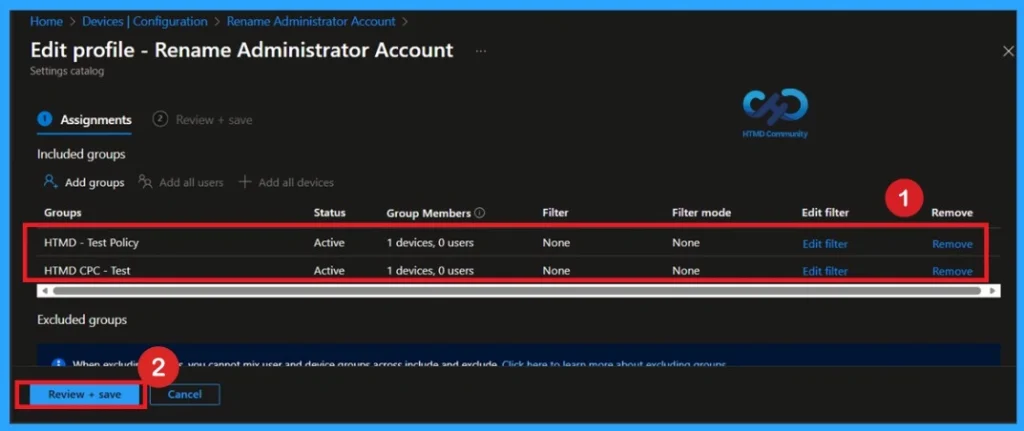
Remove Assignment Groups
To Remove Assignment Groups, Open the policy from the Configuration tab and click on the Edit button on the Assignment tab. Click on the Remove button on this section to remove the policy. Click Review + Save after making the change.
For detailed information, you can refer to our previous post – Learn How to Delete or Remove App Assignment from Intune using by Step-by-Step Guide.
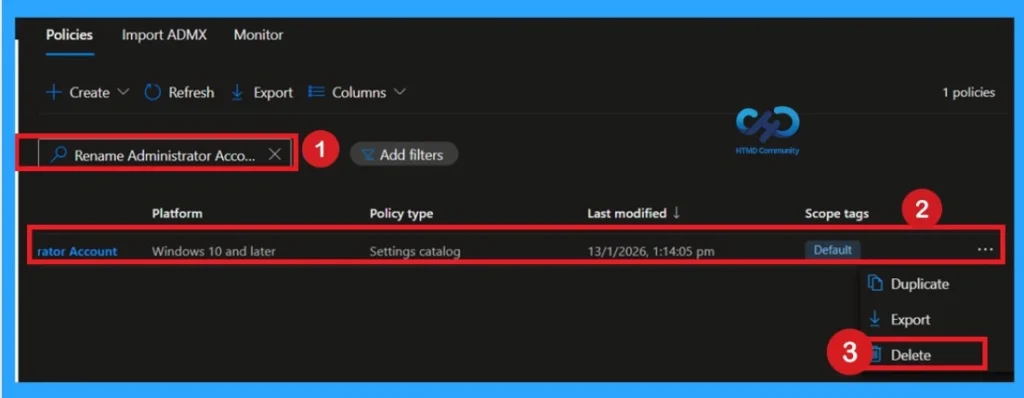
Delete Policy Permanently
To remove a configuration policy in Microsoft Intune, start by signing in to the Intune Admin Center. From the left navigation, go to Devices > Configuration Policies and locate the policy you want to delete. Open the policy details, then select the three‑dot menu in the upper‑right corner and choose Delete. This ensures the policy is removed cleanly and avoids confusion about its purpose.
Need Further Assistance or Have Technical Questions?
Join the LinkedIn Page and Telegram group to get the step-by-step guides and news updates. Join our Meetup Page to participate in User group meetings. Also, Join the WhatsApp Community to get the latest news on Microsoft Technologies. We are there on Reddit as well.
Author
Anoop C Nair has been Microsoft MVP for 10 consecutive years from 2015 onwards. He is a Workplace Solution Architect with more than 22+ years of experience in Workplace technologies. He is a Blogger, Speaker, and Local User Group Community leader. His primary focus is on Device Management technologies like SCCM and Intune. He writes about technologies like Intune, SCCM, Windows, Cloud PC, Windows, Entra, Microsoft Security, Career, etc.


