SCCM Real World Network Trace Examples Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call Configuration Manager. Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call – What is the use of it? Why is Windows using this very often? I was not aware of the details of the RPC mechanism :(.
RPC unavailable errors are also common in SCCM. I’ve blogged about one of the issues, which was again related to RPC: ConfigMgr Primary Installation Error: Attempted to perform unauthorized.
Do you know RPC Dynamic Posts? TCP 49152-65535—This time, some people in my organization and Microsoft were forced to read extensively about RPC. Thanks to them, I learned more details about RPC.
So, I thought of creating a note for myself and people like me. 🙂 Some parts of this post contain network trace or net mount analysis, which will help us troubleshoot deep into the issues related to RPC.
- FIX SCCM PXE Boot Timeout Issue with Dell Intel 825xxLM Network Adapters
- Fix SCCM PXE Issues with C Type Network Adapter Duplicate MACID
- FIX: SCCM Task Sequence Failed to find a valid network adaptor
What is Microsoft RPC (Remote Procedure Call)?
Microsoft Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is an interprocess communication (IPC) mechanism that enables data exchange and the invocation of functionality in a different process. It uses other IPC mechanisms, such as named pipes, NetBIOS, or Winsock, to establish communications between the client and the server.
The RPC components make it easy for clients to call a procedure in a remote server program. The RPC process starts on the client side. The RPC provided by Windows is compliant with the Open Software Foundation (OSF) Distributed Computing Environment (DCE). RPC enables applications to call functions remotely.
What is an RPC Endpoint Mapper or Port Mapper?
When a Client communicates with a Server, it performs an initial connection to Port 135 to communicate with the EPM “EndPoint Mapper”. The client must bind to an interface before it can call its procedures. The client has to perform a 3-way RPC EPM handshake; once these handshakes are successful, then the client will successfully bind. If the binding process is successful, it can send a request to the End Point Mapper, including the target interface’s UUID.
SCCM Real World Network Trace Examples Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call – Network Trace Example 3 Way Successful RPC EPM Handshake
Client Initiates a connection on Source port 52702 (RPC Dynamic port) to the server on destination port 135 (End Point Mapper). The server replies using source port 135 and destination port 52702.
Tcp: Flags=......S., SrcPort=52702, DstPort=DCE endpoint resolution(135), PayloadLen=0, Seq=722369472, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:36, IPv4:7}
Tcp: Flags=...A..S., SrcPort=DCE endpoint resolution(135), DstPort=52702, PayloadLen=0, Seq=1169857372, Ack=722369473, Win=8192 ( Negotiated scale factor 0x8 ) = 2097152 {TCP:36, IPv4:7}
Tcp: Flags=...A...., SrcPort=52702, DstPort=DCE endpoint resolution(135), PayloadLen=0, Seq=722369473, Ack=1169857373, Win=512 (scale factor 0x8) = 131072 {TCP:36, IPv4:7}Network Trace Example for Successful RPC Bind
After the three-way handshake, it initiates an RPC Binding to the Endpoint Mapper. Successful RPC bind! Microsoft clients connect to the RPC Endpoint Mapper on port 135. Then, the Endpoint Mapper tells the client which ports a requested service is listening on. The port numbers are assigned dynamically and can be between 1024 and 65,535.
MSRPC MSRPC:c/o Bind: IObjectExporter(DCOM) UUID{99FCFEC4-5260-101B-BBCB-00AA0021347A} Call=0x2 Assoc Grp=0x0 Xmit=0x16D0 Recv=0x16D0 {MSRPC:37, TCP:36, IPv4:7}
MSRPC MSRPC:c/o Bind Ack: IObjectExporter(DCOM) UUID{99FCFEC4-5260-101B-BBCB-00AA0021347A} Call=0x2 Assoc Grp=0x1E0D9 Xmit=0x16D0 Recv=0x16D0 {MSRPC:37, TCP:36, IPv4:7}When a service starts up, it registers with the RPC service and requests the assignment of one or more dynamic port numbers. When the remote client needs to communicate with that service, it does not know which port numbers have been assigned.
To find out, the client connects to the server on TCP port 135 (the “well-known” port number for the RPC Endpoint Mapper service) and identifies the service to which it wants to connect. The RPC Endpoint Mapper service replies with the port number the client should use to connect to the desired service. The client then reconnects to the server using the assigned port number, and communication with the desired service begins.
RPC End Point Mapper Handshake Failure (Failed) Network Trace
The entry in the below net amount analysis means [SynReTransmit #101] resending the request for RPC EPM handshake but NO acknowledgement (response) from the server as we can see in the above successful trace (Flags=…A..S. and Flags=…A….) This could be because of a Firewall issue. You may need to open the FirePorts between client and server.
While opening Firewall ports, there is no need to worry about Source Ports mentioned in the network trace. Source ports are dynamic. You must provide the Source IP, Destination IP, and destination ports. SCCM Real-World Network Trace Examples Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call?
TCP TCP:Flags=......S., SrcPort=52702, DstPort=DCE endpoint resolution(135), PayloadLen=0, Seq=2557920356, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:14, IPv4:13}
TCP TCP:[SynReTransmit #101]Flags=......S., SrcPort=52702, DstPort=DCE endpoint resolution(135), PayloadLen=0, Seq=2557920356, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:14, IPv4:13}
TCP TCP:[SynReTransmit #101]Flags=......S., SrcPort=52702, DstPort=DCE endpoint resolution(135), PayloadLen=0, Seq=2557920356, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:14, IPv4:13}Network Trace Example for Failed Client-Server Communication Network Trace on LDAP Port 389
The entry in the below net amount analysis means Flags=…A.R.. seems to me as TCP reset or Reject (I can’t confirm this )
TCP:Flags=……S., SrcPort=52705, DstPort=LDAP(389), PayloadLen=0, Seq=914145090, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:22, IPv4:13} TCP:Flags=…A.R.., SrcPort=LDAP(389), DstPort=52705, PayloadLen=0, Seq=251831252, Ack=914145091, Win=8192 {TCP:22, IPv4:13}
Network Trace Example for Failed Microsoft Global Catalog LDAP 3268 Connection
The entry in the below net amount analysis means [SynReTransmit #101] resending the request for Global Catalog LDAP 3268 but no acknowledgement (response) from the server, as we can see in the above trace (Flags=…A..S. and Flags=…A….). This could be because of a Firewall issue. You may need to open the Firewall ports between the client and server.
TCP:Flags=......S., SrcPort=52707, DstPort=Microsoft Global Catalog (LDAP)(3268), PayloadLen=0, Seq=54051677, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:43, IPv4:13}
TCP:[SynReTransmit #1238]Flags=......S., SrcPort=52707, DstPort=Microsoft Global Catalog (LDAP)(3268), PayloadLen=0, Seq=54051677, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:43, IPv4:13}
TCP:[SynReTransmit #1238]Flags=......S., SrcPort=52707, DstPort=Microsoft Global Catalog (LDAP)(3268), PayloadLen=0, Seq=54051677, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:43, IPv4:13}Network Trace Example for Failed Microsoft DNS Port 53
The entry in the below net amount analysis means [SynReTransmit #101] resending the request for DNS connection on port 53 but no acknowledgement (response) from the server, as we can see in the above trace (Flags=…A..S. and Flags=…A….). This could be because of a Firewall issue. You may need to open the Firewall ports between the client and server.
TCP:Flags=......S., SrcPort=52714, DstPort=DNS(53), PayloadLen=0, Seq=2780093052, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:54, IPv4:13}
TCP:[SynReTransmit #2312]Flags=......S., SrcPort=52714, DstPort=DNS(53), PayloadLen=0, Seq=2780093052, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:54, IPv4:13}Network Trace Example for Failed Kerberos Port 88 Connection
The entry in the below net amount analysis means [SynReTransmit #101] resending the request for Kerberos port 88 but no acknowledgement (response) from the server, as we can see in the above trace (Flags=…A..S. and Flags=…A….). This could be because of a Firewall issue. You may need to open the Firewall ports between the client and the server. Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call.
TCP:Flags=......S., SrcPort=52716, DstPort=Kerberos(88), PayloadLen=0, Seq=1708886965, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:65, IPv4:13}
TCP:[SynReTransmit #2874]Flags=......S., SrcPort=52716, DstPort=Kerberos(88), PayloadLen=0, Seq=1708886965, Ack=0, Win=8192 ( Negotiating scale factor 0x8 ) = 8192 {TCP:65, IPv4:13}
KerberosV5 KerberosV5: {UDP:69, IPv4:13}Following the Best Explanation I Found about Remote Procedure Calls (RPC)
Suppose every program and service that needed communication over the network assigned its port number. In that case, you can easily imagine that two programs would conflict over using the same port sooner or later. SCCM Real-World Network Trace Examples Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call.
To address this, many programs use the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocol to request communications with a host service on a dynamically assigned port number. When a service starts up, it registers with the RPC service and requests the assignment of one or more dynamic port numbers.
When the remote client needs to communicate with that service, it does not know which port numbers have been assigned. SCCM Real-World Network Trace Examples Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call.
To find out, the client connects to the server on TCP port 135 (the “well-known” port number for the RPC Endpoint Mapper service) and identifies the service to which it wants to connect. The RPC Endpoint Mapper service replies with the port number the client should use to connect to the desired service.
The client then reconnects to the server using the assigned port number, and communication with the desired service begins. SCCM Real-World Network Trace Examples Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call.
What are the 4 Major Components of RPC?
From the Infrastructure support person’s perspective, we must understand the importance of EndPoint Mapper:- Explain in the first section above. SCCM Real-World Network Trace Examples Microsoft RPC Remote Procedure Call.
| What are the 4 Major Components of RPC? |
|---|
| 1. MIDL compiler |
| 2. Run-time libraries and header files |
| 3. Name the service provider (sometimes referred to as the Locator) |
| 4. Endpoint mapper (sometimes referred to as the portmapper) |
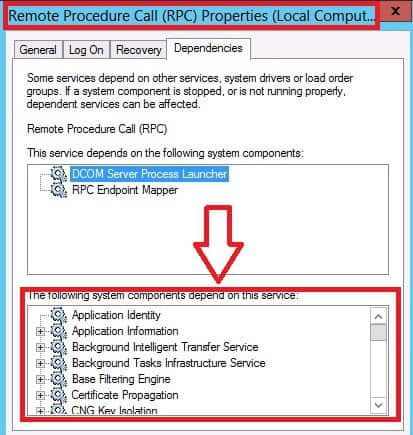
The system components or other Windows services that depend on the RPC service. The screenshot and list below provide more details.
- Background Intelligent Transfer Service
- Cluster Service
- COM+ Event System
- COM+ System Application
- Cryptographic Services
- DHCP Server
- Distributed Link Tracking Client
- Distributed Link Tracking Server
- Distributed Tracking Coordinator
- DNS Server
- Error Reporting Service
- Fax
- File Replication
- Help and Support
- Human Device Interface Access
- IIS Admin Service
- Indexing Service
- Internet Authentication Service
- IPSEC Services
- IPv6 Helper Service
- Kerberos Key Distribution Center
- Logical Disk Manager
- Logical Disk Administrator Service
- Messenger
- MS Software Shadow Copy Provider
- Network Connections
- Print Spooler
- Protected Storage
- Remote Desktop Help Session Manager
- Remote Registry
- Removable Storage
- Resultant Set of Policy Provider
- Routing and Remote Access
- Security Accounts Manager
- Shell Hardware Detection
- Task Scheduler
- Telephony
- Telnet
- Terminal Services
- Terminal Services Session Directory
- Terminal Services Licensing
- Upload Manager
- Volume Shadow Copy
- Web Element Manager
- Windows Audio
- Windows Image Acquisition (WIA)
- Windows Installer
- Windows Internet Name Service (WINS)
- Windows Management Instrumentation
- Windows Media Services
- Wireless Configuration
- WMI Performance Adapter
- World Wide Web Publishing Service
More references about RPC…..
- More details on RPC services via TechNet http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh125927(v=ws.10).aspx#BKMK_rpcss
- RPC Architecture – http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc738291(v=ws.10).aspx
- RPC Some More Details – http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc732839(v=ws.10).aspx
- How to configure RPC dynamic port allocation to work with firewalls – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/154596/en-us
- Service overview and network port requirements for Windows – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/832017/
- More Details about RPC – http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa378651(v=vs.85).aspx
We are on WhatsApp now. To get the latest step-by-step guides, news, and updates, Join our Channel. Click here. HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
Anoop C Nair is Microsoft MVP from 2015 onwards for consecutive 10 years! He is a Workplace Solution Architect with more than 22+ years of experience in Workplace technologies. He is a Blogger, Speaker, and Local User Group Community leader. His primary focus is on Device Management technologies like SCCM and Intune. He writes about technologies like Intune, SCCM, Windows, Cloud PC, Windows, Entra, Microsoft Security, Career etc…

thank you, awesome
Hello,
Only question,whether Posts? Should be “Do you know RPC Dynamic Posts ? TCP 49152-65535” replaced by “Do you know RPC Dynamic Ports ? TCP 49152-65535”?
Thank you for RPC clarifying more.
Oto
Ports 😉 obviously