Try to understand the end-to-end process to Fix Windows Bugs using Known Issue Rollback KIR – Group Policy and WMI Filter. The prerequisites and other details are explained in this post.
In this post, you will learn how to deploy Known Issue Rollback KIR Using Group Policy. Known Issue Rollback KIR, is a new capability that can quickly return an impacted device back to productive use if an issue arises during a Windows update.
If Microsoft determines that a nonsecurity update has a critical regression or similar issue, Microsoft generates a KIR. Microsoft announces the KIR in the Windows Health Dashboard and adds the information to the following locations –
- The Known Issues section of the applicable Windows Update KB article
- The Known Issues list on the Windows Health Release Dashboard at https://aka.ms/windowsreleasehealth for the affected versions of Windows (for example, Windows 10, version 20H2, and Windows Server, version 20H2)
KIRs apply to only nonsecurity updates. This is because rolling back a fix for a nonsecurity update doesn’t create a potential security vulnerability.
Recently an issue resolved using Known Issue Rollback KIR where Outlook Search not showing recent emails after Windows update KB5008212 or later updates. This issue is related to emails that have been stored locally in PST or OST files. It might affect POP and IMAP accounts, as well as Microsoft Exchange and Microsoft 365-hosted accounts.
A Known Issue Rollback KIR policy definition has a limited lifespan (a few months, at most). After Microsoft publishes an amended update to address the original issue, the KIR is no longer necessary.
Download and Install the KIR MSI files
Let’s check how to download and Install KIR files, To see an example of a KIR MSI file, Outlook search might not locate recent emails
- Check the KIR release information or the known issues lists to identify which operating system versions you have to update.
- Download the KIR policy definition .msi files that you require to update to the computer that you use to manage Group Policy for your domain.
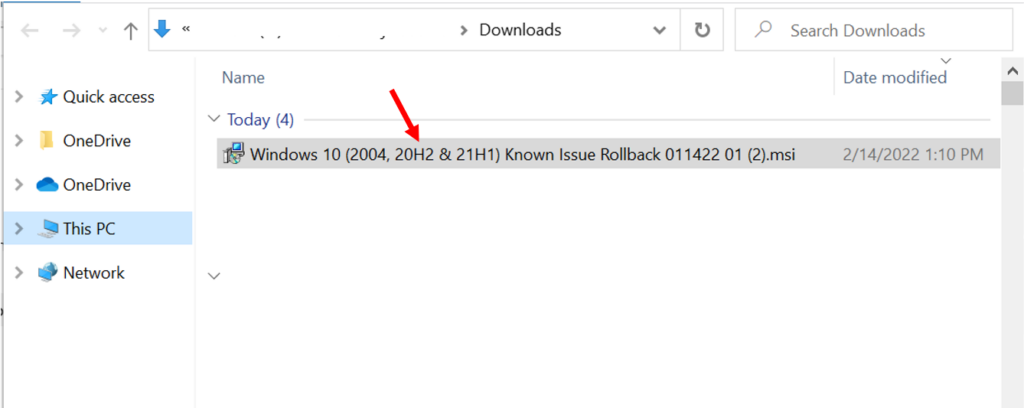
Copy the downloaded file (.MSI) to your device. Double-click the downloaded file Known Issue Rollback.msi to start the installation. Click Next.
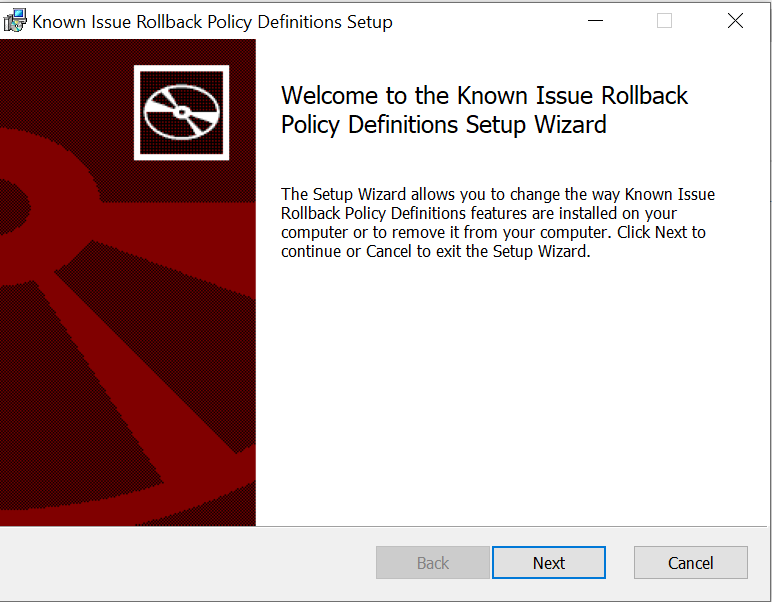
A UAC Prompt might appear, You can click on Yes to proceed. The MSI file will automatically extract the ADMX and ADML files to the default location “C:\Windows\PolicyDefinitions” folder.
Once you have successfully extracted the Known Issue Rollback policy, click the Finish button to exit the setup wizard.
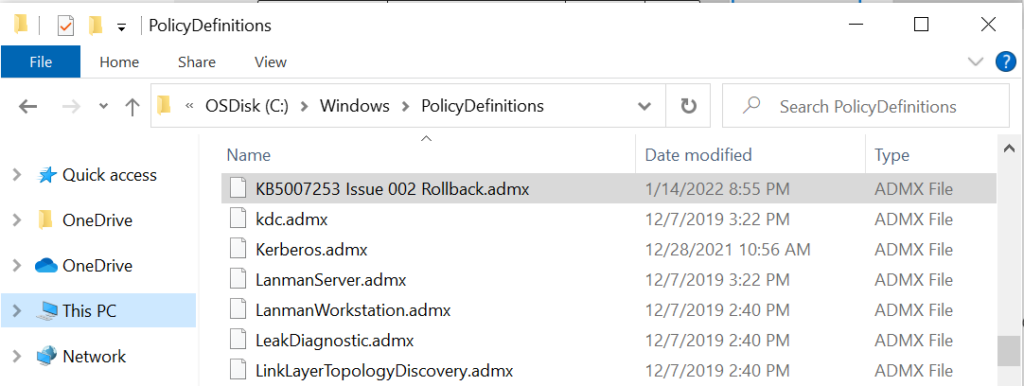
Once you extracted the file, you can see the .admx, and .adml files from the en-US folder path to “%systemroot%\PolicyDefinitions” same folder location.
Create Group Policy
If you have implemented the Group Policy Central Store, you must copy the .admx and .adml files to the Central Store.
- Open Group Policy Management Console, and then select Forest: DomainName > Domains.
- Right-click your domain name, then select Create a GPO in this domain and link it here.
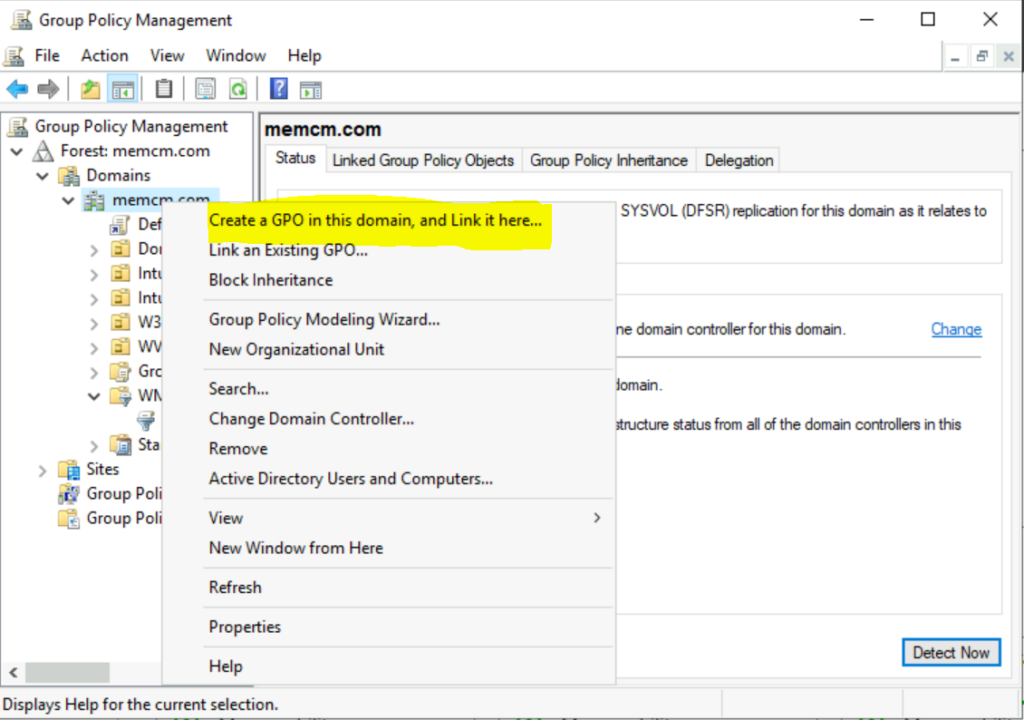
- You can specify the name (for example, KIR Issue – KB 5007253 Issue Rollback) and Select OK.
Group Policy WMI Filtering
Group Policy WMI filtering is very useful when we would like to filter a GPO based on certain conditions, for example, based on specific hardware type or OS type, or Server Role.
First, create the WMI filter and configure it to look for a specified version (or versions) of the Windows operating system.
- In the Group Policy Management console. Right-click WMI Filters, and then select New.
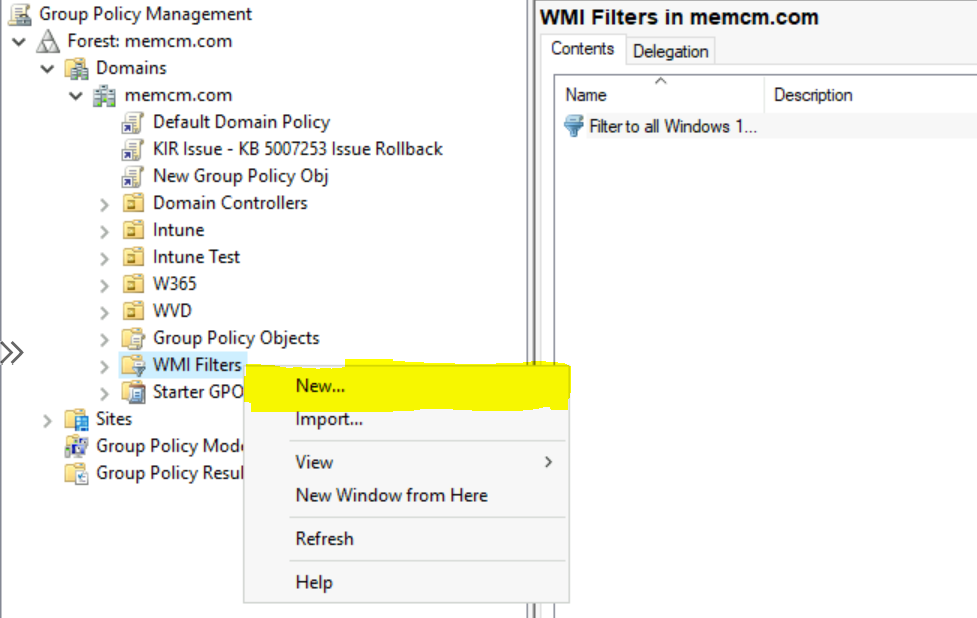
Enter a name, and description for your new WMI filter such as Filter to all Windows 10, version 20H2, 21H1 and 21H2 devices.
- Select Add. In Query, enter the following query string:
Specific versions of Windows 10 can be targeted by including the major build version in the query. For Example – The following query returns true for all devices running Windows 10 20H2 (which has a major build version of 19042), and returns false for any server operating system or any other client operating system.
Similarly, you can add different OS build version that represents the Windows version that you want the GPO to apply to. Additional information about Windows 10 build versions 👉 Windows 10 Version Numbers Build Numbers Major Minor Build Rev
SELECT version, producttype from Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version = "10.0.19042"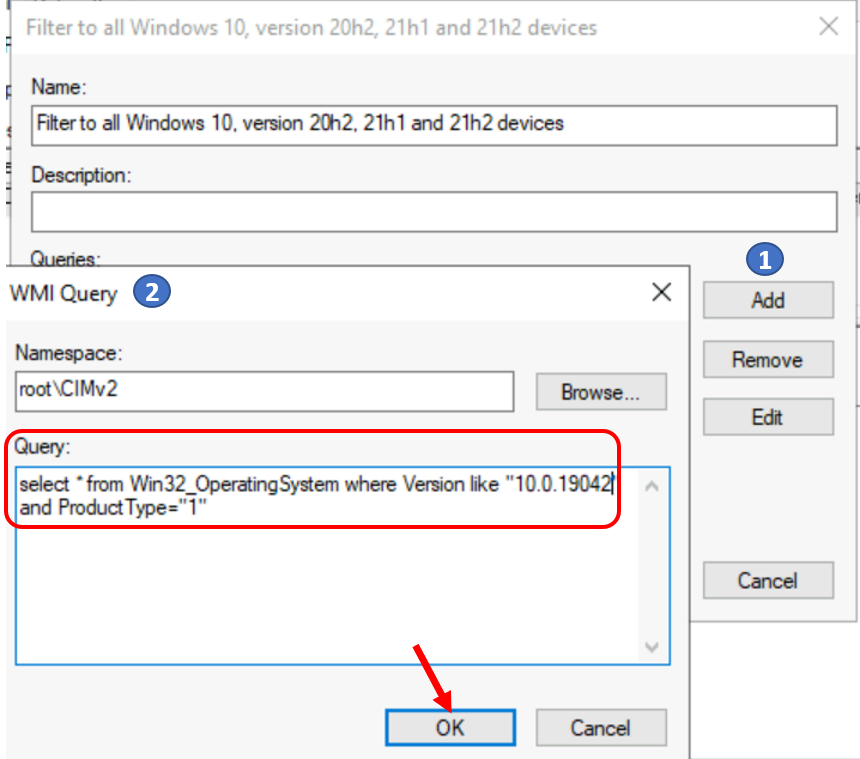
Once you added the query, Click on Save. You can also add multiple queries in single WMI Filter.
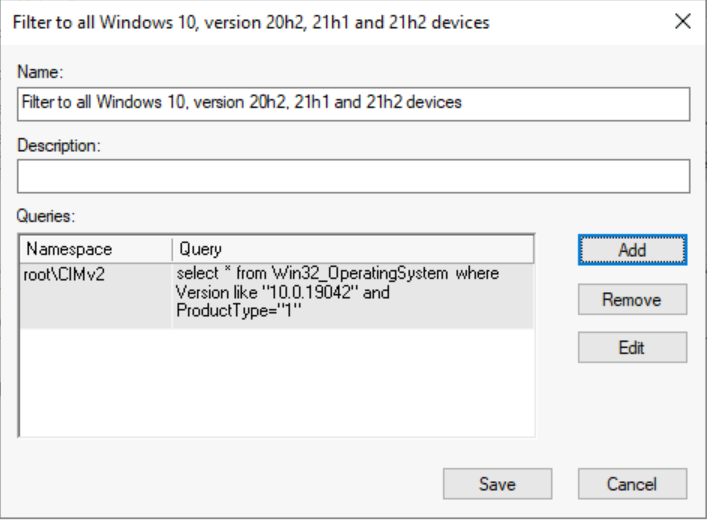
Group Policy WMI Filtering
Select the GPO that you created previously, open the WMI Filtering menu, and then select the WMI filter that you just created.
Please note that it is not possible to link multiple WMI filters with a single GPO. If there are multiple filtering criteria, add those in a single WMI filter using AND / OR Boolean operators.
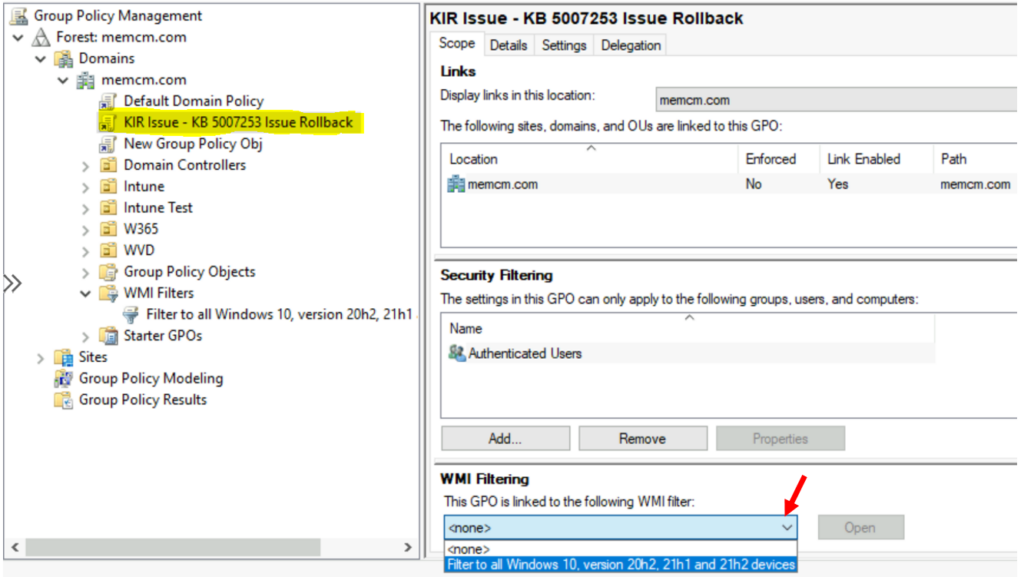
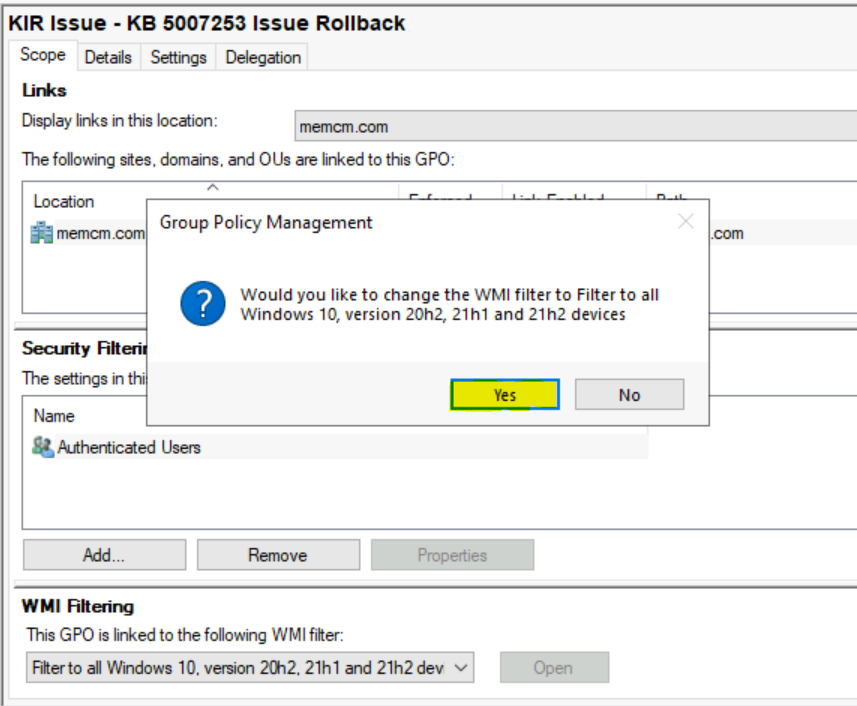
You will be prompted as shown below, Select Yes to accept the filter.
Configure the GPO – Rollback KIR Using Group Policy
Once you targeted the WMI Filter, Its time to Edit your GPO to use the KIR Activation Policy
- Right-click the GPO (for example, KIR Issue – KB 5007253 Issue Rollback) that you created previously, and then select Edit.
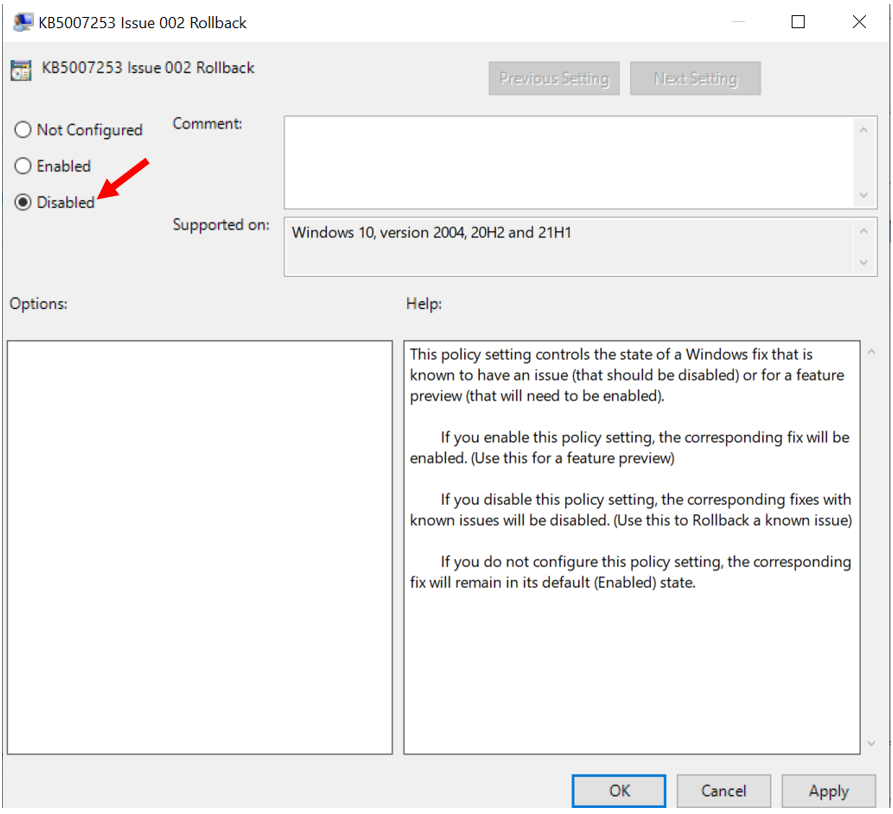
- In the Group Policy Editor, select GPOName > Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > KB ####### Issue XXX Rollback > Windows 10, version YYMM.
For Example : Here we had selected KB5007253 Isssue 002 Rollback > Windows 10, version 2004, 20H2 and 21H1
- Right-click the policy, and then select Edit > Disabled > OK.
In the default configuration of Group Policy, managed devices should apply the new policy within 90 to 120 minutes. To speed up this process, you can run gpupdate on affected devices to manually check for updated policies.
Important – You have to restart the affected computers to apply the policy.

hi,
but why do you disable the gpo setting?
if i understand it correctly you have to enable it to apply the fix.
Read it more carefully: “If you disable this policy setting, the corresponding fixes with known issues will be disabled (Use this to Rollback a known issue).”
It’s quite obvious the statement in parentheses was added by Microsoft to clarify that Disabled means APPLY THE ROLLBACK.