Hello everyone, I’m back with another interesting topic Secure Android Devices using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint in Intune. In this blog, let’s learn how to integrate Defender for Endpoint with Intune, publish Defender on Android devices, and use Defender application configuration policies to protect the data.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint(MDE) will help organizations protect enrolled devices from Pishing and malicious applications. It also helps to safeguard unsafe networks as well. Admins with access to the Security Defender portal can view all alerts and notifications for events under the Microsoft Security Defender portal.
Admins can view alerts and remediate or take action against the alerts. Admins can create custom indicators to block or allow certain URLs and domains. It provides a single-pane view for all alerts and events occurred on devices. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint also analyses the threat level and provides the attack risk level on user devices.
In this article, let’s see how we can integrate Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune, how to create App configuration policies for the Defender application, and create Compliance policies to block the devices which are under attack.
- Free Intune Trial Tenant Forever | Renewable Intune Tenant with 25 Microsoft E5 Licenses for Free
- Enable Internet Explorer Mode in Microsoft Edge
Integrate Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune
We need access to Microsoft Security Defender Portal to integrate Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune. In most organizations, this portal is managed by the Security team. The users should have Security Reader and Security Administrator or Global Administrator Azure roles to access the Security Defender portal.
- Log in to the Microsoft Security Defender Portal
- Click on Settings > Endpoints > Advanced features
- Now enable the toggle for the Microsoft Intune connection. This will allow sharing of device details with MDE.
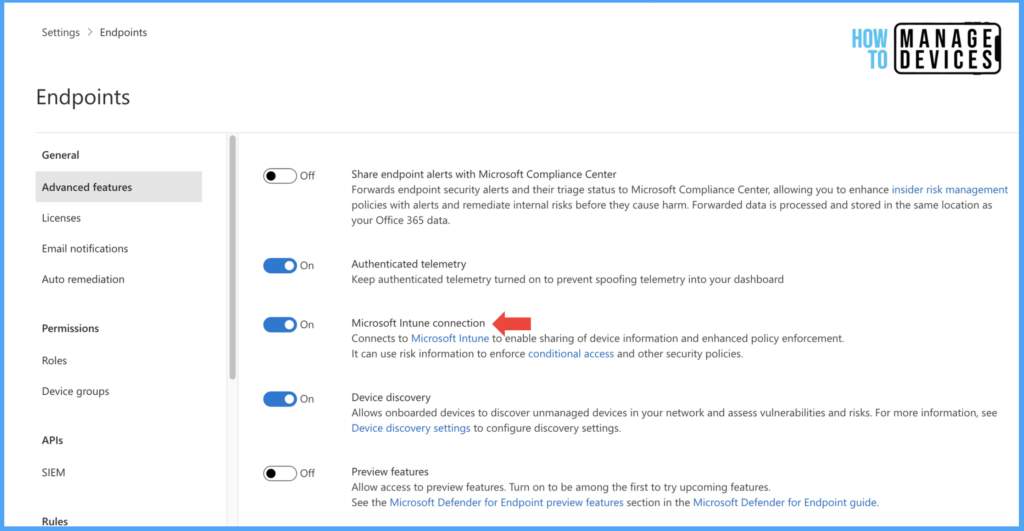
Once enabled, click on save changes. This simple step integrates Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune. Now on Intune, we need to enable Defender for Android devices. Microsoft Defender requires a minimum of Android OS version 6.0 and above.
Enable Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for Android Devices
In the above steps, we have connected Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune. Now we need to enable MDE for Android devices on Intune end. Once enabled, the data/Threat level shared by MDE can be used to evaluate Compliance policy and App Protection Policies.
- Sign in to Microsoft Intune Admin Center
- Click on Endpoint Security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
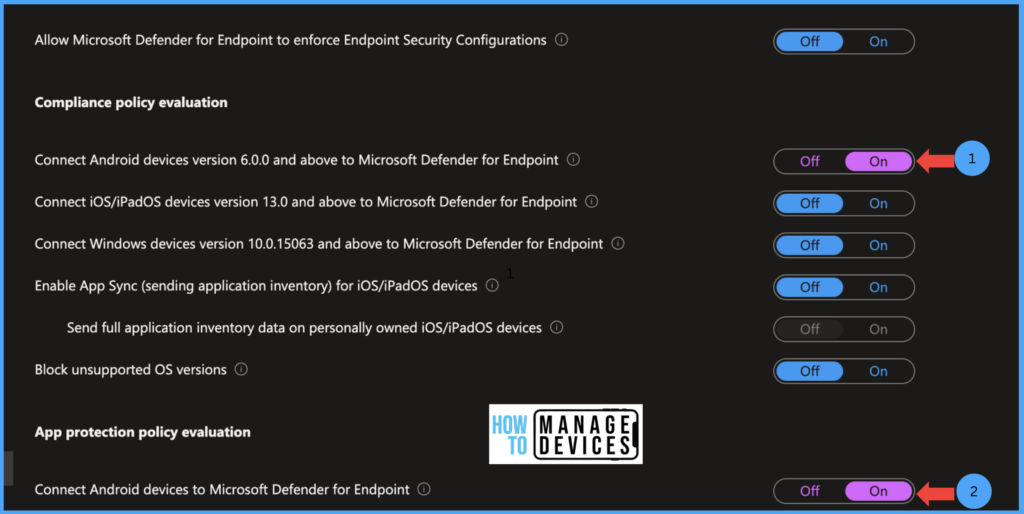
Now we need to enable Defender for Android under the Compliance policy evaluation and App protection policy evaluation. Under compliance policy evaluation, enable Connect Android devices version 6.0.0 and above to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. When this value is set to ON, Intune uses the device threat level sent by the MDE to define compliance of the device.
Under App protection policy evaluation, enable Connect Android devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, as shown in the above figure. When this value is set to ON, Intune uses the device threat level sent by the MDE to evaluate App Protection policies. Now click on Save. Now you can see the connection status as Enabled.
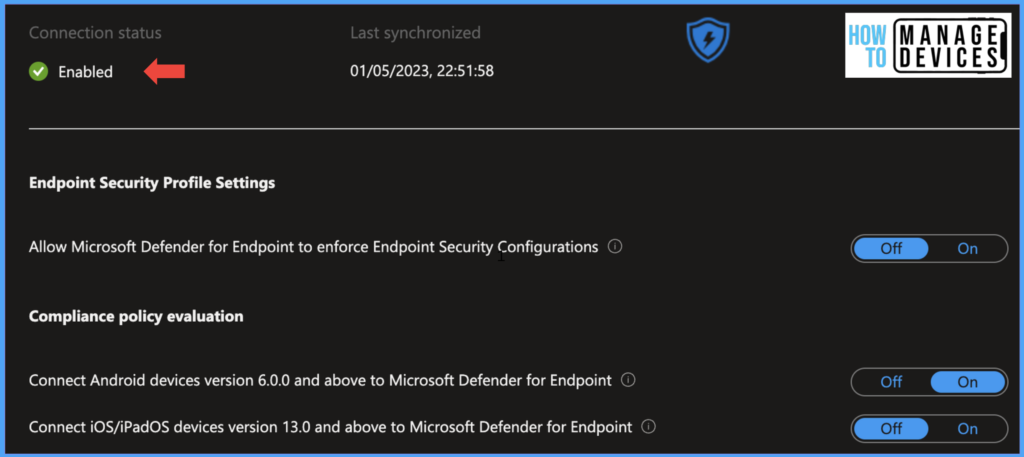
Create a Compliance Policy to Evaluate the Device Risk Level
Compliance policies help evaluate the device’s state against the compliance rules configured in Intune. Compliance policy in line with Conditional access allows us to block access to organizational data. Just configuring and deploying the Defender application will suffice to protect the device. We should create a compliance policy that evaluates the device’s compliance based on the risk/threat level sent by MDE.
- Sign in to Microsoft Intune Admin Center
- Click on Devices > Compliance Policy > Create a new policy
- Now select Android Enterprise as Platform and Personally-owned work profile under Profile type
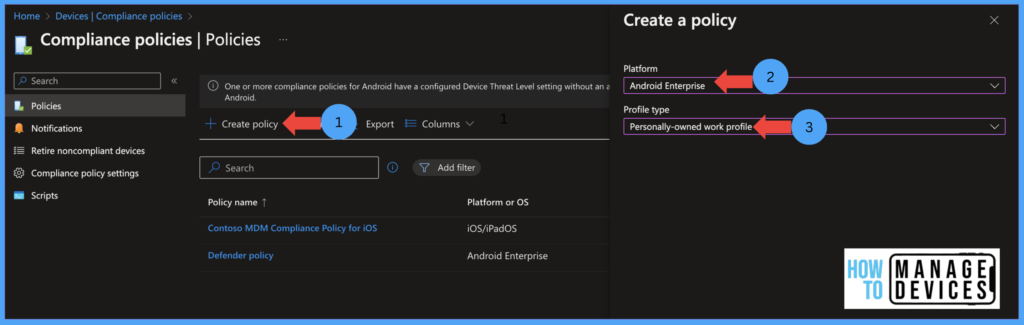
On the Basics page, provide the compliance policy’s Name and a Description of the compliance policy. These are required to identify why the policy is created and click on Next to Compliance Settings page.
On the Compliance Settings page, click on Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and select the risk level for Require the device to be at or under the machine risk score, the risk levels are defined as per the below table.
| Risk Level | Compliance state |
|---|---|
| Not Configured | Devices with all types of threat levels, Low, Medium, and High, are treated as compliant |
| Clear | When set clear, if the Defender found any threat level on the device Intune treats the device as non-compliant. This most secure configuration. |
| Low | When selected, the devices flagged as low threat level are treated as compliant, If the threat is identified as Medium or High, Intune evaluates the device as non-compliance |
| Medium | Devices with threat level Low and Medium are treated as compliant, and with High Threat levels are treated as non-compliant |
| High | Devices with all types of threat levels, Low, Medium, and High, are treated as compliant. This is the least secure configuration |
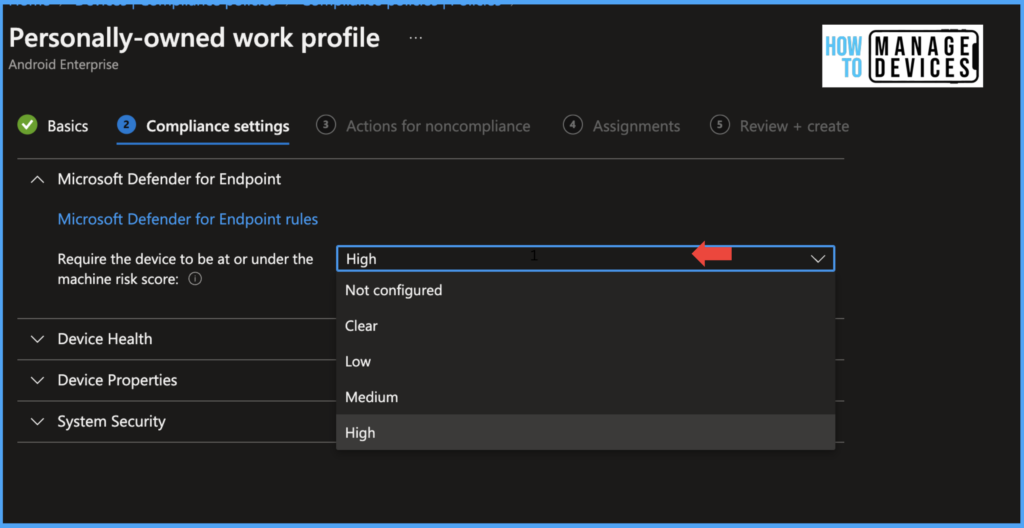
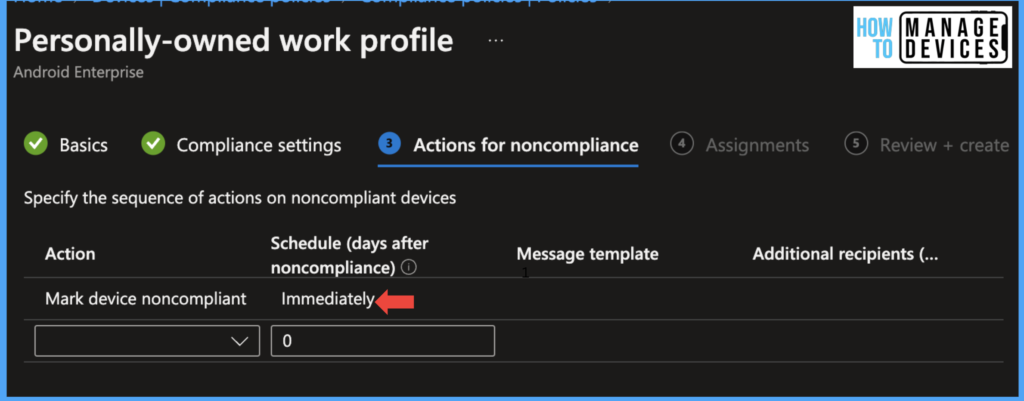
Define the risk level you want to be set and click on Next. Under the Action for Non-compliance page, define actions when the device becomes non-compliant. For our testing, I added only one action for non-compliance,e i.e., Mark the device as non-compliant immediately. We can add action to send email notifications regarding the non-compliance state of the device and Retire the device as well.
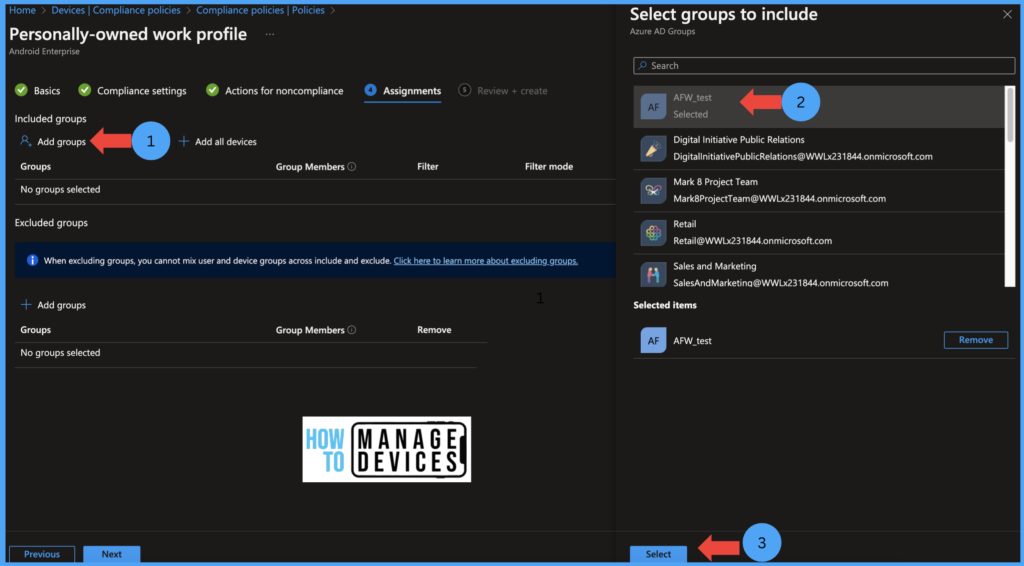
Under the Scope tag page, assign the policy to the scope tags, you wish to and click Next to the Assignment page. Now Assign the policy to the group, click Next,d review the settings under the Review page,e and click Create the policy.
Deploy Microsoft Defender app for Android for Work Devices
In order to protect the devices, the Defender app should be installed on the user’s devices. To install the app, the admin has to add, assign, and deploy the app to the user’s device. Microsoft Defender is publicly available in Google PlayStore. We must approve the app from Managed Google Play Store and assign the app to users. Let’s see how we can do that.
- Sign in to Microsoft Intune Admin Center
- Click on Applications > All Application > Add > Managed Google Play App
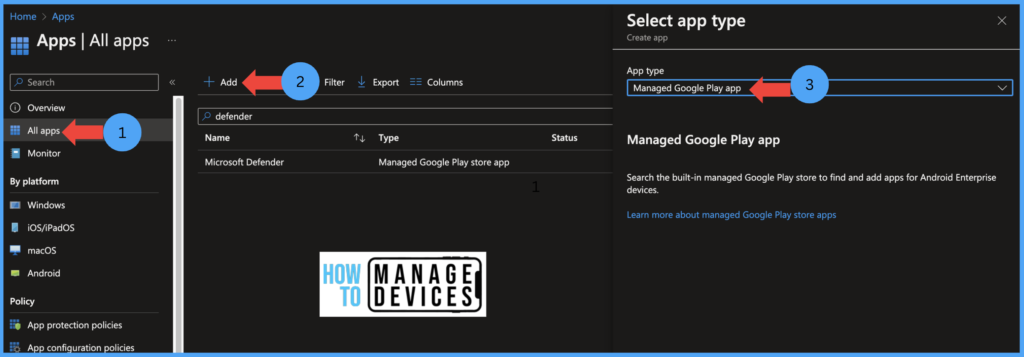
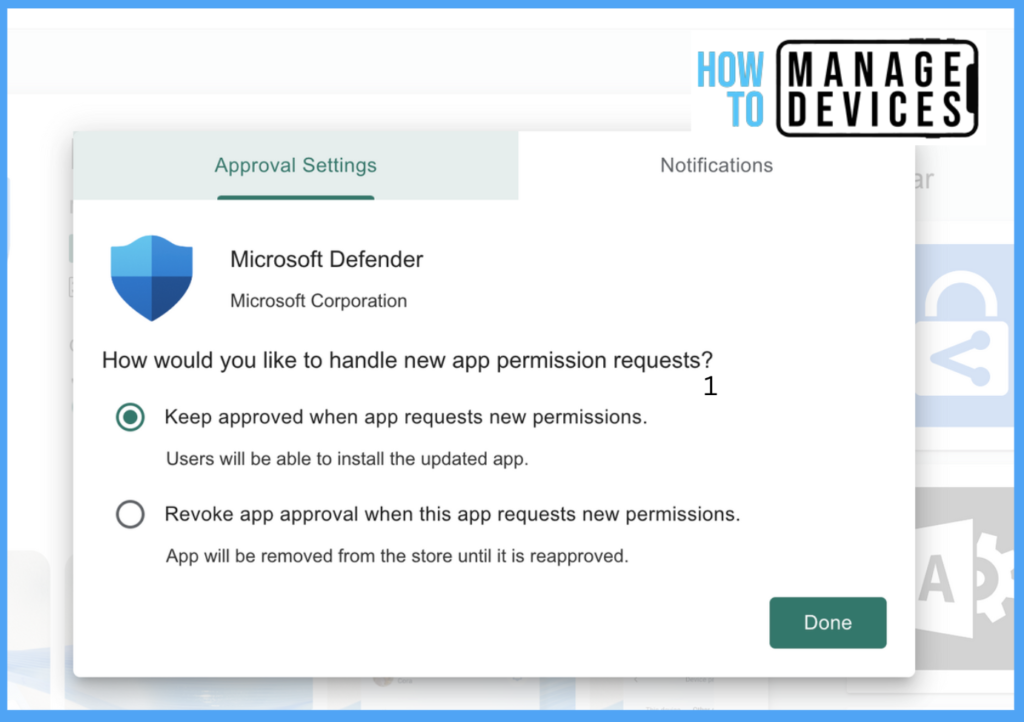
Click on Select and Search for Microsoft Defender on managed Google PlayStore and click on Approve. Under the Approval settings page, choose any one option, “Keep approved when the app requests new permission.”. When selected, Appp will be available to install even if there are changes to app permission.
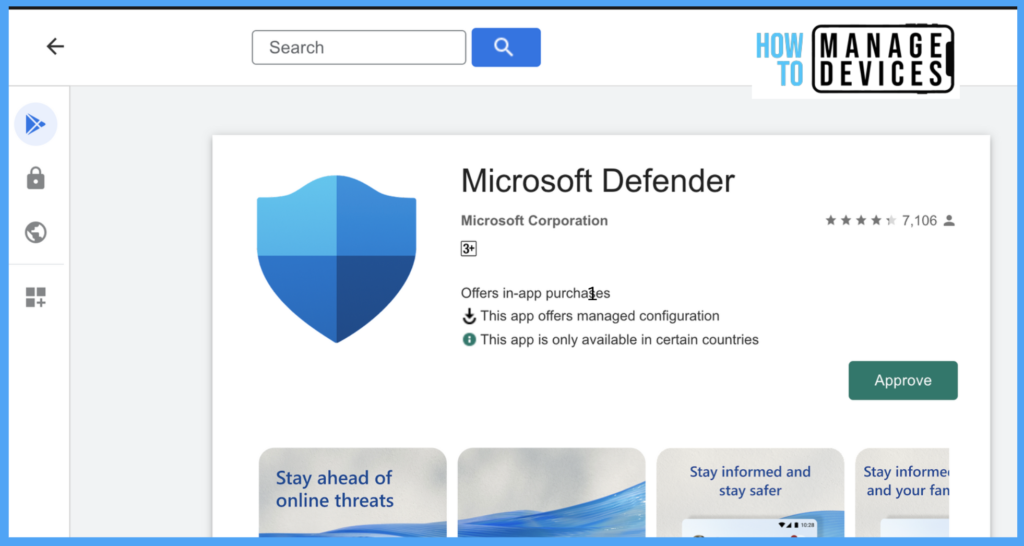
the second option would be “Revoke app approval when this app requests new permissions, by selecting this option app will be removed from the store until reapprove the permissions. Select one option based on your organization’s requirements and click on Done.
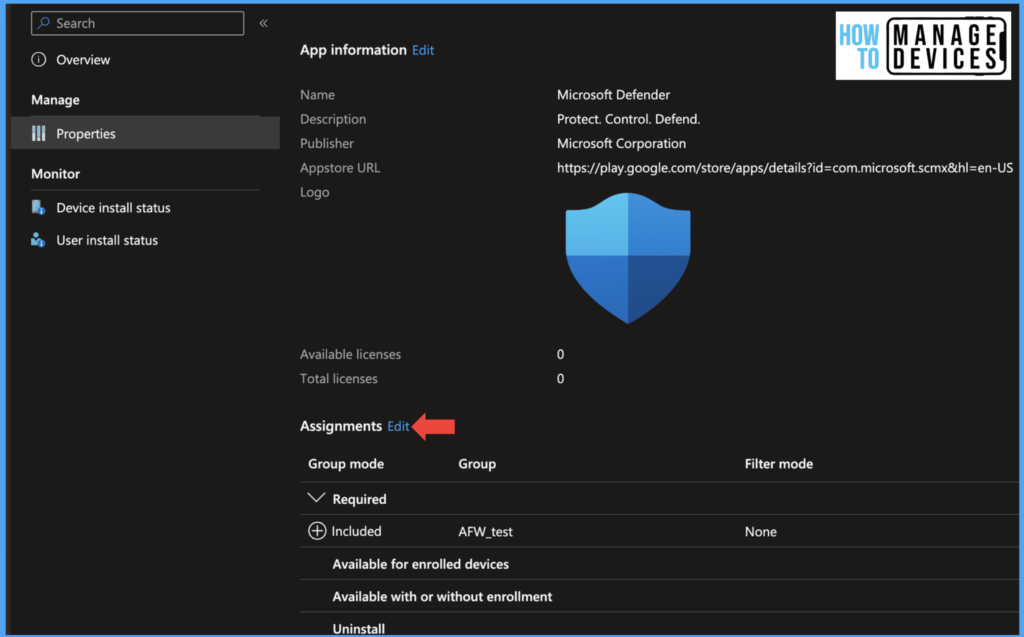
Now click on Sync. This might take a couple of minutes, after which the app will be ready for deployment to the user. Now search for the app, click on the app, and click on properties. Now scroll down to Assignments and click on Edit.
As this app is mandatory to install on all devices, let’s assign the app required app. Intune will silently install the app on the user’s device. Under the required section, click on Add Groups and search for the group to which the app needs to assign.
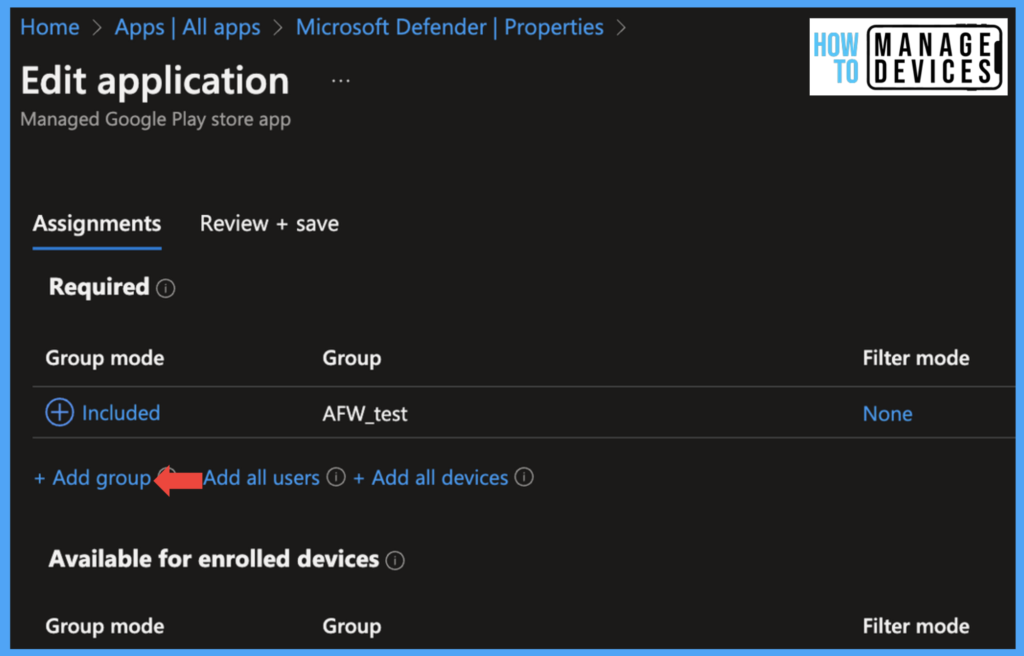
Now select the groups and click on Select and click on Review+Save. This will assign the app to users and install it on the user’s device silently after enrolling the device to Intune. If the device is already enrolled,d the app will be installed once the device is synced to Intune.
We have deployed the app to user devices, next we need to create the application configuration for the Defender app to detect the threats on the user’s devices. We can also configure a few of the Defender app properties with the help of Application configurations. Let’s see how we can configure the application configuration policies.
Create Application Configuration Policies for the Defender App
Application configuration policies help to configure the properties of the app. App Configuration policies can be configured for Managed devices or Managed apps. In our scenario, we will create App Configuration policies for Managed devices.
- Sign in to Microsoft Intune Admin Center
- Click on Applications > Application Configuration Policies > Add > Managed Devices
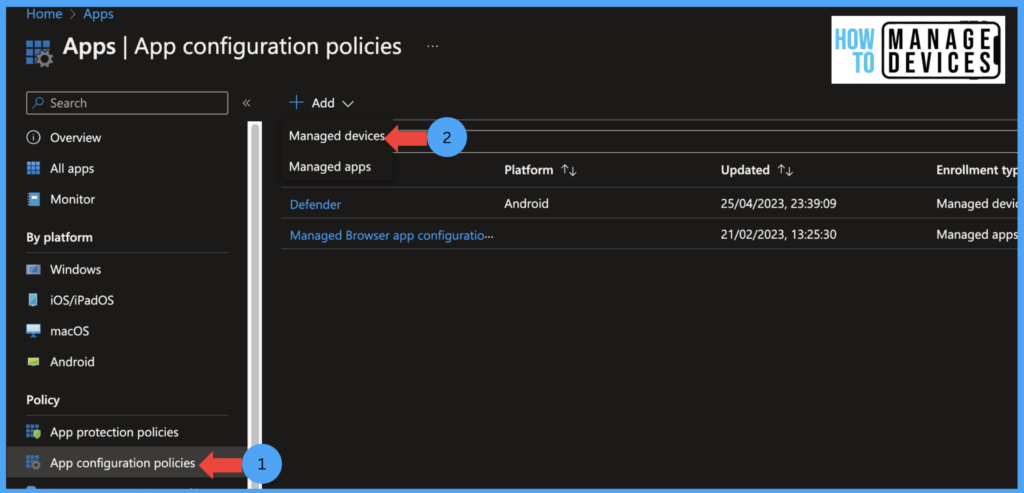
In the Basics section, provide the policy’s Name and a Policy description. Now under the platform, select Android Enterprise. Select the profile type as All Profile Types, this will support both Personal devices enrolled in the Work profile and Corporate devices (If your organization decides to have a different application configuration, select the respective profile type).
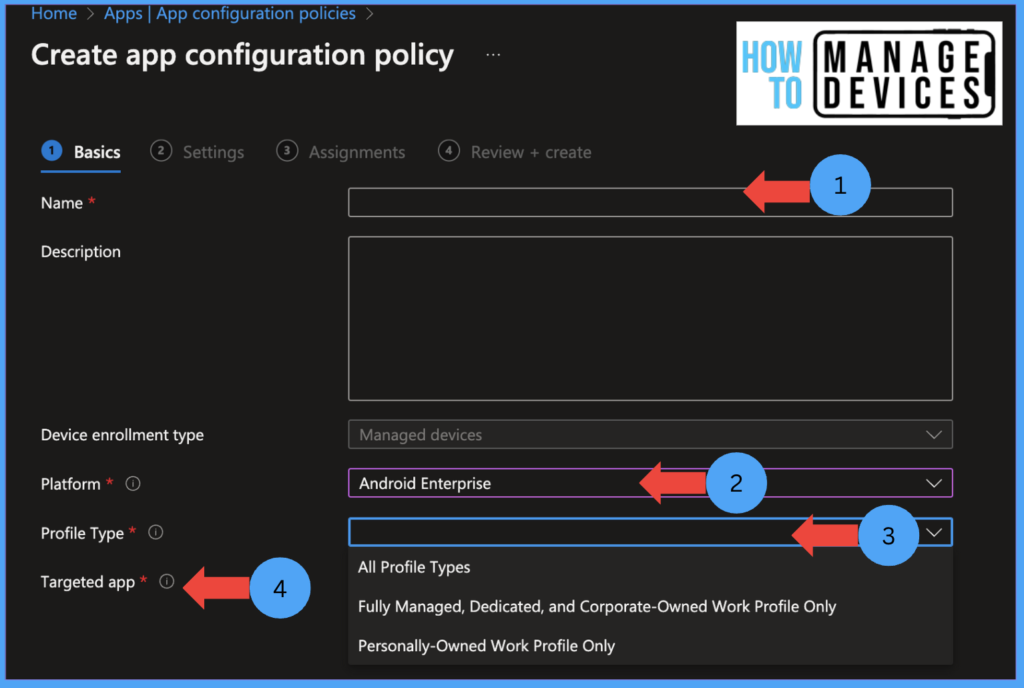
Now for Targeted apps, click on select apps, select the Microsoft Defender app, and click OK, now click on Next to move to the Settings page. On this settings page, we will configure the required settings for the Defender app.

We can provide some default permission to the Defender app, when provided user will not get prompts to provide permissions after installing the app. This is not mandatory, but this will help in enhancing the user experience. In this example, I have provided Storage Access to Auto Grant and Phone state to Prompt user.
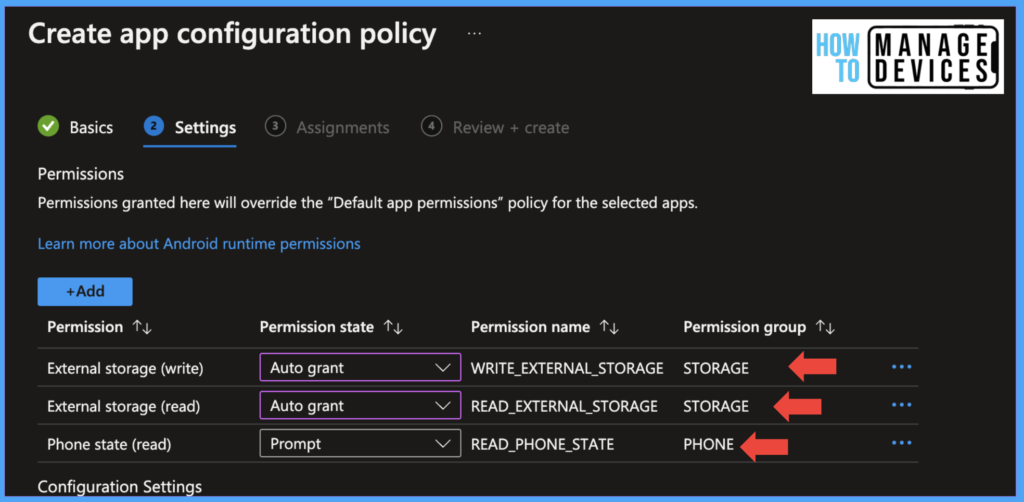
Now we need to configure the Settings for the Defender app. These configurations can be configured in two ways, as shown in the below table.
| Configuration type | Configuration values |
|---|---|
| JSON | We can use JSON script to define the values to configure the Defender settings |
| Use Configuration desiger | Using Configuration Designer, we need to select the required settings and set the value to 1, to enable the setting ad value 0, to disable the setting |
We have configured the Defender app for Anti-Pishing and enabled Microsoft Defender for both Work Profile and Personal profile, to enable we have selected the below settings as per the screenshot. We have also enabled the settings “Enable users to connect this app across the work and personal profile.”. This setting helps users to protect their personal data and alert them if any malicious application is detected.
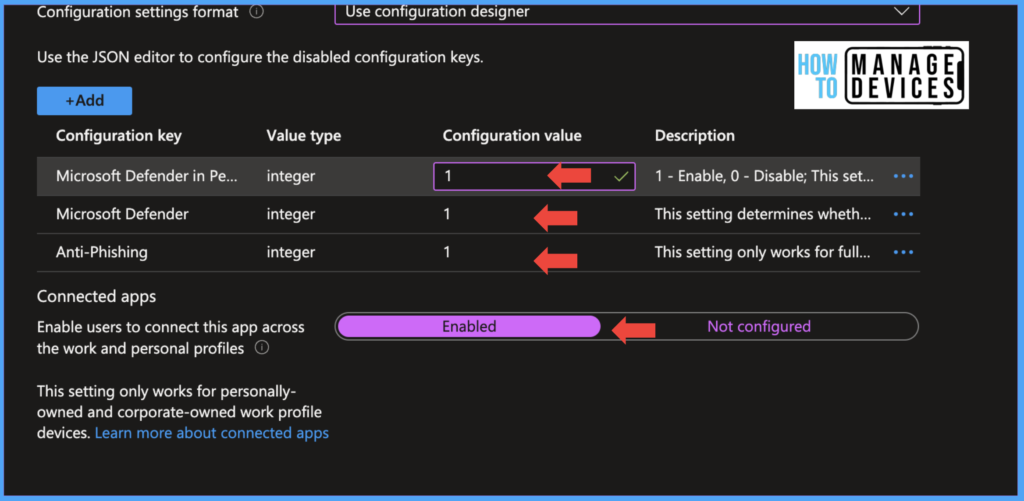
Now click Next, and assign the policy to the required groups. Click Next and click on Create. Now we are ready with the Compliance and App configuration policy and the Microsoft Defender app deployed to users.
End User Experience
When users enroll in the devices, they get the Microsoft Defender app installed as the app is pushed as required. All the policies will be pushed. If Microsoft Defender detects any malicious activity or threats on devices, it alerts users and captures the alerts in Security Portal. Let’s enroll one of the Android devices in our environment. Once I enroll the device, my work profile installs the Microsoft Defender applications.

Open the Microsoft Defender app and sign in with user credentials. On successful authentications, the user is presented with License Term; click Agree after reading the terms. The user is shown the app permissions screen, as we have already given storage permissions via configuration policy, and they are already provided the permissions. Provide the rest of the required Permissions.
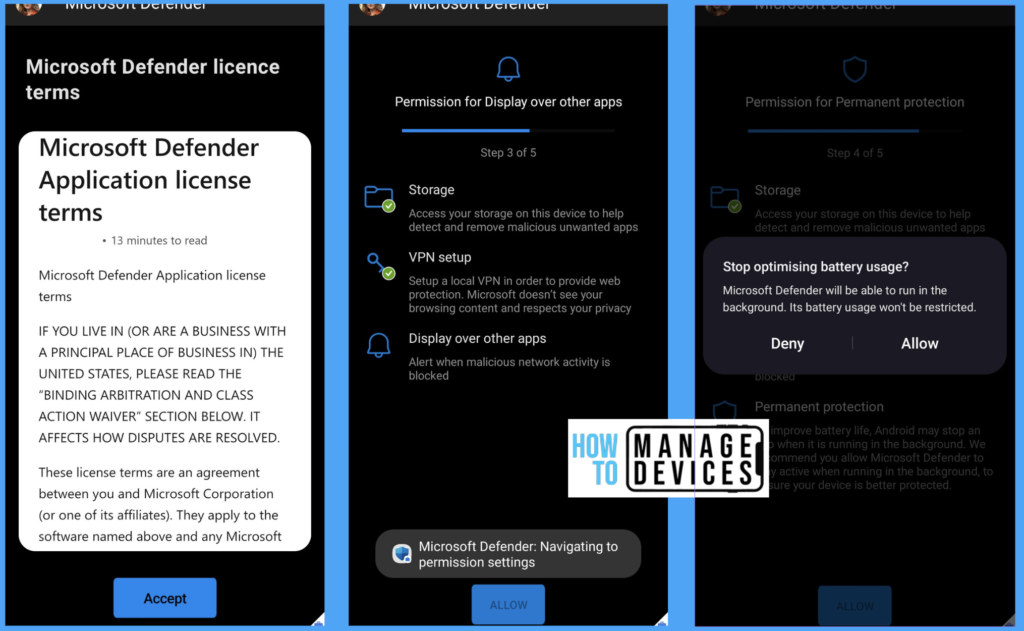
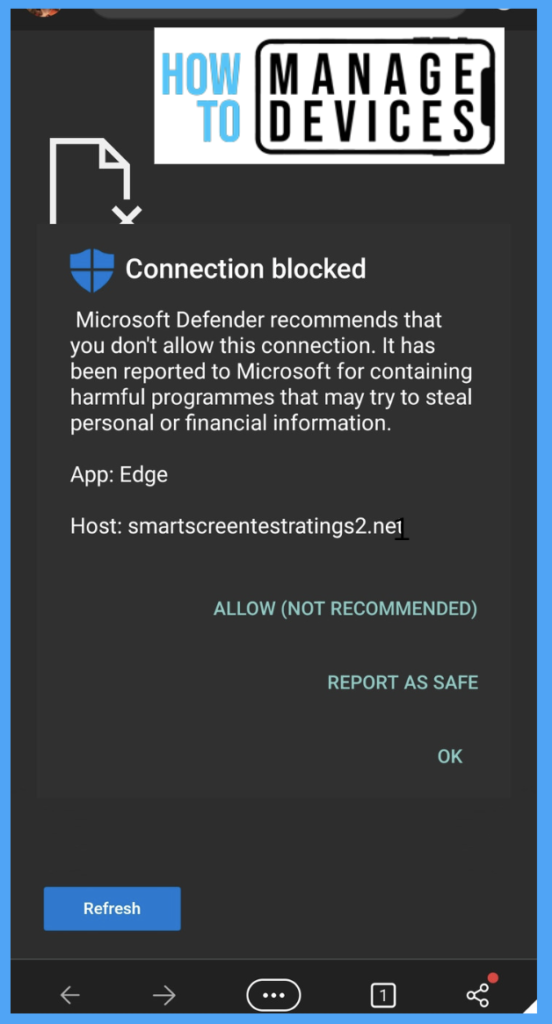
All the required policies and configurations will be deployed to users as per assignment. Microsoft Defender is also configured. Now open any malicious webpage. Microsoft provides a test URL to generate the test scenario (https://smartscreentestratings2.net/). Microsoft Defender detects and blocks the website, as shown below.
Now install any malicious application, Microsoft Defender detects the app and recommends the user to Uninstall the app.
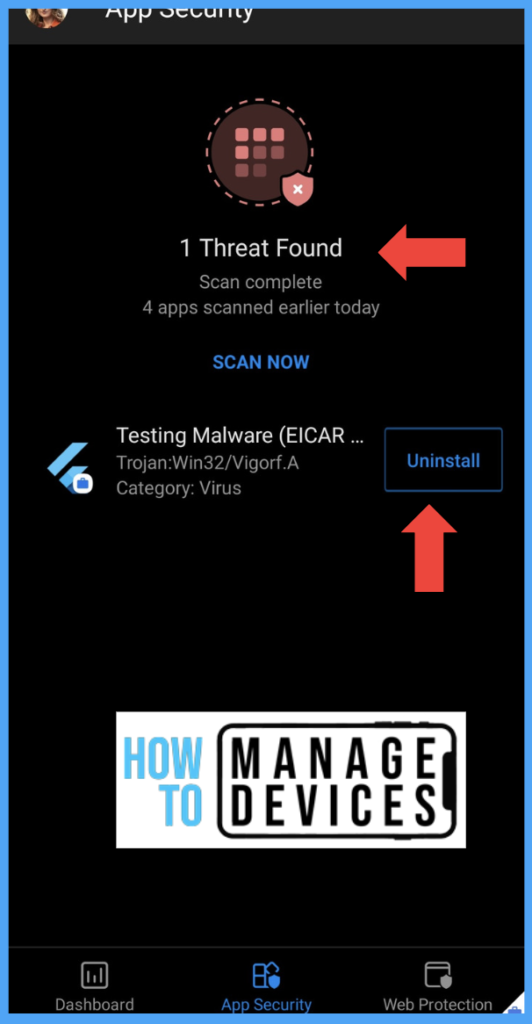
The Defender application dashboard can be viewed with details of the number of applications scanned and the number of URLs suspicious Urls are blocked in Work Profile.
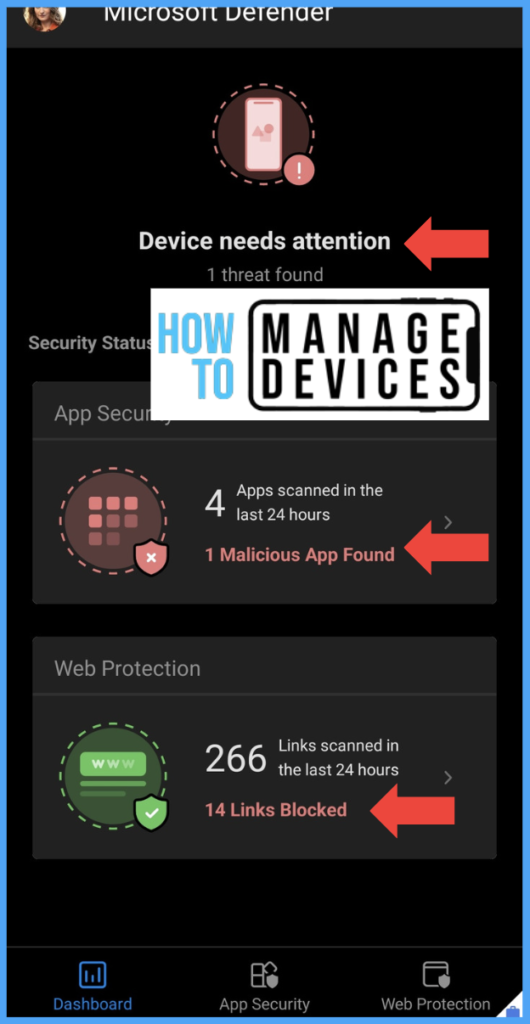
Alerts on Security/Microsoft Defender Portal
On the Security portal, the threats are captured, and the alerts are shown in the dashboard. Microsoft Defender classifies the severity of these alerts. Based on the severity of the alerts, the device becomes compliant or non-compliant.
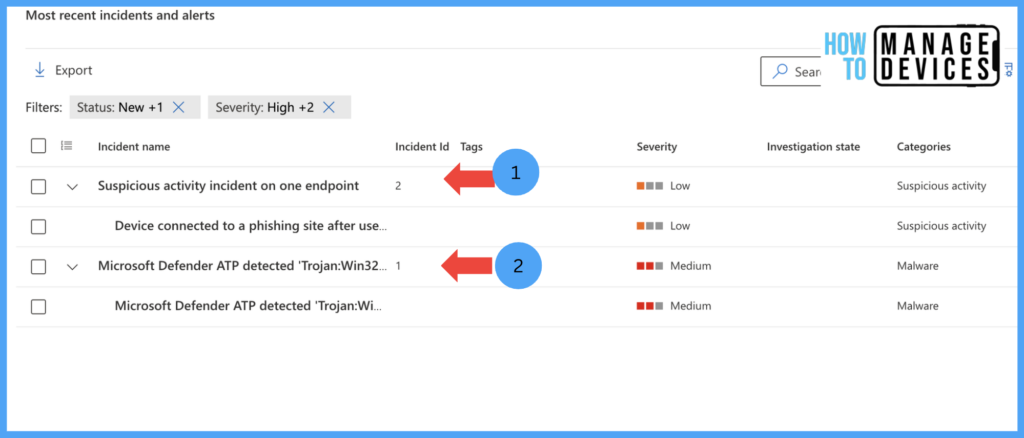
In the above screenshot, the first threat indicates Web access to a malicious website. The second threat shows the Malware application that is installed in Work Profile. We can click on the alert, analyze it in-depth, and provide remediation for the threat.
Devices in Intune
Once the threat level in the Microsoft Defender portal is identified, and Defender app sed the threat level to Intune. Based on the threat level we have configured in the Compliance policy, the device will become Non-compliant.
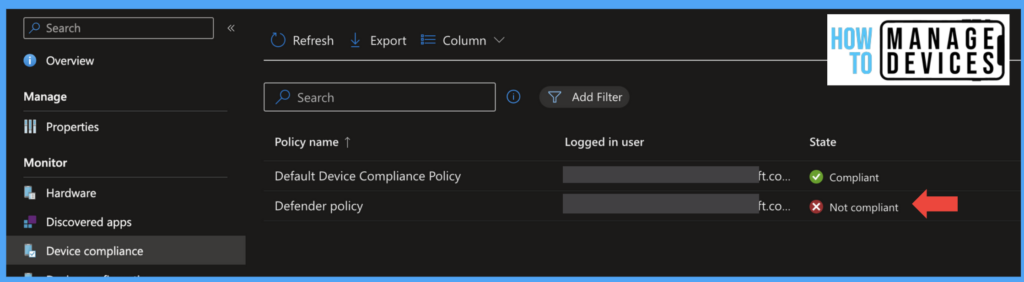
Suppose you have configured Conditional access policy that requires the device to be compliant to access corporate data as soon as the device detects Malware or any threat on the device. In that case, the device becomes Non-Compliant, and access to Corporate data will be blocked.
Conclusion
So, in this way, we can protect our Android devices with the help of Microsoft Defender. This article shows only the basic way to protect the device from Malware and unauthorized websites. You can configure more secure policies based on your organization’s requirements.
Author
About Author – Narendra Kumar Malepati (Naren) has 11+ years of experience in IT, working on different MDM tools. Over the last seven years, Naren has been working on various features of Intune, including migration from different MDMs to Intune. Naren mainly focuses on Android, iOS, and MacOS.

Hello Narendra Kumar Malepati and thank you so much for this helpful Article. I just have one question, is there any way that at the end-user experience they don’t have to follow some manual steps in order to activate MSD? Such as clicking in MS Defender, then selecting the email and agree to the License terms and eventually to give manual permissions? We would like to grant ALL permissions remotely in silent mode. We have already 100 + Tablets deployed and we want to avoid end-users following these manual steps. Thanks in advance.
Hi Julian,
We can approve app permissions by creating a configuration profile for Defender. I have mentioned the same in the article. Please refer image 17, where I have given auto permissions to Defender app. Hope this helps
The auto permissions assignments do no seem to work. The user still needs to allow every permissions manually. Do you have a fix for this?
Hello Naren, Is there any setting which can detect the personal malicious app through work profile defender app.