Hi, we are discussing Protecting Sensitive System Memory by Configuring Debug Programs using Intune Policy. This is an important security control because debugging tools allow very deep access to the operating system. When this ability is given only to trusted users, it prevents unnecessary exposure of sensitive system areas and keeps the environment safer.
Debugging access is powerful, but most users do not need it. Even normal application developers rarely require system-level debugging rights. They can work on their applications without touching kernel-level processes. This means only a very small set of people in the organization should have this privilege.
Giving debugging rights to all users would be risky because the debugger can access memory, process details, and internal system components. Limiting this ability helps avoid accidental changes or unauthorized access to system behavior, making the overall environment more stable and secure.
One of the biggest benefits of this policy is that it protects sensitive system memory. Debugging tools can be credentials, tokens, and other private data stored inside running processes. When only administrators have this right, the organization reduces the chance of data leakage or misuse.
Table of Contents
Protecting Sensitive System Memory by Configuring Debug Programs using Intune Policy
his user right provides complete access to sensitive and critical operating system components. This Cause Assigning this user right can be a security risk. Only assign this user right to trusted users. CIS also explains that this is considered a sensitive privilege, meaning it can expose private security information if used incorrectly. This is why CIS strongly advises restricting it to administrators only.
- Unlock Optimal Remediation Action for High-Severity Threats using Intune
- Stop Hidden Threats Your Step by Step Guide to Activating Network File Scanning using Intune
- How to Delete Attack Surface Reduction ASR Policy from Microsoft Intune
Create the Profile
To begin creating this policy, open the Microsoft Intune Admin Center and go to Devices > Configuration profiles > Create profile. Choose Windows 10 and later as the platform and select Settings catalog as the profile type. This setup is necessary because the User Rights Assignment settings, including Debug Programs, are only available through the Settings catalog.
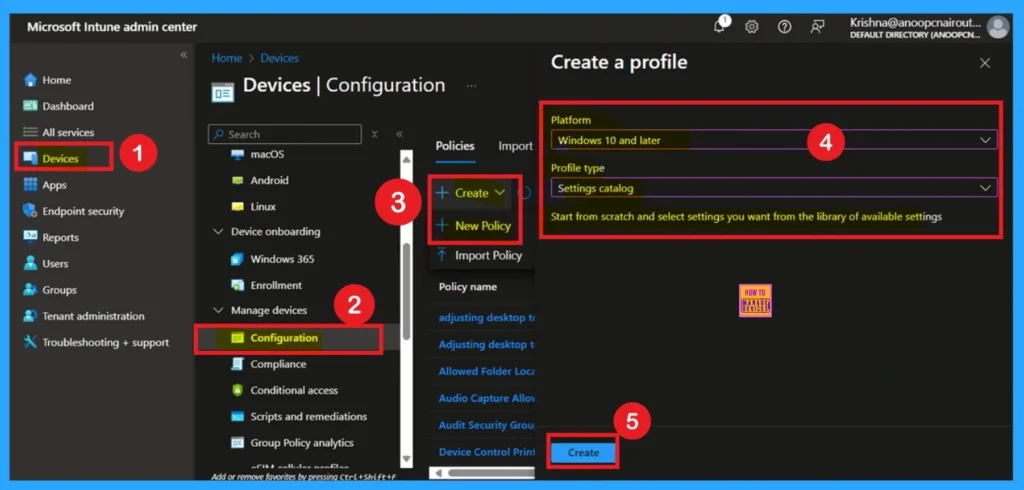
Naming the Profile in Basics Page
On the Basics page, provide a clear name like Debug Programs so that you and other administrators can easily recognize its purpose later. Add a helpful description such as “Restricts Debug Programs privilege to Administrators as recommended by CIS Benchmark to protect sensitive memory and prevent privilege misuse.”
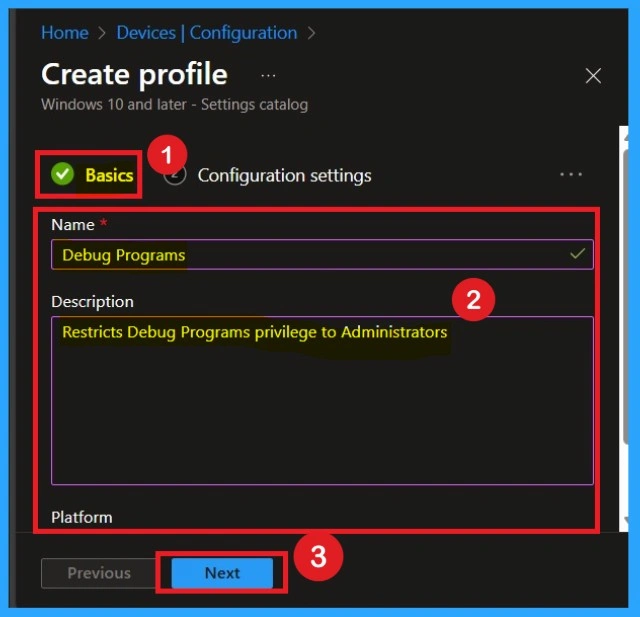
Configuration Settings
After the Basics section, go to Configuration settings and click on Add settings. Use the search bar to type User Rights, and from the available options, select User Rights > Debug Programs. This is the exact setting required to control debugging privilege. Once added, you will see a text field where you must enter the correct SID for the group that should have permission.
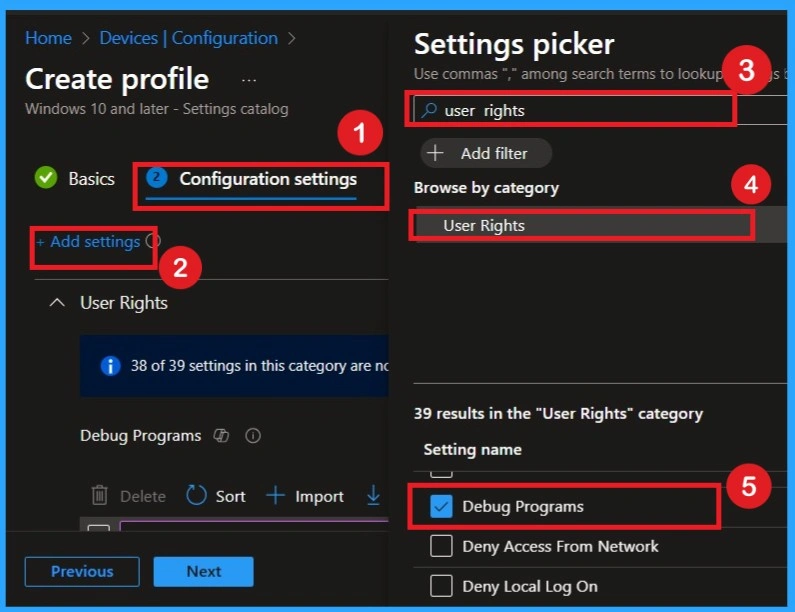
Applying the CIS-Recommended Value
In the Debug Programs configuration box, type S-1-5-32-544, which represents the built-in Administrators group. This SID is required by the CIS Benchmark to ensure only administrators have debugging capability. Make sure there is only one entry and avoid adding extra spaces, because one incorrect entry can cause the policy to fail.

Scope Tags Settings
The next step is the Scope tags section. Scope tags are optional and only required when your organization has different teams managing different sets of devices. Here I skip this section.
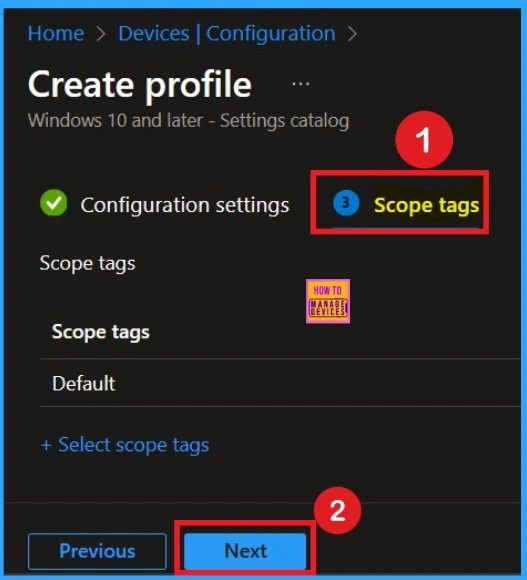
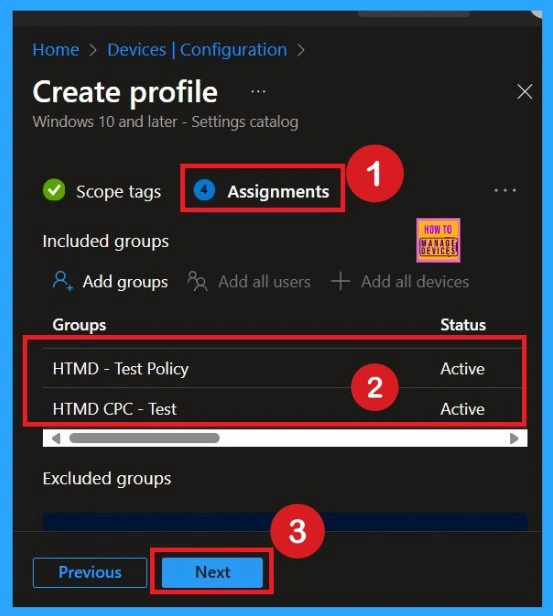
What is Assignments
To assign the policy to specific groups, you can use the Assignment Tab. Here I click, +Add groups option under Included groups. I choose a group from the list of groups and click on the Select button. Again, I click on the Select button to continue.
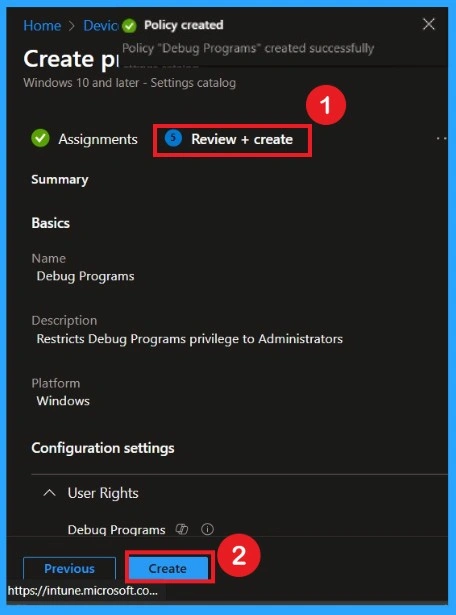
Review + Create Tab
Before completing the policy creation, you can review each tab to avoid misconfiguration or policy failure. After verifying all the details, click on the Create Button. After creating the policy, you will get a success message. Ensuring accuracy at this stage prevents deployment failures and avoids troubleshooting issues later.
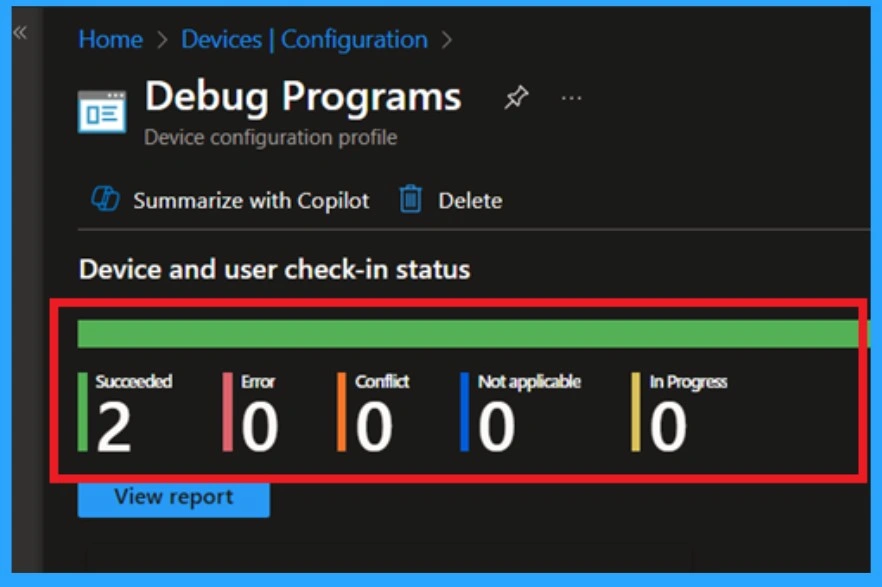
Monitoring Status
After the policy is live, open the profile again and check the Device status and User status sections. These pages show which devices successfully applied the policy and which ones did not. We can verify the policy’s status directly in the Intune Portal. Policy deployment usually takes about 8 hours. To avoid the time consumption, try a manual sync from the Company Portal app on the device, then recheck the status.
- Navigate to Devices, then Configuration.
- Select the policy name from that.
- We can see its status as succeeded (2).
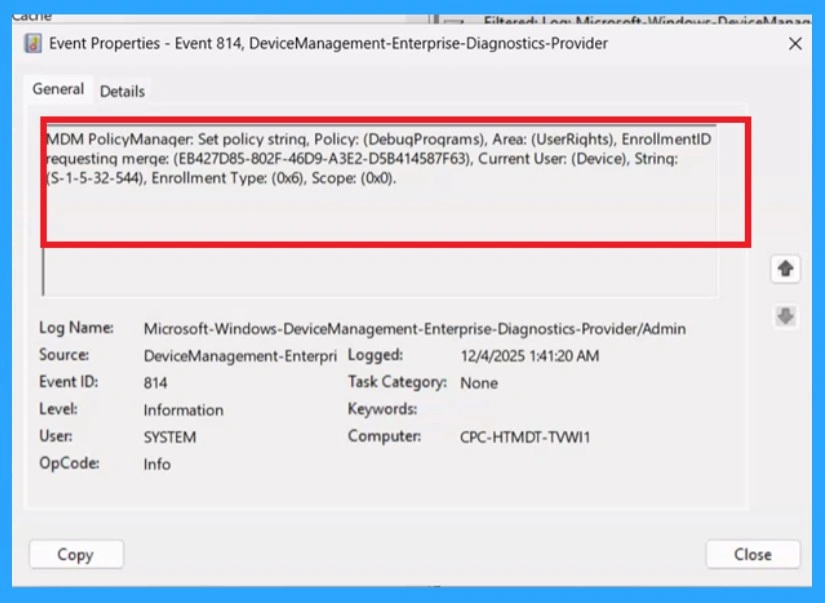
End User Result
Once the policy applies, only administrators will have permission to attach a debugger to system processes or the Windows kernel. Normal users cannot access sensitive memory or use debugging tools in a harmful way. You can check this with the client-side verification.
| Policy Info |
|---|
| MDM PolicyManager: Set policy strinq, Policy: (DebuqProqrams), Area: (UserRiqhts), EnrollmentID requestinq merqe: (EB427D85-802F-46D9-A3E2-D5B414587F63), Current User: (Device), Strinq: S-1-5-32-544), Enrollment Type: (0x6), Scope: (0x0). |
Remove the Policy
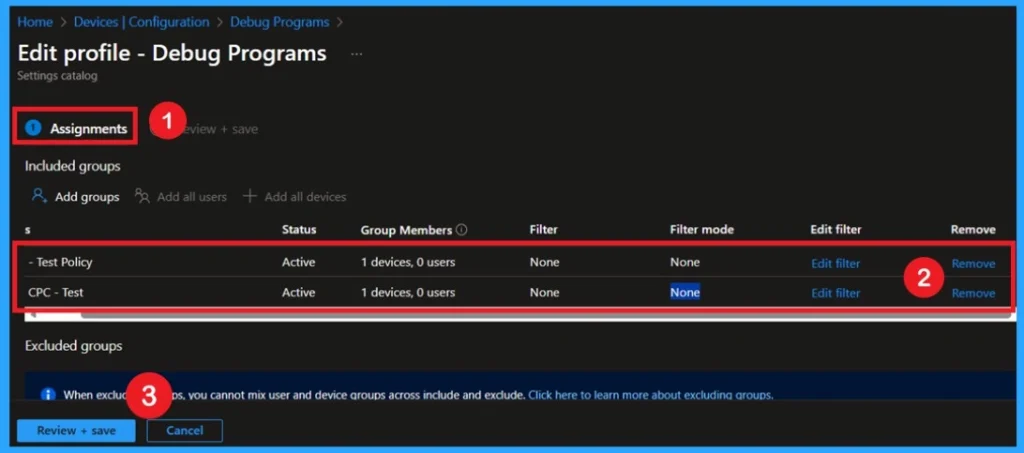
We can easily remove groups from a policy. Just open the policy from the Configuration section, then click the Edit button on the Assignments. From there, click the Remove button to unassign the policy from the desired groups.
For detailed information, you can refer to our previous post – Learn How to Delete or Remove App Assignment from Intune using by Step-by-Step Guide.
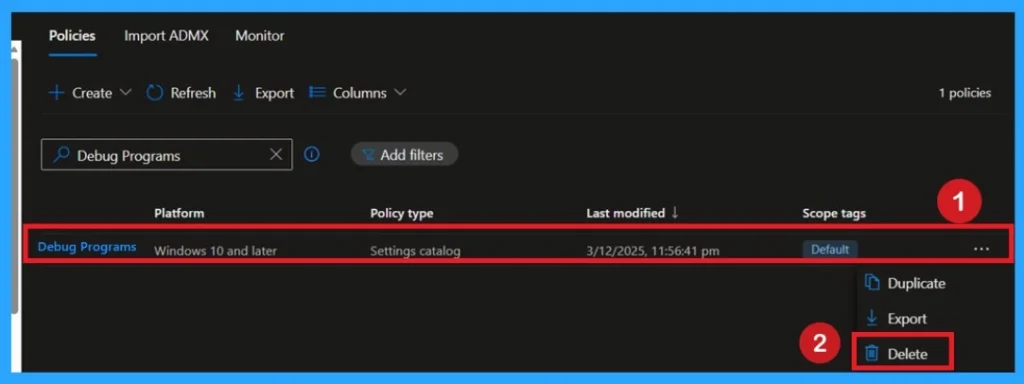
Delete the Policy Permanently
To delete a policy in Microsoft Intune, first sign in to the Microsoft Intune Admin Center. Navigate to Devices and then select Configuration. Locate and select the specific policy you want to remove. Once you’re on the policy details page, click the 3 -dot menu in the top right corner and choose Delete from the available options. This makes the intention of the policy easy to understand.
For more information, you can refer to our previous post – How to Delete Allow Clipboard History Policy in Intune Step by Step Guide.
Need Further Assistance or Have Technical Questions?
Join the LinkedIn Page and Telegram group to get the step-by-step guides and news updates. Join our Meetup Page to participate in User group meetings. Also, Join the WhatsApp Community to get the latest news on Microsoft Technologies. We are there on Reddit as well.
Author
Anoop C Nair has been Microsoft MVP for 10 consecutive years from 2015 onwards. He is a Workplace Solution Architect with more than 22+ years of experience in Workplace technologies. He is a Blogger, Speaker, and Local User Group Community leader. His primary focus is on Device Management technologies like SCCM and Intune. He writes about technologies like Intune, SCCM, Windows, Cloud PC, Windows, Entra, Microsoft Security, Career, etc


