Let’s learn the Various Critical Windows 11 Event ID. The Event IDs are also known as Event Identifiers. Event identifiers uniquely identify a particular event. Each event source can define its own numbered events and the description strings to which they are mapped in its message file.
Event viewers can present these strings to the user. They should help the user understand what went wrong and suggest what actions to take. Direct the description to users solving their problems, not administrators or support technicians.
Messages are defined in the event message file. The description strings in the event message file are indexed by the event identifier, enabling Event Viewer to display event-specific text for any event based on the event identifier. All descriptions are localized and language-dependent.
The Windows operating system hunts particular events in the log files, such as application installations, security management, system setup operations on initial startup, and problems or errors. Microsoft first presented the Windows event log on the Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 releases. It has been included in all the later versions of Windows.

- Fixes for 6 Exchange Server Vulnerabilities Released in August
- MDE Portal Security Settings Policy Creation and Troubleshooting using Windows Sense Event Logs
What is Critical Event ID?
Event identifiers uniquely identify a particular event. Each event source can define its own numbered events and the description strings to which they are mapped in its message file. Event viewers can present these strings to the user.
Windows 11 Event ID 2: Event Subscription Activation
Each event subscription can deliver events from multiple sources. Each subscription may also have an expiration date. When a subscription is activated, and the subscription expiration date is still in the future, the subscription will attempt to receive events by connecting to remote sources.
As long as the subscription can connect to at least one source, it becomes active. This is applied to Windows Server 2008 only. EVTCOLL_SUBSCRIPTION_ACTIVATION_ERROR is the Symbolic Name.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Event Subscription Activation | Microsoft-Windows-EventCollector | Due to an error, subscription %1 could not be activated on machine %2. Error Code is %3. The subscription will remain inactive on this target until the subscription is resubmitted / reset. |
Event ID 1056: DHCP Event no DNS Credentials on DC
According to Microsoft, this event is logged when the DHCP service has detected that it is running on a DC and has no credentials configured for use with Dynamic DNS registrations initiated by the DHCP service.
You can configure the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server service to impersonate an account to perform Domain Name Service (DNS) registrations and secure dynamic updates. The Netsh.exe tool can be used to configure the impersonation credentials. You must create a dedicated user account in Active Directory Domain Services before you use the Netsh.exe tool to configure the use of impersonation credentials.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1056 | DHCP Event no DNS Credentials on DC | Microsoft-Windows-DHCP-Server | The DHCP service has detected that it is running on a DC and has no credentials configured for use with Dynamic DNS registrations initiated by the DHCP service. This is not a recommended security configuration. Credentials for Dynamic DNS registrations may be configured using the command line “netsh dhcp server set DNS credentials” or via the DHCP Administrative tool. |
To resolve this issue, configure impersonation credentials for dynamic updates. To perform these procedures, you must be a member of the Administrators group or have been delegated the appropriate authority.
You can configure the DHCP Server service to impersonate an account to perform DNS registrations. The Netsh.exe tool can be used to configure the impersonation credentials.
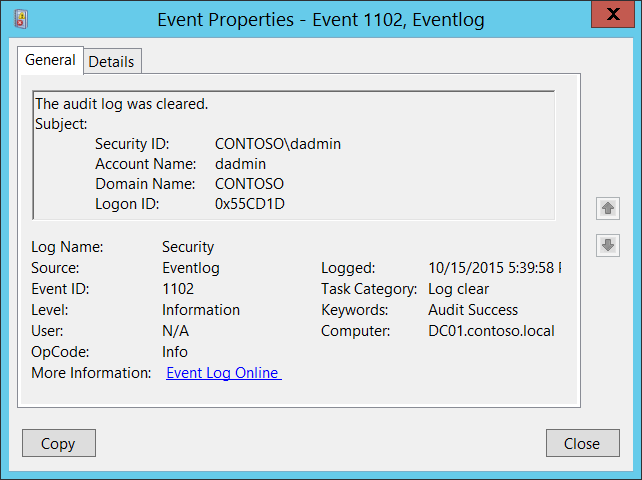
Event ID 1102: The Audit Log was Cleared
According to Microsoft, this event is logged whenever the Security log is cleared, REGARDLESS of the status of the Audit System Events audit policy. Microsoft says, this is an information event, and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1102 | The Audit Log was Cleared | Microsoft Windows Eventlog | This event generates every time the Windows Security audit log was cleared. |
Event ID 2003: Firewall Rule Processing
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security receives its rules from local security policy stored in the system registry and from Group Policy delivered by Active Directory.
After receiving a new or modified policy, Windows Firewall must process each rule in the applied policies to interpret what network traffic will be blocked, allowed, or protected by using Internet Protocol security (IPsec). This event is logged when a Windows Firewall setting in the profile has changed.
Note Typically, the warning messages are related to the W3svc driver service or the Active Server Pages (ASP) service.
This event is logged when the configuration information of the performance library for the service does not match the trusted performance library information stored in the registry. This is a normal condition. No further action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | WFProfileConfigurationChangedEvent | Microsoft Windows Windows Firewall with Advanced Security | A Windows Firewall setting in the %1 profile has changed. New Setting: %tType:%t%2 %tValue:%t%5 %tModifying User:%t%7 %tModifying Application:%t%8 |
Event ID 4624: An Account was Successfully logged on
This event is generated when a logon session is created. It is generated on the computer that was accessed. No user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4624 | An Account was Successfully logged on | Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing | This event generates when a logon session is created (on the destination machine). It generates on the computer that was accessed, where the session was created. |
Event ID 4625: An Account Failed to Log-on
This event is logged for any logon failure. It generates on the computer where a logon attempt was made, for example, if a logon attempt was made on the user’s workstation, then the event will be logged on this workstation. This event generates on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4625 | An Account Failed to Log-on | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event is logged for any logon failure. |

There are some reasons for the event are User name does not exist, User name is correct but the password is wrong, User is currently locked out, and Account is currently disabled.
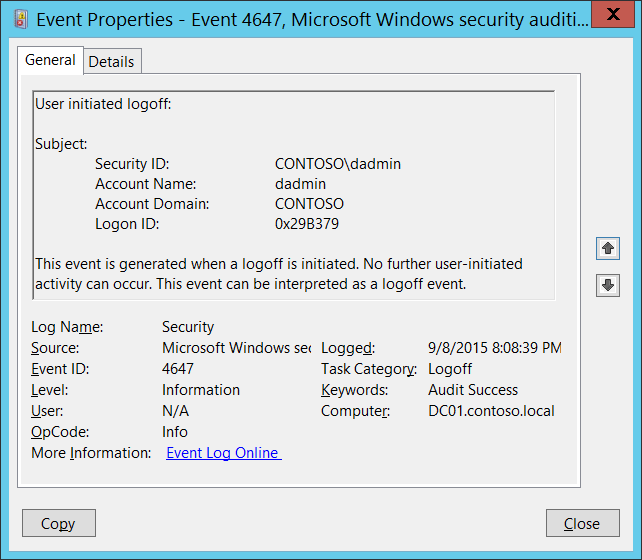
Event ID 4647: User Initiated Logoff
This event is generated when a logoff is initiated. No further user-initiated activity can occur. This event can be interpreted as a logoff event.
An account was logged off.” event is that 4647 events are generated when the logoff procedure was initiated by a specific account using the logoff function, and 4634 event shows that the session was terminated and no longer exists.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4647 | User-Initiated Logoff | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | 4647 is more typical for Interactive and RemoteInteractive logon types when a user was logged off using standard methods. You will typically see both 4647 and 4634 events when the logoff procedure was initiated by a user. |
Event ID 4659: File Delete on Close
This event should be logged whenever the user installs a patch that requires the replacement of a file that is already opened by Windows and can’t be closed until shut down. No user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4659 | File Delete on Close | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | A handle for an object was requested with the intent to delete it. |
Event ID 4660: An Object was Deleted
This event is logged when an object is deleted where that object’s audit policy has auditing enabled for deletions for the user who just deleted it.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4660 | An object was deleted | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates when an object was deleted. The object could be a file system, kernel, or registry object. |
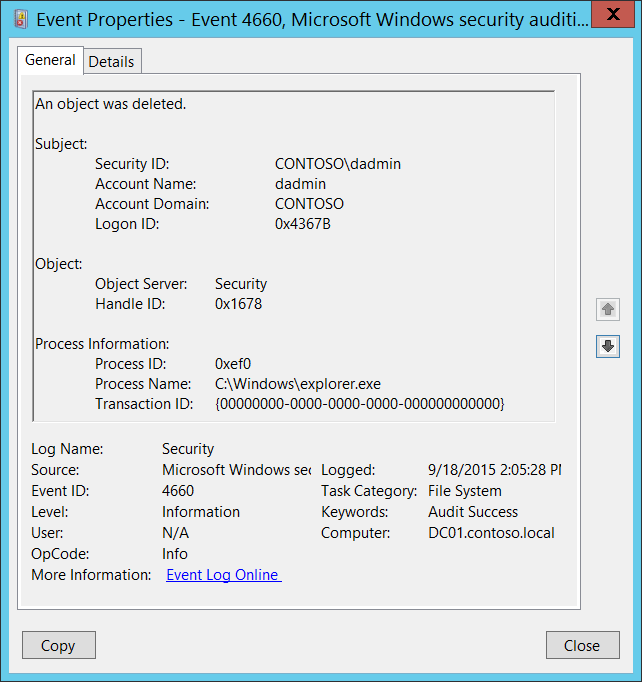
Event ID 4663: An Attempt was Made to Access an Object
This event indicates that a specific operation was performed on an object. The object could be a file system, kernel, registry object, or a file system object on removable storage or a device. This event is logged when an attempt was made to access an object. No user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4663 | An attempt was made to access an object | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event indicates that a specific operation was performed on an object. The object could be a file system, kernel, or registry object, a file system object on removable storage, or a device |
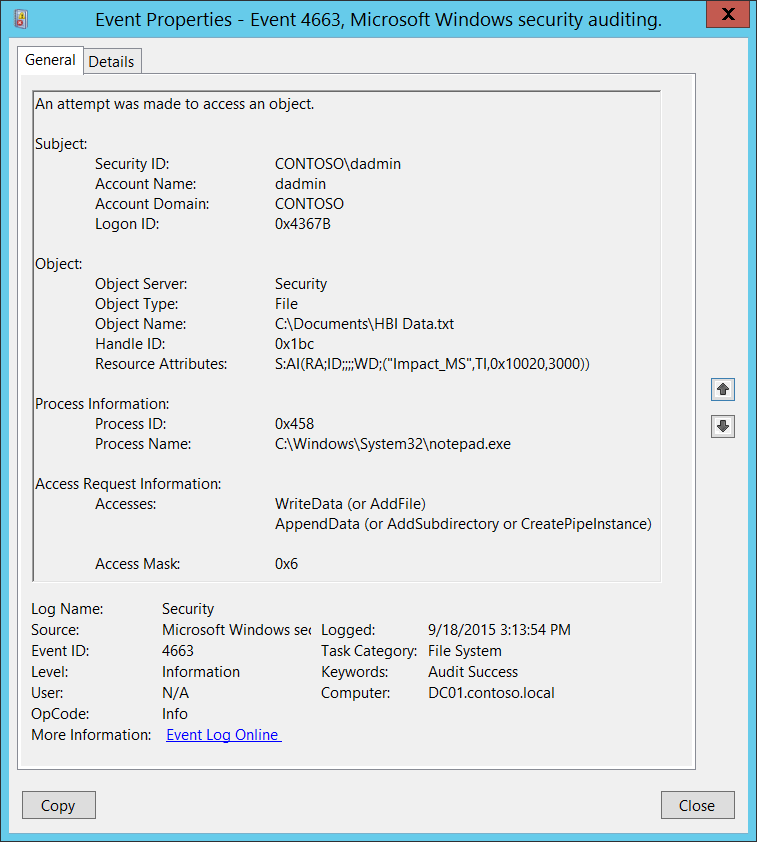
Event ID 4670: Permissions on an Object were Changed
Windows logs this event when a user changes the access control list on an object. The event identifies the object, that changed the permissions and the old and new permissions. No user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4670 | Permission on an object were changed | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates when the permissions for an object are changed. The object could be a file system, registry, or security token object. |
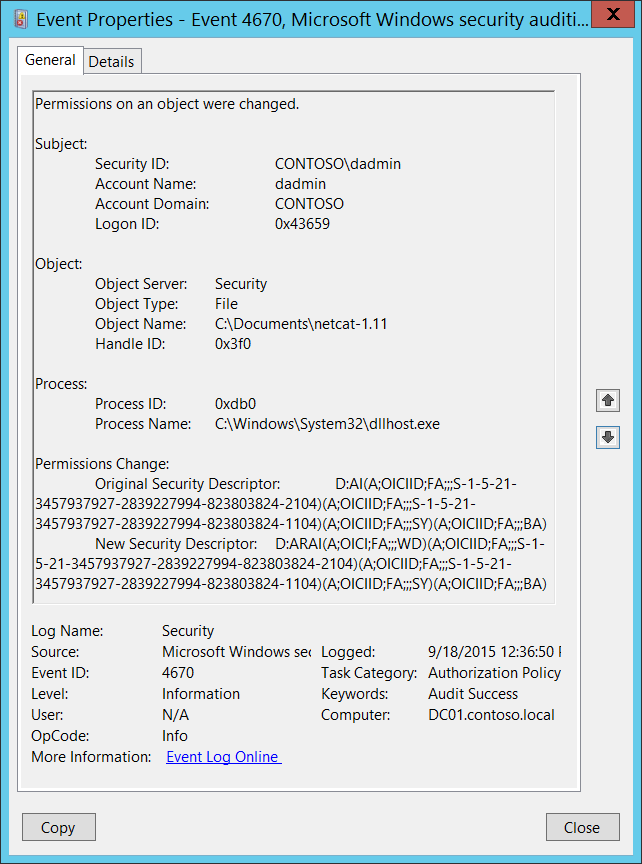
Event ID 4688: A New Process Has Been Created
This Event ID is logged when a new process has been created. Token Elevation Type indicates the type of token that was assigned to the new process by the User Account Control policy.
- Type 1 is a full token with no privileges removed or groups disabled.
- Type 2 is an elevated token with no privileges removed or groups disabled.
- Type 3 is a limited token with administrative privileges removed and administrative groups disabled.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4688 | A new process has been created | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time a new process starts. |
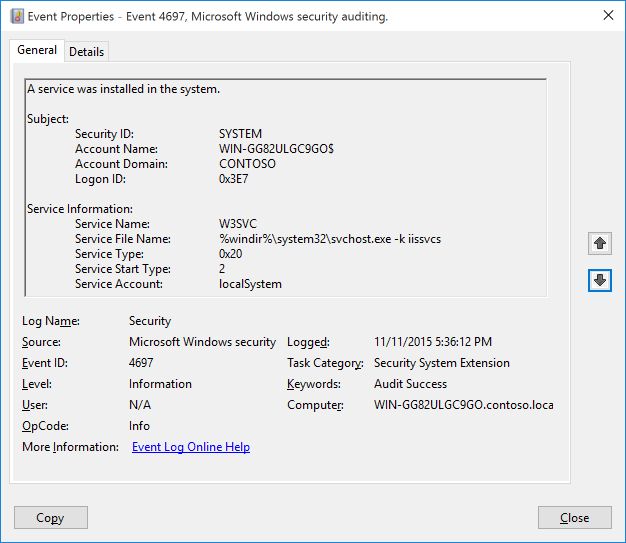
Event ID 4697: A Service was Installed in the System
This event is logged when a new service is installed by the user and User Name and Domain identify the user who installed the service. Verify the user is authorized to install the service.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4697 | A service was installed in the system | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates when a new service was installed in the system. |
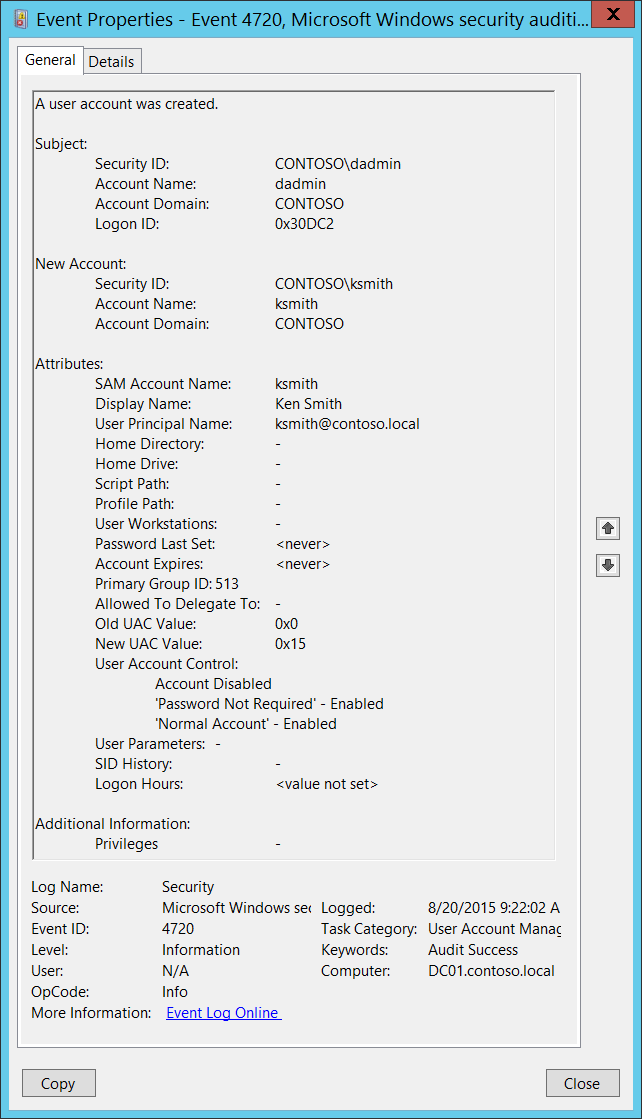
Event ID 4720: A User Account was Created
This event is logged when a user account was created in the Active Directory of a Domain Controller. This is an information event and no user account is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4720 | A user account was created | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time a new user object is created. This event generates on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations. |
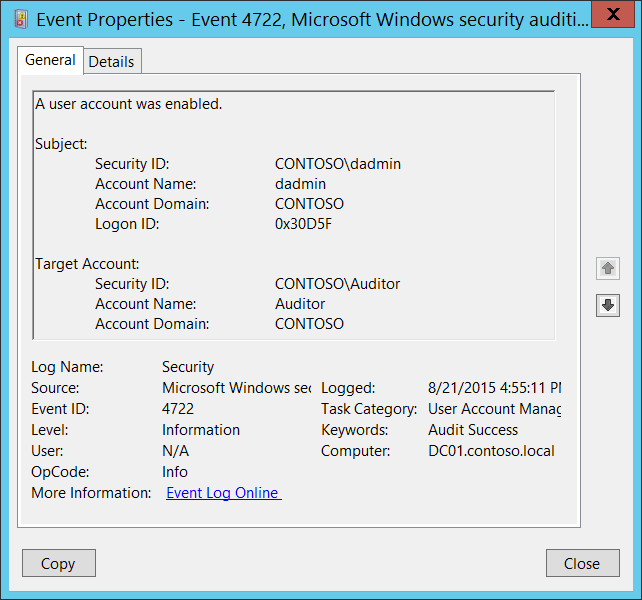
Event ID 4722: A User Account was Enabled
This event generates every time user or computer object is enabled. For user accounts, this event generates on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations. For computer accounts, this event generates only on domain controllers. According to Microsoft, this is an information event and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4772 | A User Account was Enabled | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time user or computer object is enabled. |
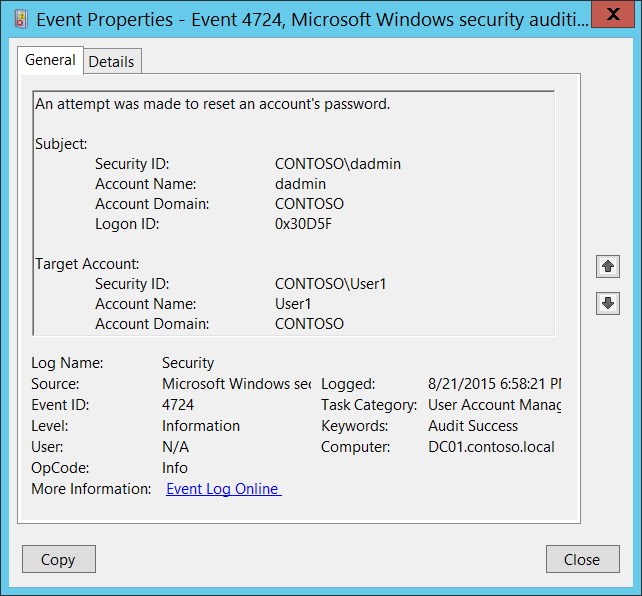
Event ID 4724: An Attempt was made to Reset an Account’s Password
This event is generated when a logon session is created. It is generated on the computer that was accessed. This event generates every time an account attempts to reset the password for another account.
For user accounts, this event generates on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations. For domain accounts, a Failure event generates if the new password fails to meet the password policy. A Failure event does NOT generate if a user gets “Access Denied” while doing the password reset procedure.
This event also generates if a computer account reset procedure was performed. For local accounts, a Failure event generates if the new password fails to meet the local password policy. Microsoft says, this is an information event and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4724 | An attempt was made to reset an account’s password | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time an account attempts to reset the password for another account. |
Event ID 4728: A Member was Added to a Security-Enabled Global Group
This event is logged when a member is added to a Security enabled Global group in the Active Directory of a Domain Controller. Microsoft says, this is an information event and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4728 | A Member was Added to a Security-Enabled Global Group | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event is logged when a member is added to a Security enabled Global group in the Active Directory of a Domain Controller |
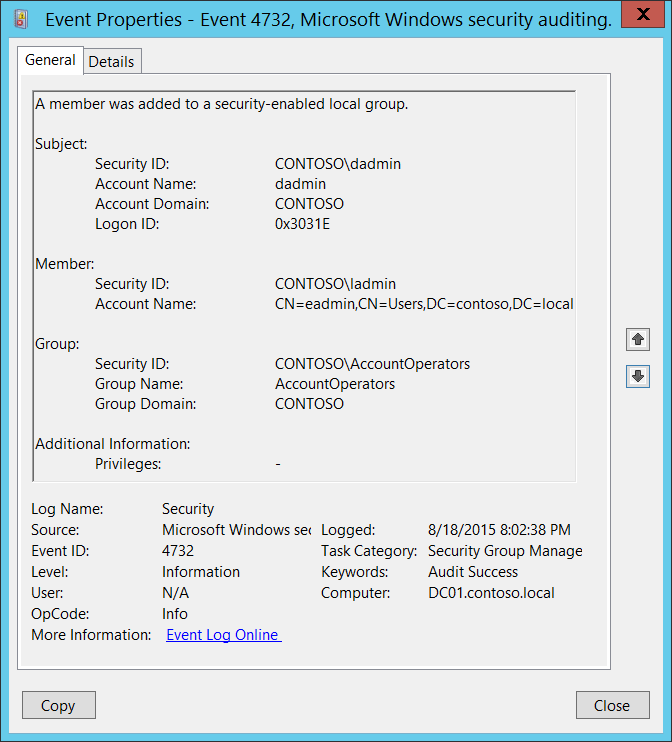
Event ID 4732: A Member was Added to a Security-Enabled Local Group
This event is logged on domain controllers when a member was added to a security-enabled local group in Active Directory. Microsoft says, this is an information event and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4732 | A Member was Added to a Security-Enabled LocalGroup | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time an account attempts to reset the password for another account. |
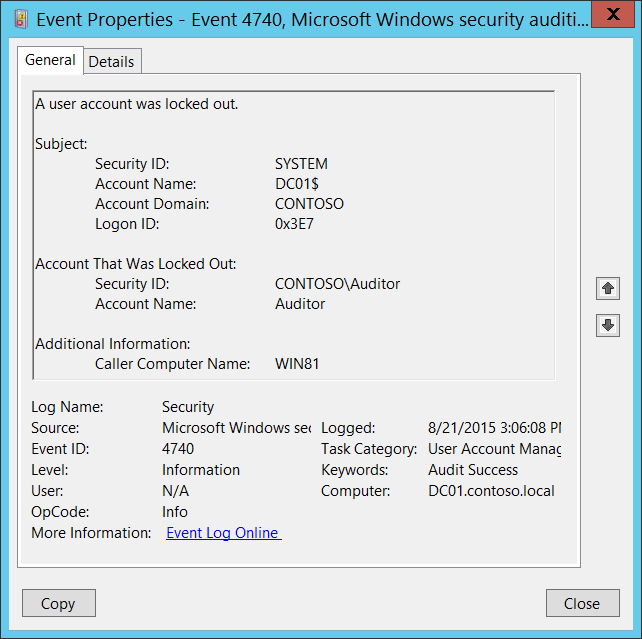
Event ID 4740: A User Account was Locked Out
This event is logged when a user account was locked out. For user accounts, this event generates on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4740 | A user account was locked out | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event is logged when a user account was locked out. |
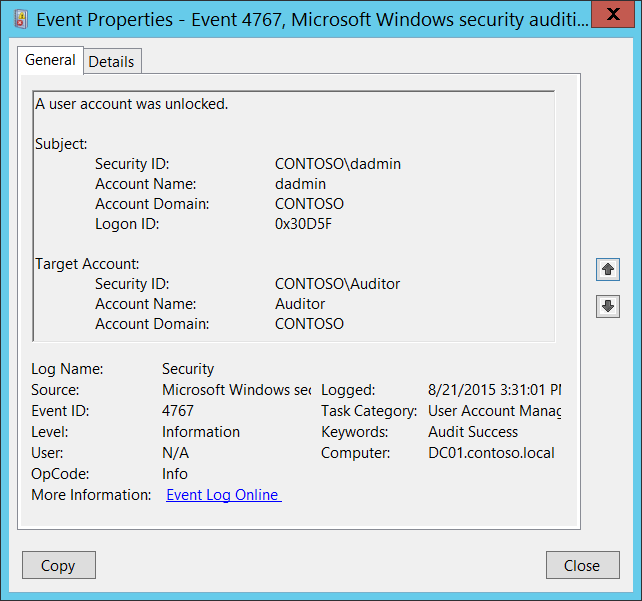
Event ID 4767: A user account was unlocked
This event is logged on when you unlock an account that was locked out. The subject field in the description contains the account information of the user who unlocked the account. The target account field contains the account information of the user whose account was unlocked.
The action is to verify that the target account information and the account information of the user who unlocked the account are authorized.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4767 | A user account was unlocked | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time a user account is unlocked. |
Event ID 4778: A Session was Reconnected to a Window Station
This event generates when a user reconnects to a disconnected terminal server (Remote Desktop) session. This event is also logged when a user returns to an existing logon session via Fast User Switching.
This event also generates when a user reconnects to the virtual host Hyper-V Enhanced Session, for example. Microsoft says, this is an information event and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4778 | A session was reconnected to a Window Station | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time a user account is unlocked. |

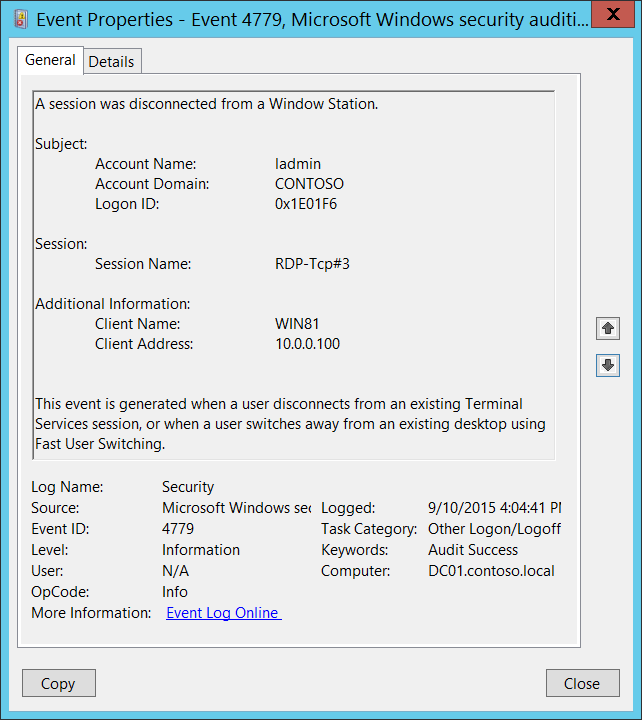
Event ID 4779: A Session was Disconnected from a Window Station
This event is logged when a user disconnects from a terminal server session and also logged when a user returns to an existing logon session via Fast User Switching. Microsoft says, this is an information event and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4779 | A session was disconnected from a Window Station | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event is generated when a user disconnects from an existing Terminal Services session. |
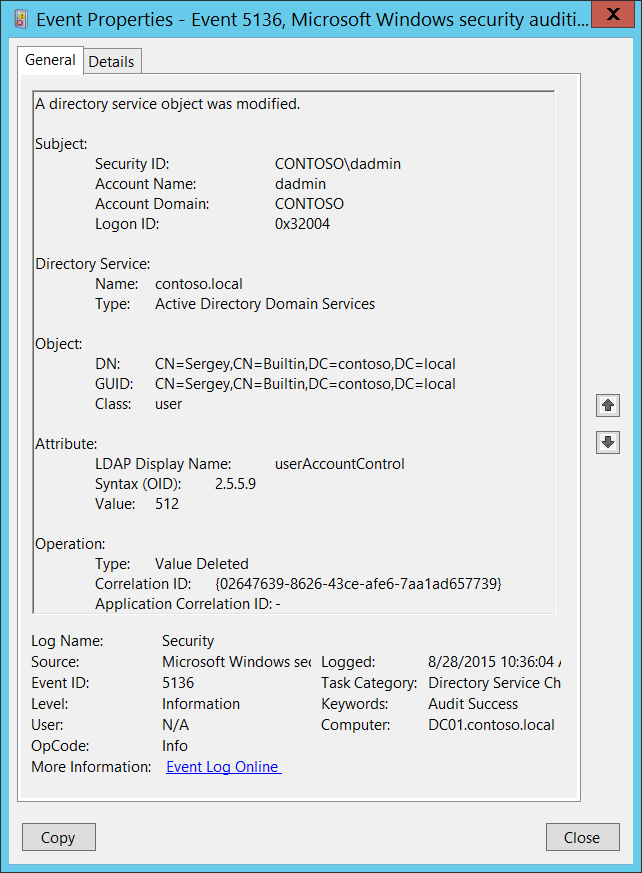
Event ID 5136: A Directory Service Object was Modified
This event generates every time an Active Directory object is modified. To generate this event, the modified object must have an appropriate entry in SACL: the “Write” action auditing for specific attributes.
For a change operation, you’ll typically see two 5136 events for one action, with different Operation\Type fields: “Value Deleted” and then “Value Added”. The “Value Deleted” event typically contains a previous value and the “Value Added” event contains a new value. According to Microsoft, this is an information event and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5136 | A directory service object was modified | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time an Active Directory object is modified. |
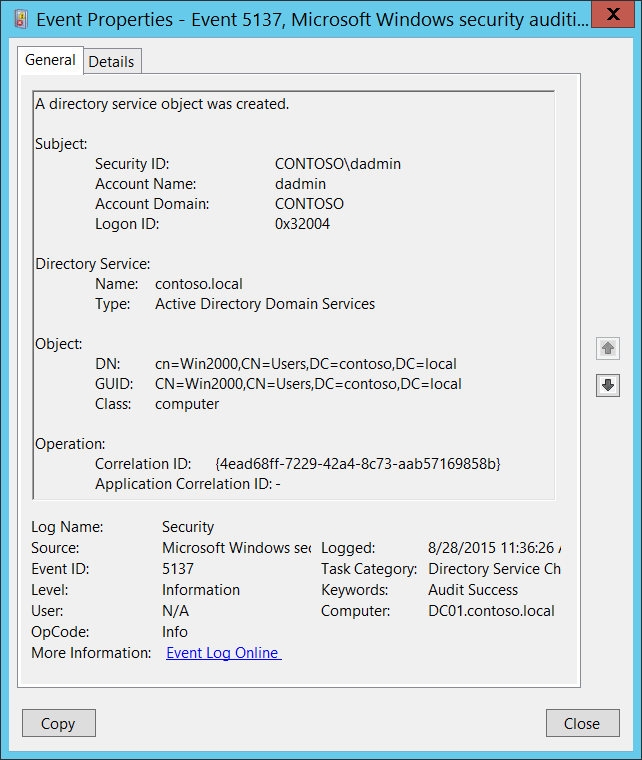
Event ID 5137: A Directory Service Object was Created
This event generates every time an Active Directory object is created. This event only generates if the parent object has a particular entry in its SACL: the “Create” action, auditing for specific classes or objects.
An example is the “Create Computer objects” action auditing for the organizational unit. According to Microsoft, this is an information event and no user action is required.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5137 | A directory service object was created | Microsoft Windows Security Auditing | This event generates every time an Active Directory object is created. |
Event ID 7030: Interactive Services Disabled
According to Microsoft, this event is logged when the service has been configured to allow the service to interact with the desktop. Interactive services can display a user interface and receive user input.
If you allow the service to interact with the desktop, any information displayed on the desktop will also be displayed on an interactive user’s desktop. A malicious user could then take control of the service or attack it from the interactive desktop.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7030 | Interactive Services Disabled | Service Control Manager | The %1 service is marked as an interactive service. However, the system is configured not to allow interactive services. This service may not function properly. |
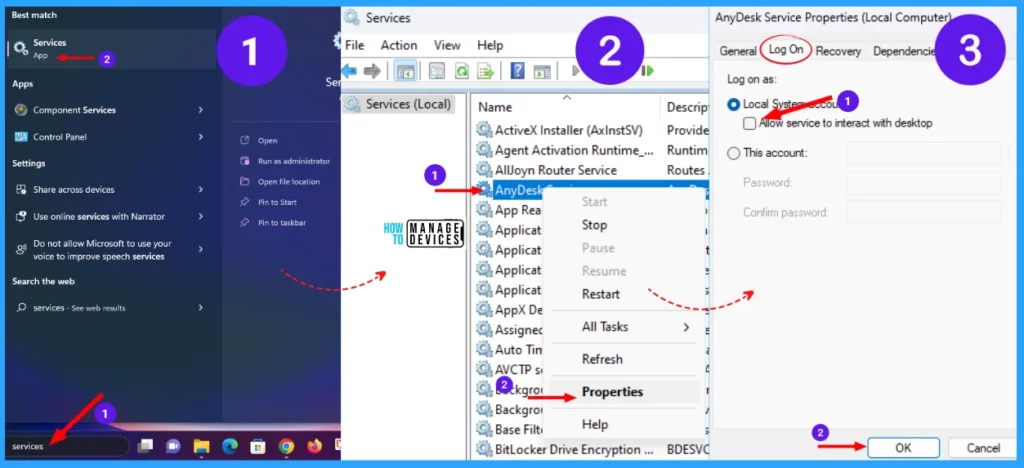
To resolve this issue, change the interaction with the desktop setting for the service. Follow the procedure listed below to enable interactive services.
- Type Services in Search Box in the Taskbar and hit Enter.
- Right-click on any service you want to start, and click on Properties.
- Move to the Log On tab, and clear the Allow service to interact with the desktop checkbox.
- Click OK.
Event ID 7034: Service Stop Operations
The Service Control Manager (SCM) stops services and driver services. It also reports when services terminate unexpectedly or fail to restart after it takes corrective action. This event is logged when the service is terminated unexpectedly.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7034 | Service stop operations | Service Control Manager | The service terminated unexpectedly. It has been done this time(s). |
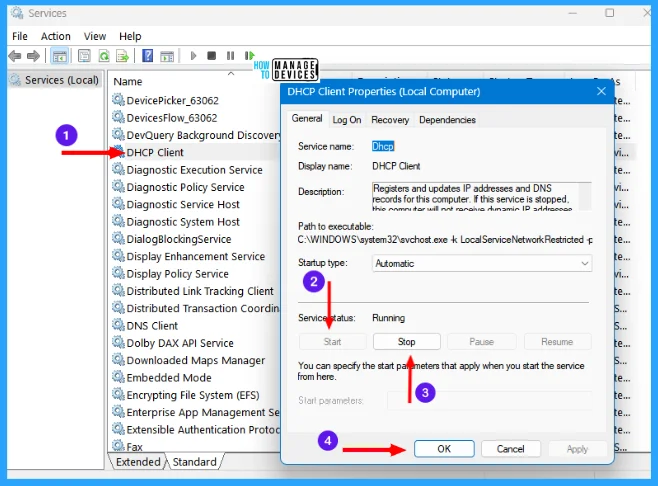
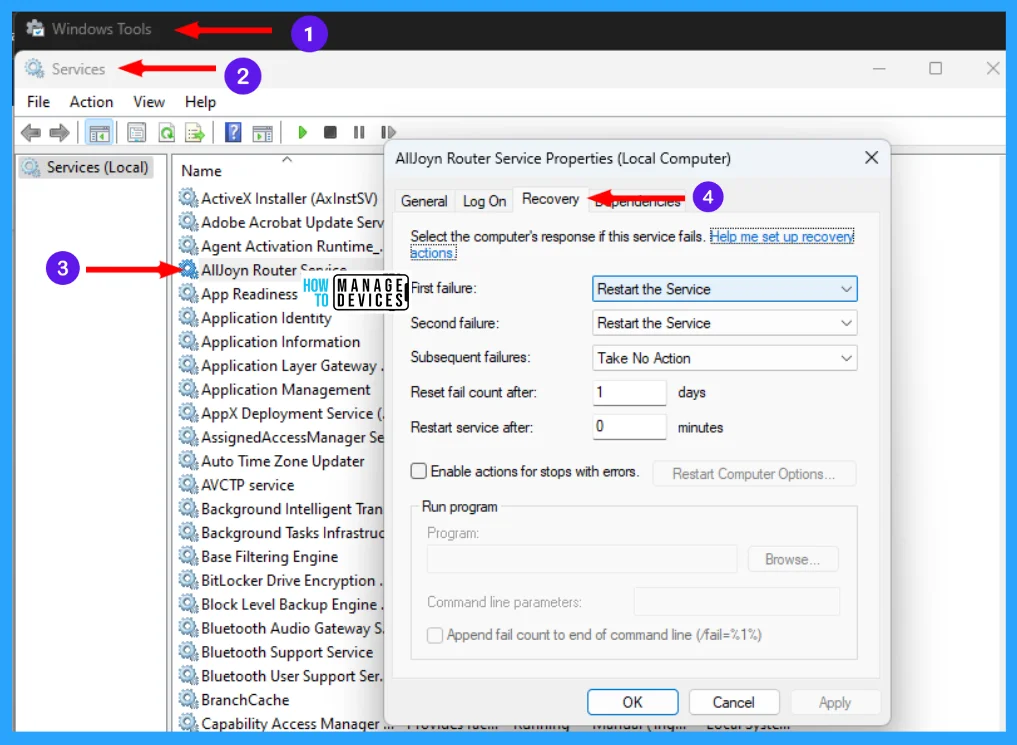
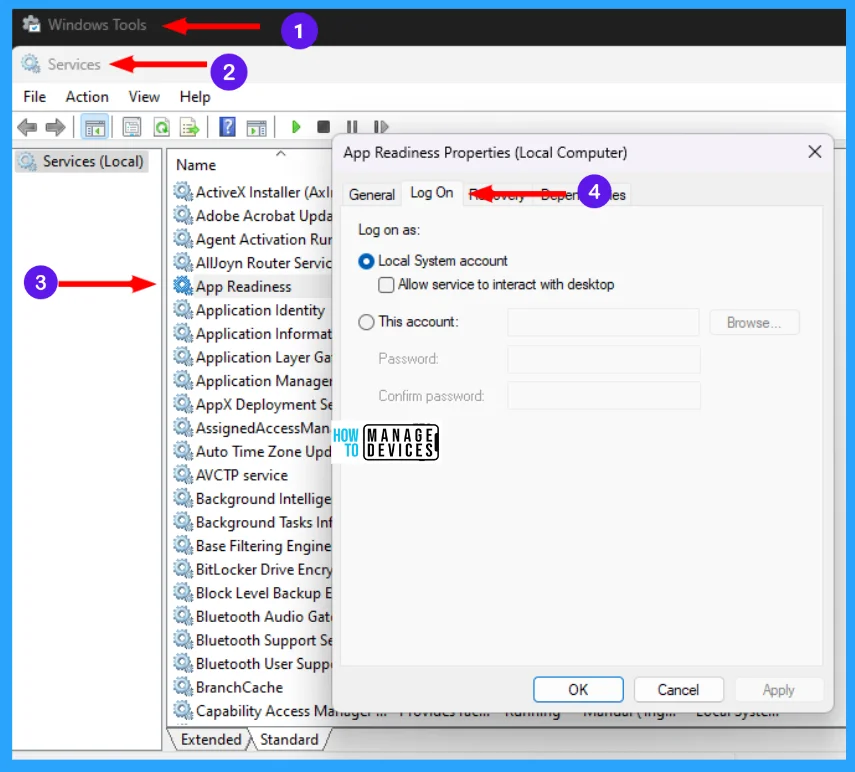
To resolve this issue, change the recovery actions that the Service Control Manager will take when a service fails.
To do so, open Windows Tools and double-click on Services. From the list of services select one and double-click on it, when it opens click on the Recovery tab.
Event ID 7036: Services Indicating Error Messages
The event services running on the PC get affected by corrupt system files that create errors in its process. It prevents services from accessing the needed files for performing tasks and operations, resulting in the event ID 7036 error.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7036 | Services Indicating Error Messages | Service Control Manager | The Print Spooler service entered the running state. The Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) service entered the stopped state. |
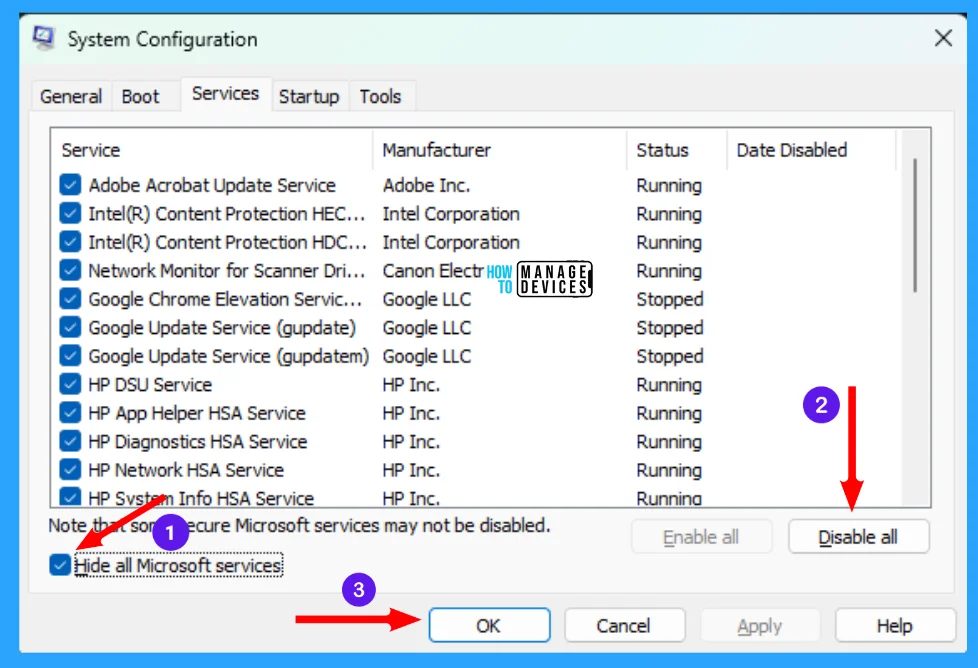
To resolve the issue, open System Configuration, click Winkey + R and type msconfig and press enter. Then select the Services tab, and checkmark the Hide all Microsoft services. Now click Disable all button and click OK to apply.
Event ID 7040: Basic Service Operations
The service Control Manager transmits control requests to running services and driver services. It also maintains status information about those services and reports configuration changes and state changes.
This event is logged when there were changes in the service settings (for example, the start-up type was changed from Automatic to Manual), the service may be unable to start.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7040 | Basic Service Operations | Service Control Manager | The start type of the IPSEC Services service was changed from disabled to auto start. The start type of the %1 service was changed from %2 to %3. |
To perform this procedure, you must have membership in Administrators, or you must have been delegated the appropriate authority.
Open Windows Tools and double-click on Services. From the list of services, select one and double-click on it, when it opens, click on the Log On tab.
Event ID 7045: New Service Installed
This issue may occur if the version of the SharePoint Portal Server that is installed on the server where you performed the backup operation is different from the version of the SharePoint Portal Server that is installed on the server where you restore the backup to.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7045 | New Service Installed | Microsoft Search | The catalog was not propagated because no new files were detected. |
To resolve it, make sure that the server where you perform the backup operation and the server where you restore the backup are running the same version of SharePoint Portal Server and the same SharePoint Portal Server service pack.
Event ID 8003: Unable to Connect to the Internet
The master browser has received a server announcement from computer %2 that believes that it is the master browser for the domain on transport %3. The master browser is stopping or an election is being forced.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8003 | Unable to Connect to the Internet | MRxSmb | The master browser is stopping or an election is being forced. |
The subnet mask of the Windows 2000 client computer is incorrect or is different from the primary domain controller.
The client computer has attempted to promote itself to the master browser of the subnet and has failed because only one computer in a domain can be running as the master browser. To resolve the issue change the TCP/IP protocol configuration to the correct subnet mask.
Event ID 8004: Enriched NTLM Authentication Data
In the browser, the computer can be any one of the following client, potential, backup, or master. When the browser comes online, it announces to the master browser. The master browser asks some of the browsers the become backups.
The request is received from the master browser itself. There should be only one master browser functioning properly.
| Event ID | Event Name | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8004 | Enriched NTLM Authentication Data | Browser | A request has been submitted to promote the computer to backup when it is already a master browser. |
I hope the Various Critical Event IDs in Windows 11 information is helpful. Please follow us on HTMD Community and visit our website HTMD Forum if you like our content. Suggest improvements, if any, and we love to know which topic you want us to explore next.
Author
Alok is a Master of Computer Applications (MCA) graduate. He loves writing on Windows 11 and related technologies. He likes to share his knowledge, quick tips, and tricks with Windows 11 or Windows 10 with the community.

a good text (very good in fact) i like