Let’s learn how to start Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting. This is a beginner’s guide to beginning troubleshooting Windows Autopilot-related issues.
Windows Autopilot is a collection of technologies that simplifies the process of setting up and configuring new devices. Autopilot pre-configures devices to meet your org’s requirements, saving you time and effort. This solution provides a seamless end-to-end experience that ensures optimal productivity and efficiency.
Windows Autopilot is an Azure service for provisioning Windows 10 or Windows 11 builds. The Autopilot service simplifies Windows OOBE, and it happens primarily at the Windows 10 OOBE stage.
You will learn about the basics of Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting from this post.
Related Topic – Windows Autopilot Hybrid Azure AD Join Troubleshooting Tips
The Basics
In the OOBE stage of autopilot deployment, many issues can fail. Below are some of the common problems.
- The Machine is not getting an IP address
- Firewall issue
- Network proxy, etc.
Michael has written an excellent post on Autopilot troubleshooting. For more details on autopilot implementation, refer step by step guides.
In Traditional SCCM/MDT deployments, you must press the “F8” key in the WinPE stage to get command prompt support. In this post, we will see similar troubleshooting features in Windows 10 during Autopilot deployment.
How to Get-Command Prompt for Windows Autopilot Deployment Troubleshooting
During the Autopilot OOBE screen, press Shift + F10. This key combination launches the command prompt, which helps troubleshoot network activity, event viewer, and registry. I also think this feature might be a concern for the security team.
- This step is the first step towards Windows Autopilot troubleshooting.
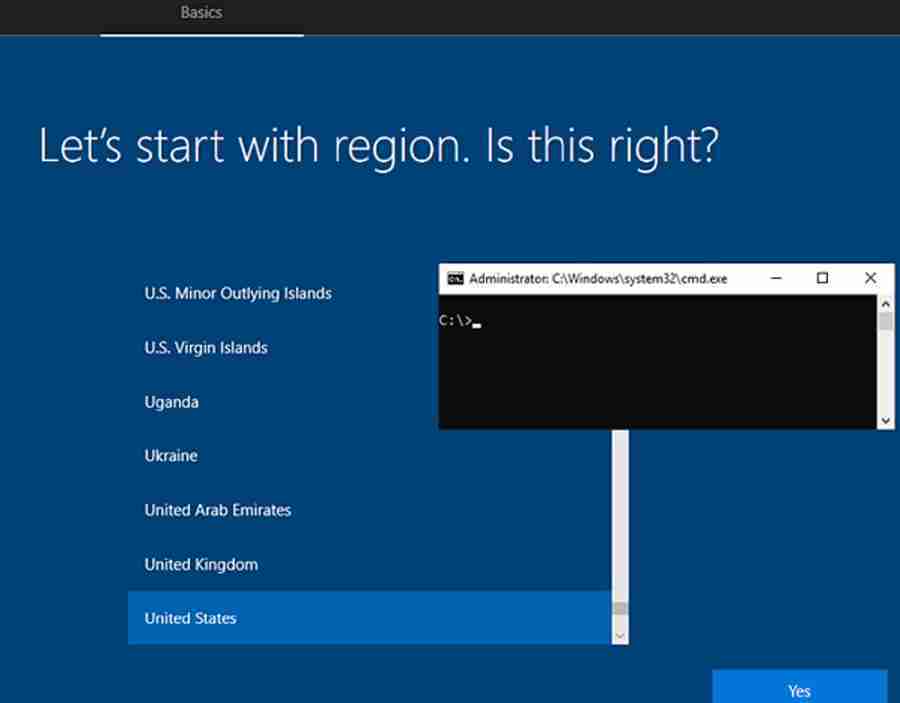
The command prompt will be launched in the “default user” profile.
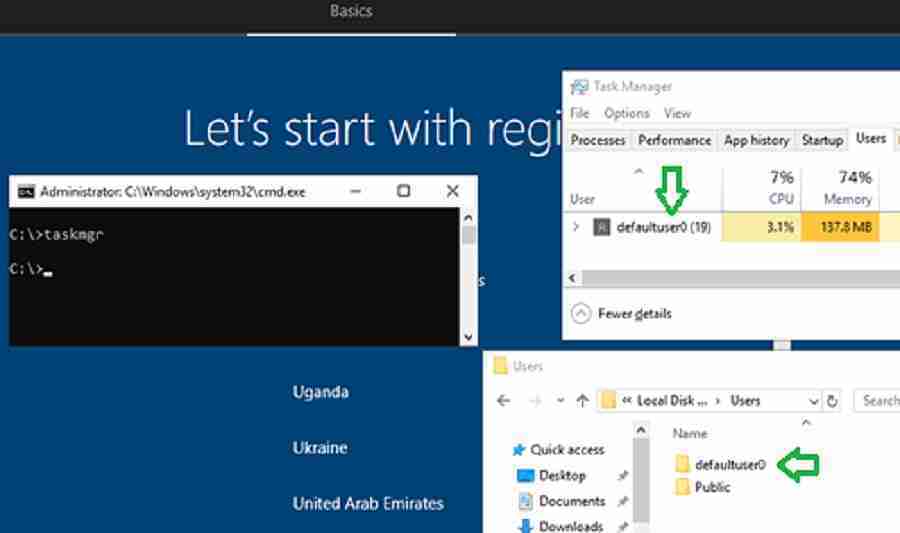
In this post, we will focus on 3 key areas of Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting:
- Network Activity
- Registry
- Event viewer
Windows Autopilot Network Activity
We need to ensure internet connectivity is working fine for successful autopilot deployment. Refer to this link for complete Autopilot network requirements. I want to share some of my observations while Windows Autopilot troubleshoots network issues.
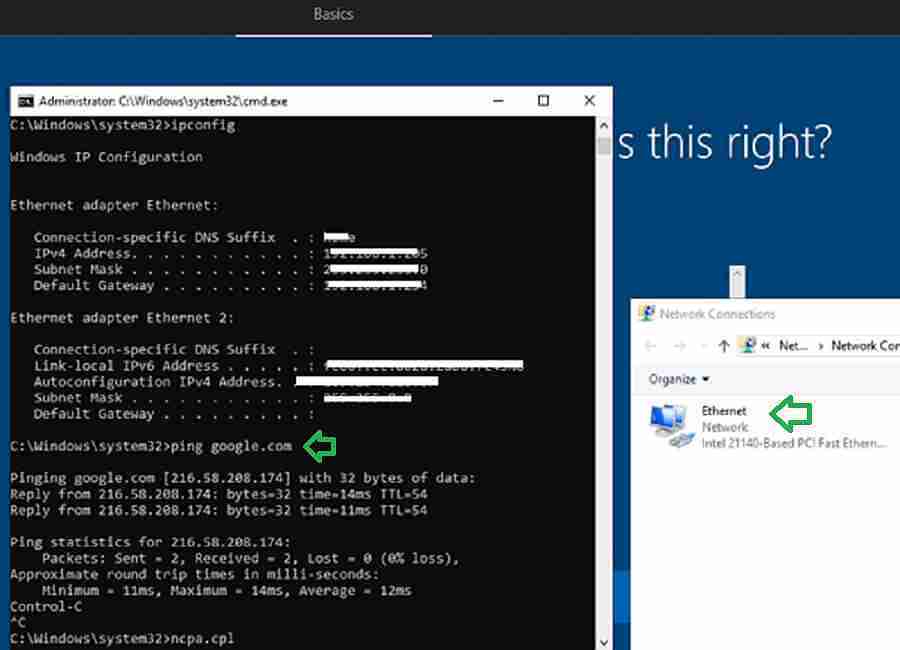
Basic Network Analysis
Check whether the device received an IP address, and you can ping any Internet URL (Ex: google.com). If you suspect an issue with your default network adapter configuration, execute the command “ncpa.CPL”
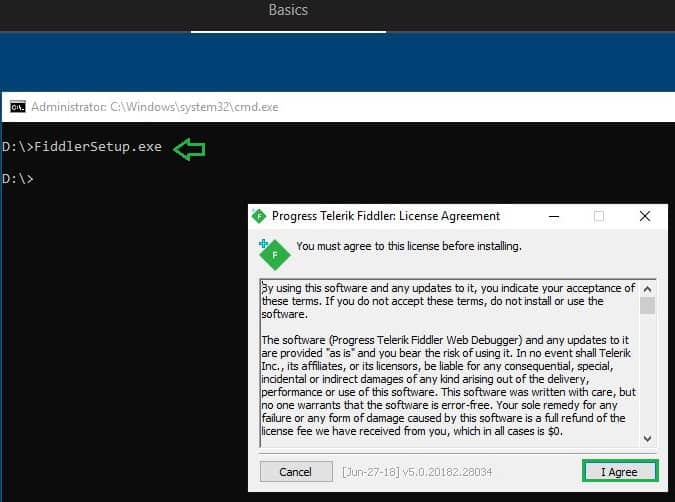
Advanced Network Analysis Using Fiddler
I use fiddler to troubleshoot autopilot network activity at each OOBE stage. You can download Fiddler from and save it to USB. Next, install the Fiddler app in the Autopilot system.
After installation, you can launch Fiddler GUI from the below location.
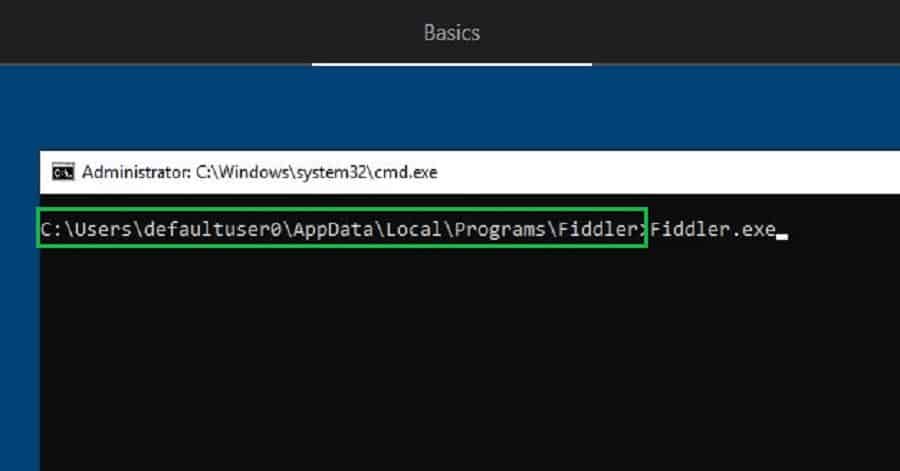
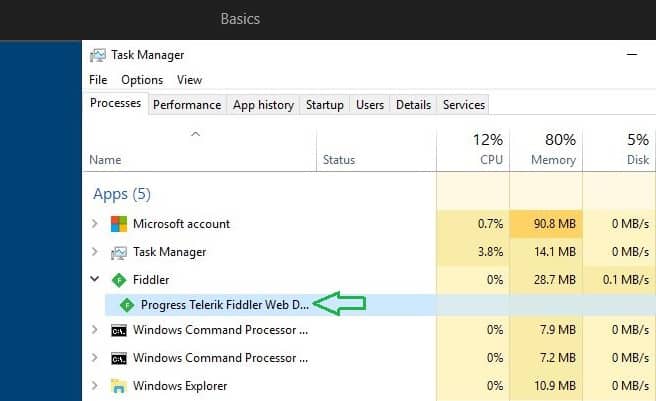
Let the Fiddler app run in the background to capture network communication. Use task manager to bring Fiddler to the front when required (just double click ).
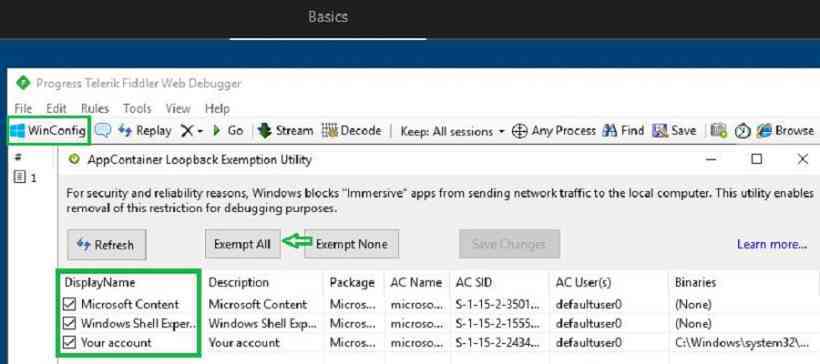
In Fiddler, we need to ensure the below process required during autopilot OOBE is exempted. This will unblock Windows apps from sending network traffic to the local computers.
After installation, let’s trace network activity in each stage of autopilot. Autopilot client-side events can be divided into 6 stages.
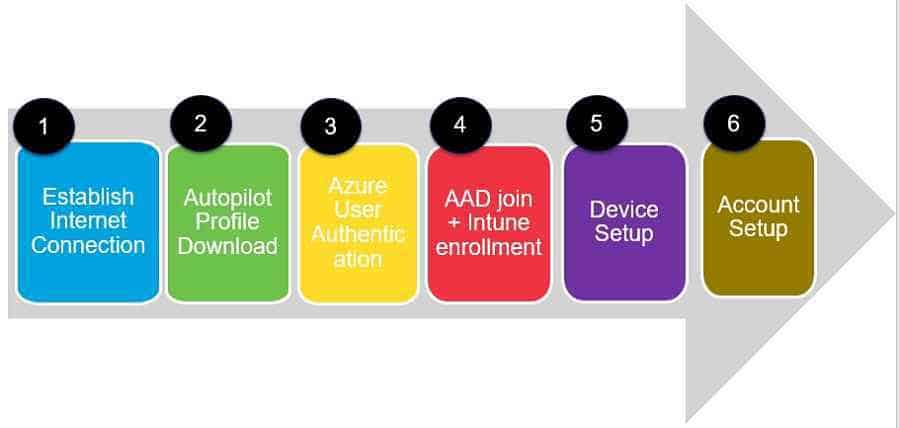
Establish Internet Connection – Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting – Beginners Guide
In this stage 1, the device will try to establish an internet connection (wired or wireless). Note: As per Microsoft documentation, “Windows 10 device will contact the Windows Autopilot Deployment Service using the same services used for Windows Activation.”
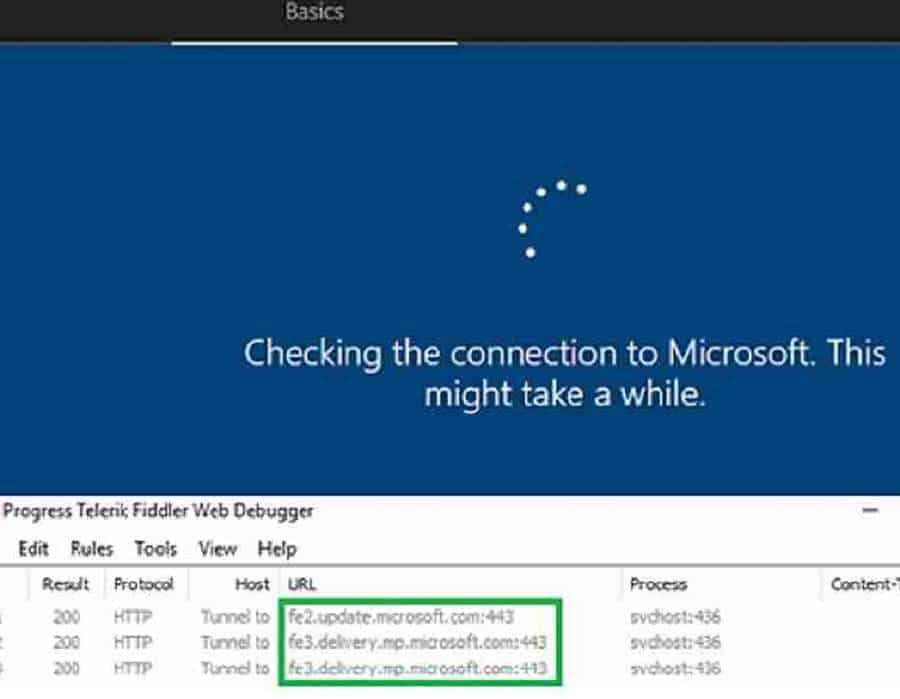
- You can see the device start reaching out to the below Microsoft URLs.
| Result | Protocol | Host | URL | Body | Caching | Content-Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | HTTP | Tunnel | to | fe2.update.microsoft.com:443 | 0 | svchost:436 |
| 200 | HTTP | Tunnel | to | fe3.delivery.mp.microsoft.com:443 | 0 | svchost:436 |
| 200 | HTTP | Tunnel | to | fe3.delivery.mp.microsoft.com:443 | 0 | svchost:436 |
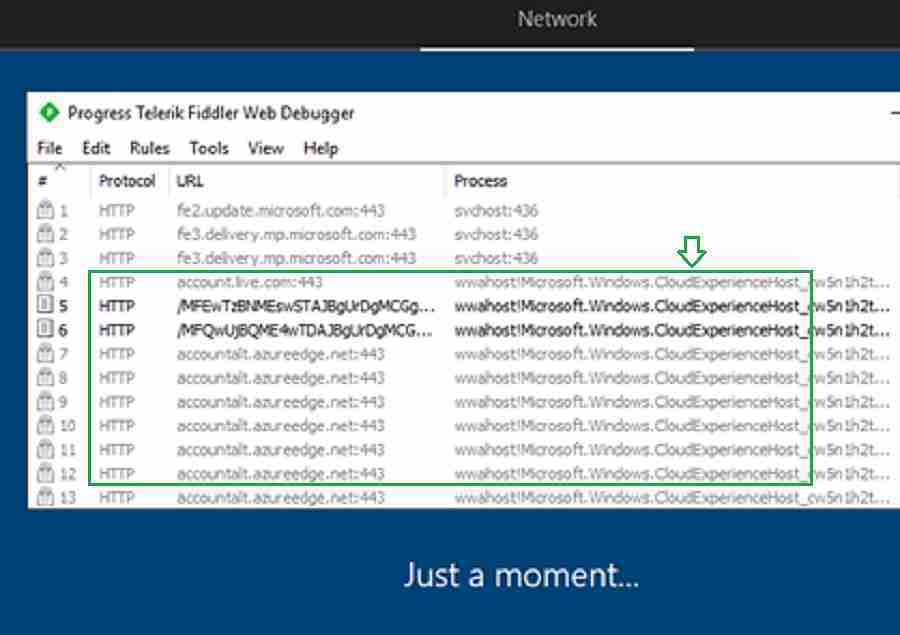
After some time, you can see the application “CloudExperienceHost” communicating with the below MS URLs…
200 HTTP Tunnel to account.live.com:443 0 wahost!Microsoft.Windows.CloudExperienceHost_cw5n1h2txyewy!App:3108
200 HTTP Tunnel to accountalt.azureedge.net:443 789 wwahost!Microsoft.Windows.CloudExperienceHost_cw5n1h2txyewy!App:3108
200 HTTP Tunnel to accountalt.azureedge.net:443 789 wwahost!Microsoft.Windows.CloudExperienceHost_cw5n1h2txyewy!App:3108
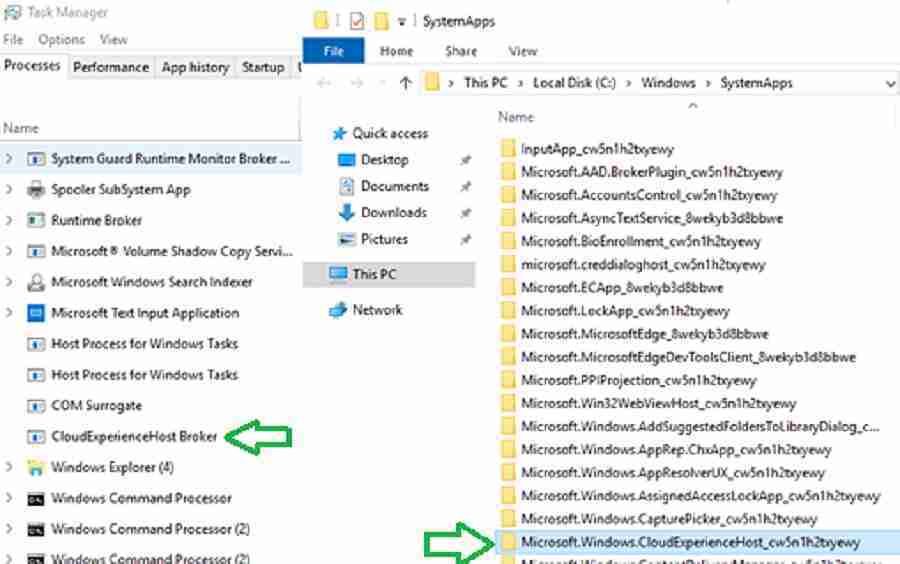
CloudExperienceHost is a system app that is located within c:\windows\systemapps.
Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting – Beginners Guide – Fig.11
Windows Autopilot Profile Download Stage
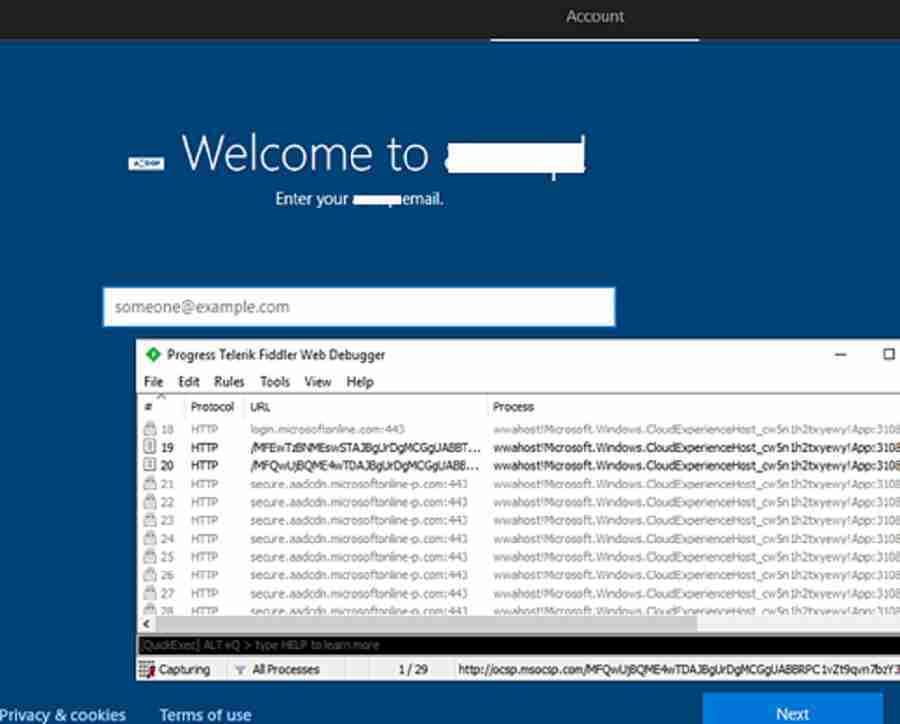
After establishing internet connectivity, the device will download the Windows Autopilot profile from the Azure Autopilot deployment service. After the autopilot profile download, you will be prompted to enter your corporate email ID.
You can see the device access the below URL.
HTTP Tunnel to login.microsoftonline.com:443 0 wwahost!Microsoft.Windows.CloudExperienceHost_cw5n1h2txyewy!App:3108
HTTP Tunnel to secure.aadcdn.microsoftonline-p.com:443 725 wwahost!Microsoft.Windows.CloudExperienceHost_cw5n1h2txyewy!App:3108
Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting – Beginners Guide – Fig.12
Azure User Authentication
In the user-driven autopilot deployment, the device prompts the user to enter their Azure Active Directory credentials. In Fiddler, you can see the device connects to the authentication URL below.
200 HTTP Tunnel to login.microsoftonline.com:443 0 wwahost!Microsoft.Windows.CloudExperienceHost_cw5n1h2txyewy!App:3108
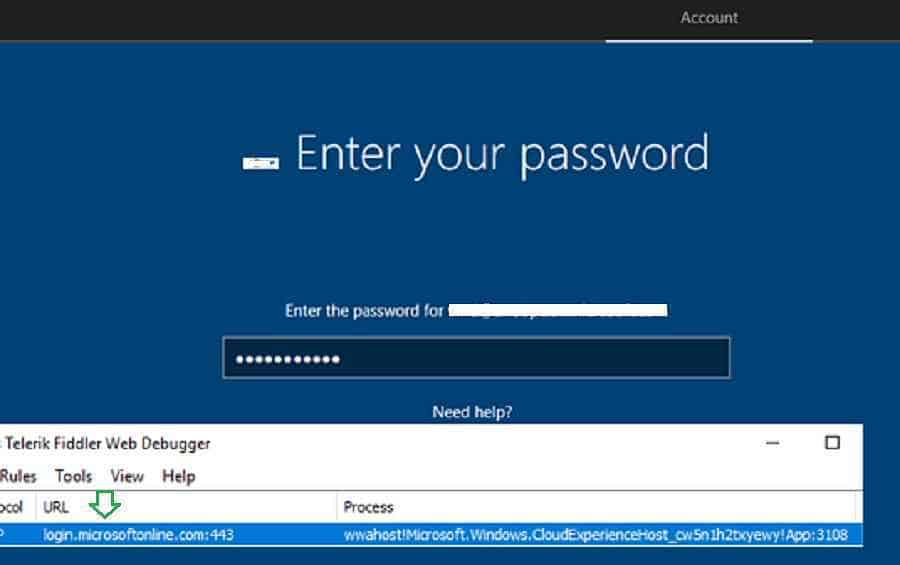
Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting – Beginners Guide – Fig.13
AAD Join and Intune Enrollment
In this stage, the device will join Azure Active Directory and auto-enroll to Intune MDM. You can see the device connecting to Azure and Intune MDM URL: “Portal.manage.microsft.com”
200 HTTP Tunnel to portal.manage.microsoft.com:443 0 wwahost!Microsoft.Windows.CloudExperienceHost_cw5n1h2txyewy!App:3108
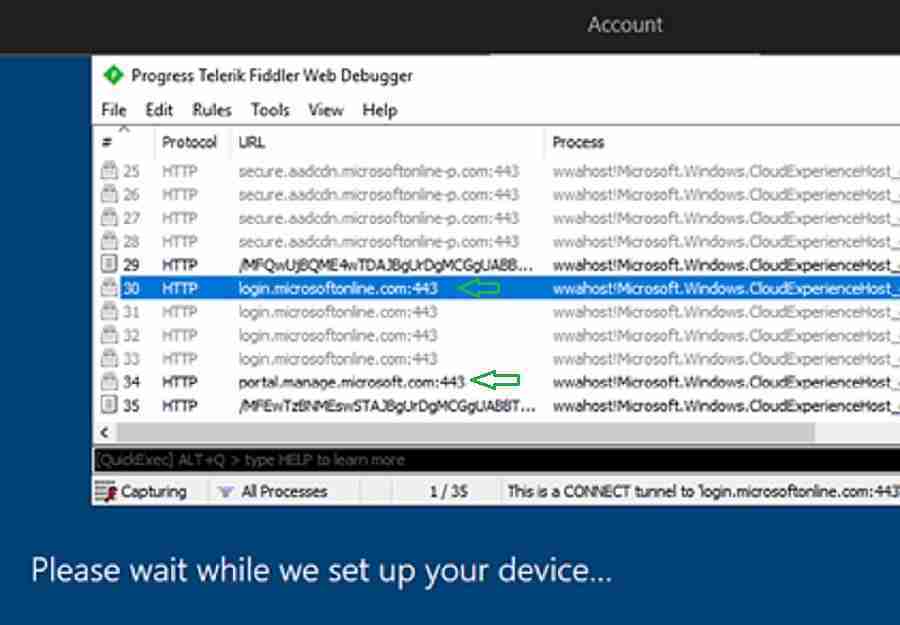
Device Setup
In stage 5, the Intune client plays a major role. Certificates, Intune applications, and profiles will be configured. You can see OMADMclient.exe communicate with cloud services for policies, apps, etc.
Note: OMA-DM is a device management protocol used by Intune client agents. You can see the Intune client process connecting to the URLs below.
200 HTTP Tunnel to r.manage.microsoft.com:443 0 omadmclient:2212
200 HTTP Tunnel to r.manage.microsoft.com:443 0 omadmclient:3288
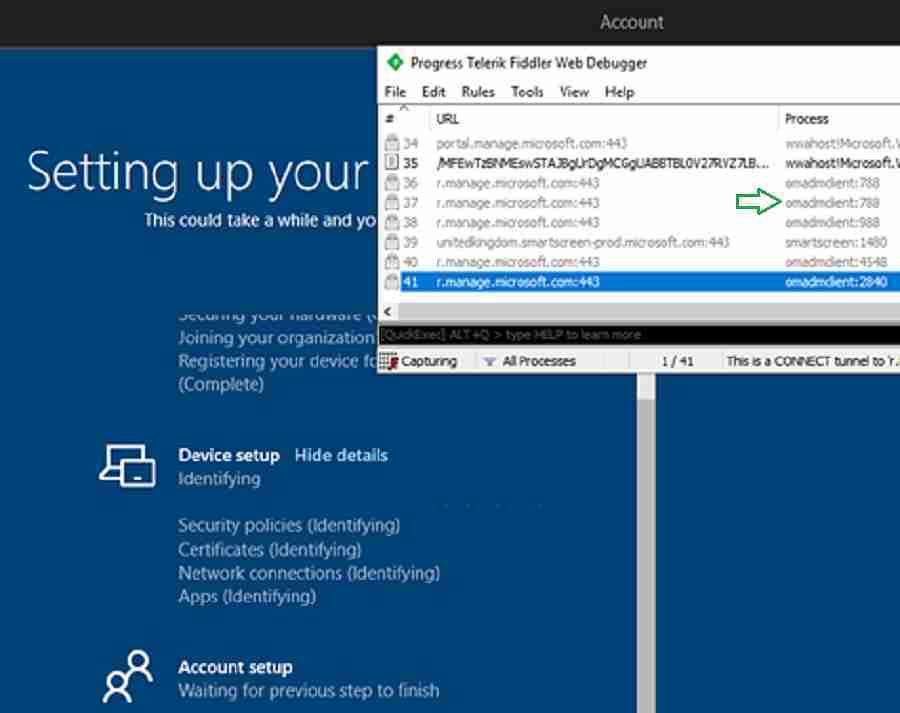
Note: During the OOBE process, the Windows Update service will try to download and install needed updates. However, the AutoPilot process will continue even if Windows Update is inaccessible.
Account Setup
In this stage, observed the device also accesses the below-listed URL.
- 200 HTTP Tunnel to geo-prod.do.dsp.mp.microsoft.com:443 0 svchost:96
- 200 HTTP Tunnel to kv601-prod.do.dsp.mp.microsoft.com:443 0 svchost:96
- 200 HTTP Tunnel to cp601-prod.do.dsp.mp.microsoft.com:443 0 svchost:96
- 200 HTTP Tunnel to swdc01.manage.microsoft.com:443 0 svchost:96
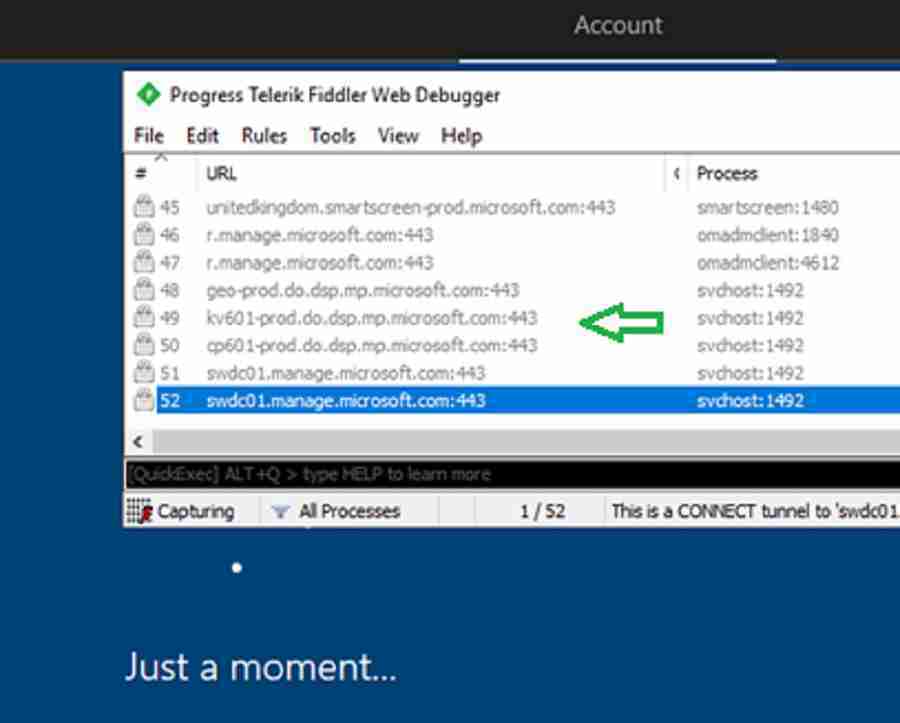
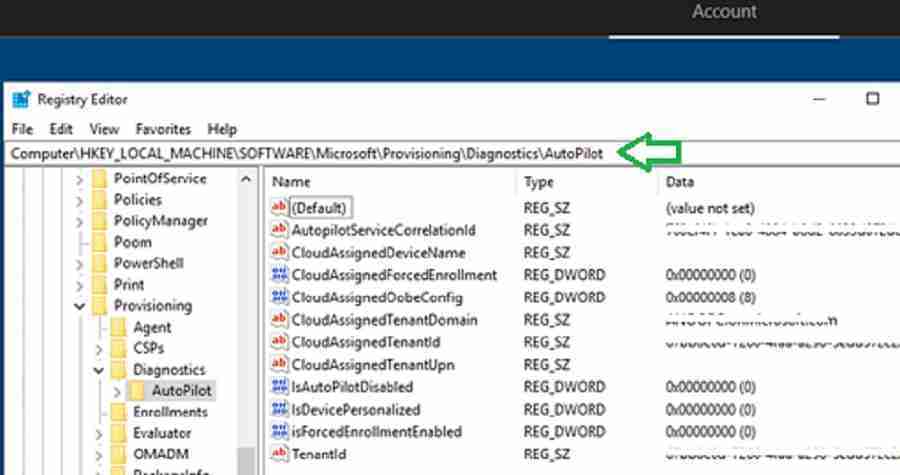
Windows Autopilot Registry – Diagnostics – Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting
The registry is another area to focus on while performing Windows autopilot troubleshooting. You can see autopilot configurations recorded in the registry below.
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Provisioning\Diagnostics\AutoPilot
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| AadTenantId | The GUID of the Azure AD tenant the user signed into. |
| CloudAssignedTenantDomain | The Azure AD tenant the device has been registered with, e.g., “contosomn.onmicrosoft.com.” If the device is not registered with Autopilot, this value will be blank. You can use this value while troubleshooting |
| CloudAssignedTenantId | The GUID of the Azure AD tenant. If the device isn’t registered with Autopilot, this value will be blank. |
| IsAutoPilotDisabled | The GUID of the Azure AD tenant. If the device isn’t registered with Autopilot, this value will be blank. |
| TenantMatched | Indicate whether the tenant ID of the user matches the tenant ID that the device was registered with. |
| CloudAssignedOobeConfig | This is a bitmap that shows which Autopilot settings were configured. Values include: SkipCortanaOptIn = 1, OobeUserNotLocalAdmin = 2, SkipExpressSettings = 4, SkipOemRegistration = 8, SkipEula = 16 |
For more details on the autopilot registry
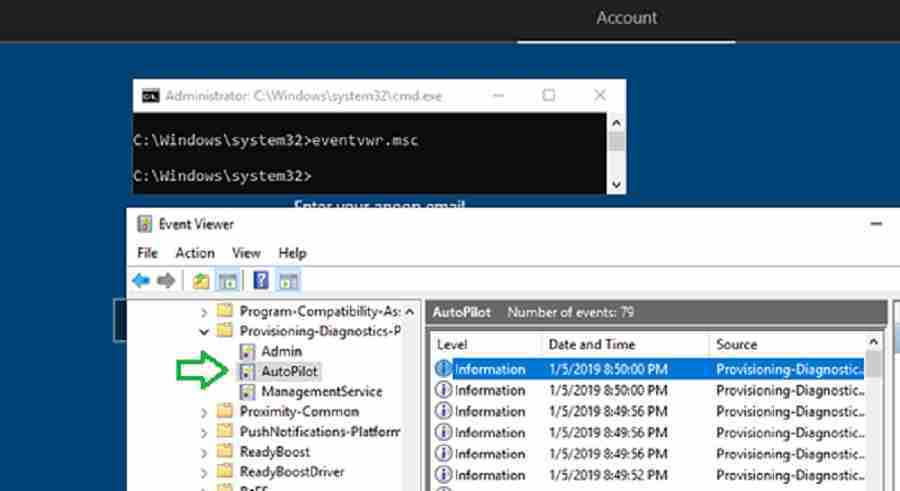
Autopilot Event Viewer – Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting
Event viewer is something we admins always use for troubleshooting. But currently, I think event viewer is still not getting into detailed events. These logs will help in your Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting.
Navigate to “Application and Services Logs –> Microsoft –> Windows –> Provisioning-Diagnostics-Provider –> AutoPilot
For more details on autopilot event viewer events.
Conclusion – Windows Autopilot Troubleshooting
Command prompt support is very helpful in troubleshooting autopilot deployments. You can also use this command prompt to launch other tools like task manager, process monitor, Windows Performance Recorder (WPR), etc, for troubleshooting.
Resources
- Windows Autopilot Deployment Scenarios – On-Prem Hybrid Domain Join
- Repurpose Existing Devices to Windows Autopilot – SCCM or MDT?
- Windows Enrollment Status Screen Troubleshooting
We are on WhatsApp. To get the latest step-by-step guides and news updates, Join our Channel. Click here –HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
Vimal has more than ten years of experience in SCCM device management solutions. His main focus is on Device Management technologies like Microsoft Intune, ConfigMgr (SCCM), OS Deployment, and Patch Management. He writes about SCCM, Windows 10, Microsoft Intune, and MDT.

Thanks for this post
Hello Vimal,
Are there any more URL that needed to be whitelisted on client proxy for HAAD join to work. we have whitelisted the listed URL’s mentioned in this page and also from the below link but still there is traffic block from some MS public IP’s and the process fails with the error code 80070774 everytime. Any guidance on this would be helpful
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/intune-endpoints
Thank you
Do you find a solution ?
I have same problem but i think it’s a timeout when deploying msix application.
Hi Vimal,
Thanks for sharing this article on Autopilot troubleshooting.
I have device getting failed at stage 4(Per your troubleshooting guide). Error displays as Failed to establish connectivity couldn’t perform ODJ. I had to run Get-AutopilotDiagnostics.PS1 script to know where exactly it is getting failed.
Should this be investigated at Client side or from server side (Intune Connectors for AD). I don’t see issues with another test device.
Also, will re-importing Hash ID back into Autopilot Services can help ?
Regards,
Vishal