Hello Everyone. In today’s article, let’s see how we can protect devices by Creating a Compliance Policy for Android Devices in Intune. In our previous article, we learned how to protect Android devices from Malware and Threat attacks using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Compliance policies are a set of device properties that can be used to validate before providing access to organizational data. Compliance policies are important for ensuring that devices used by employees meet certain requirements before they are given access to corporate data.
These policies are device properties that must be met, such as installing the latest software updates and security features like having a device Passcode for unlocking the device, etc. By using compliance policies, organizations can ensure that their data remains safe and secure while giving employees the tools they need to do their jobs effectively.
By combining Compliance Policies with Conditional access policies, we can restrict access to company data on devices not compliant with our security requirements. This helps ensure that sensitive information is protected and only accessible by devices compliant with organizational security requirements.
- Create Intune Compliance Policy for iOS iPadOS Devices
- Enroll Android Devices to Android for Work in Intune
Creating Compliance Policy for Android Devices in Intune
Intune supports Device Admin and Android Enterprise enrollment. So we can create Compliance Policies for Device Admin and Android Enterprise. As the Device Admin Enrolment type is almost deprecated, we will discuss Compliance Policy creation for Android Enterprise devices in this article.
Compliance policy also helps admins to configure non-compliant actions such as notifying users about the non-compliant state of the device via Email, Push Notification and moving the devices to Retrire state, and Remotely locking the non-compliant devices.
Before creating a Compliance policy, let’s create an Email Notification to send non-compliant devices. This Notification will be triggered once the device becomes non-compliant. Intune adds device details at the end of the Email Notification. Let’s see below the steps to create an Email Notification.
- Sign in to Microsoft Intune Admin Center http://intune.microsoft.com/
- Click on Devices > Compliance policies
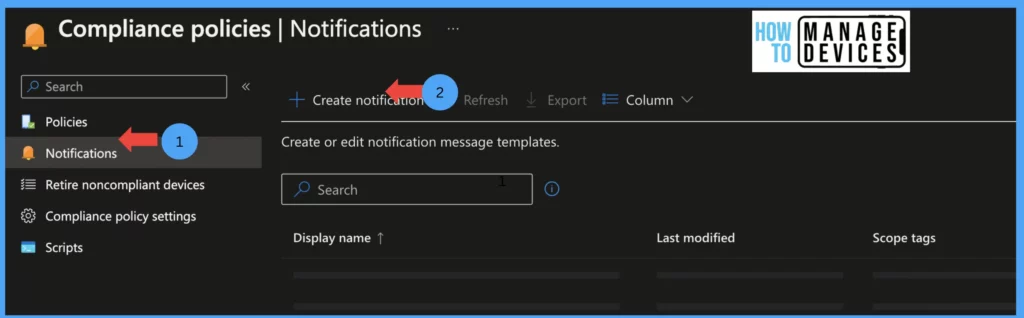
Now click on Notifications and click on Create new Notification. On the basics page, provide the name for Notification. A few other options are Enabled by default, like Email header – Include company logo, Email footer – Include company name, Email footer – Include contact information.
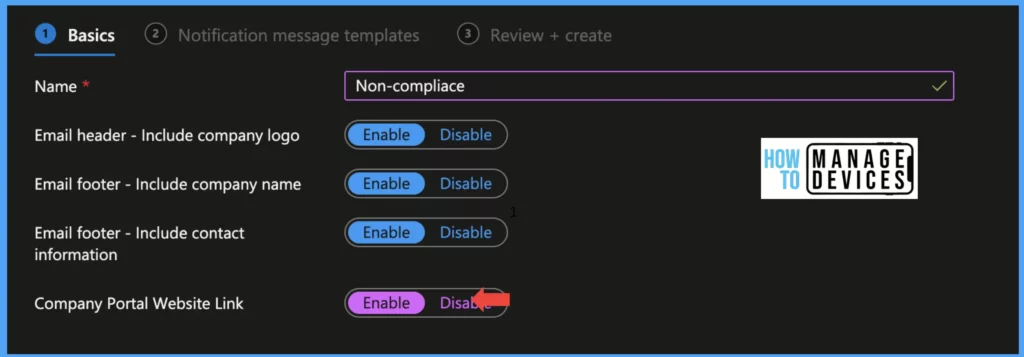
These three options will add Company Logo to the Email Header—Company Name, and the Support contact number to the Email Footer. We can also add a link to Intune Self-service by enabling Company Portal Website Link. Now click on Next and move to the Notification Template screen.
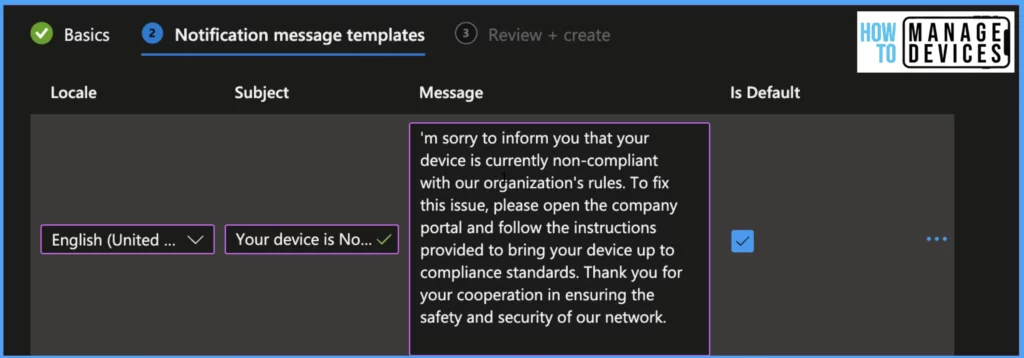
Now Select the Locale for language and enter the Subject, this will be the Subject of the Email received by the users. Enter the message to be sent to users in Email in the Message field. We can have multiple notifications. Select one of the messages as default, Click Next and Recview, and Create a Notification template.
Create a Compliance Policy for Android Devices
The Email Notification is ready to be sent for Non-Compliant devices. Now we need to create a Compliance policy for Android for Work Devices. Before creating compliance policies, be clear about your organization’s compliance requirements, like the length of Password required, the Minimum OS version required to access corporate data, etc.
- Sign in to Microsoft Intune Admin Center http://intune.microsoft.com/
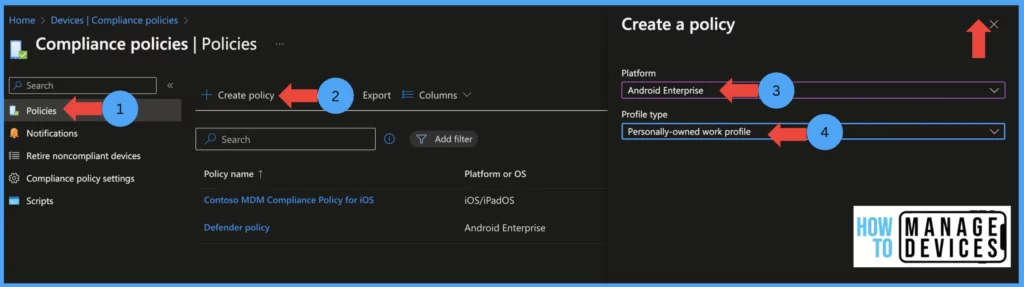
- Click on Devices > Compliance policies > Create Policy
- Now select the platform as Android Enterprise and Porfile type as Personally-Owned Work profile
- Then click on Create
Enter the policy’s name and description on the Basics page and click Next to the Compliance settings page. In this screen, we will define the Compliance rules for the devices. The Compliance rules are divided into four categories.
| Restrictions configured | Rules configured |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Defender | In this category, we will define what should be the threat level of the device to be compliant |
| Device Health | We will validate some of the devices root level properties |
| Device Properties | Here we will define the required OS levels |
| System Security | In this category, we will define screen lock and other security rules |
Let’s see what rules can be configured for each category in the compliance policy. If the device does not satisfy Any of the rules in the four categories, the device will be marked as Non-Compliant.
Microsoft Defender
In this section, we will ensure the safety of the devices by validating their threat level. To do this, we will integrate Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune. For more information, please refer to this post. We will require the device to meet a certain machine risk score, which can be set to “Clear,” “Low,” “Medium,” or “High.” Clear is the most secure device, while High is the most vulnerable.
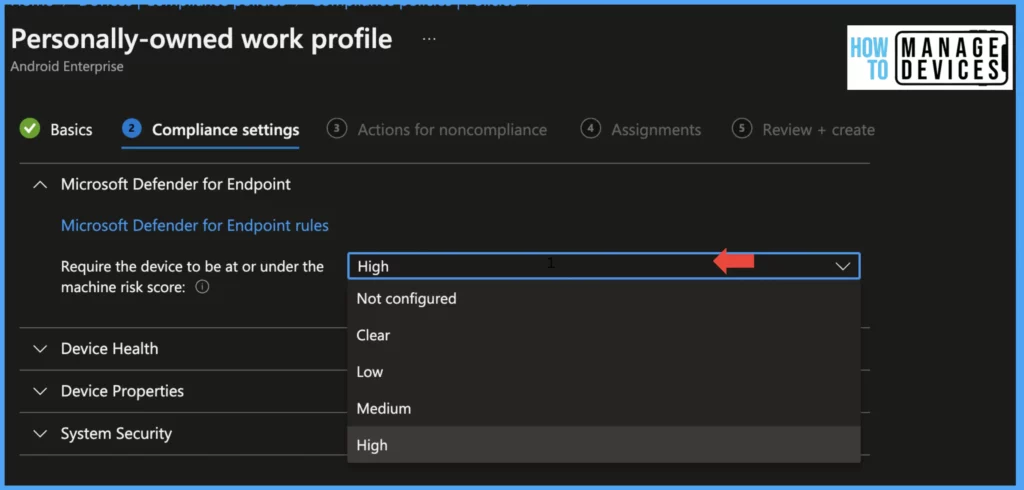
By default, this value is set to Not Configured. Our goal is to make sure that each device is operating optimally and free of any potential threats. Microsoft Defender also monitors web traffic if the user tries to access any malicious URL.
Device Health
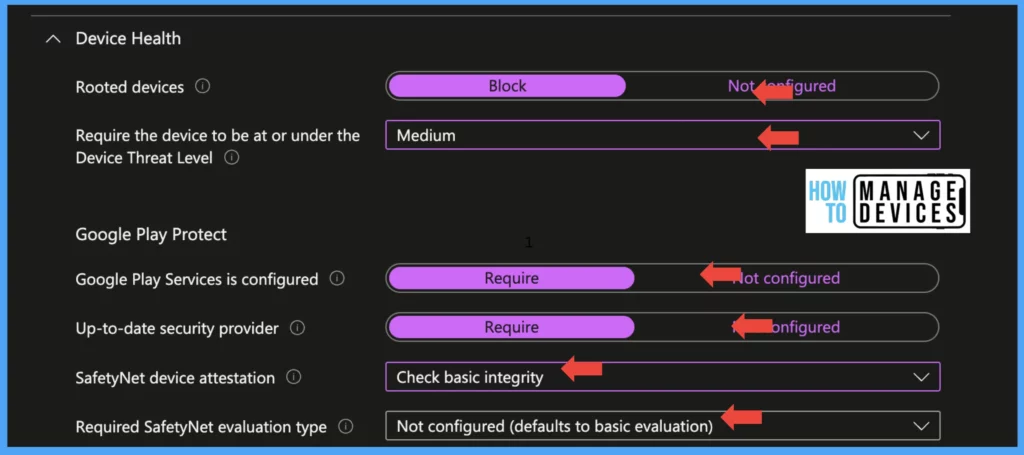
To keep corporate data safe, verifying root-level properties and turning on Google Play Protect is crucial. Failing to do this could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information if the device is Rooted or Jailbroken. It’s important to activate these settings promptly. Here are the instructions to make it easy
- Rooted devices: Select Block if you want to restrict access to corporate data on Rooted devices
- Google Play Services is configured: Set value to Required, this will force users to have the Google Play services app installed on their device.
- Up-to-date security provider: Set the value to Required, an up-to-date security provider required to make the device compliant
- SafetyNet devie Attestation: This is an API that can be used to validate the device’s Integrity. Under device safetyNet Device attestation, we can set it to 2 values, check basic Integrity, and check basic Integrity & certified devices.
Device Properties
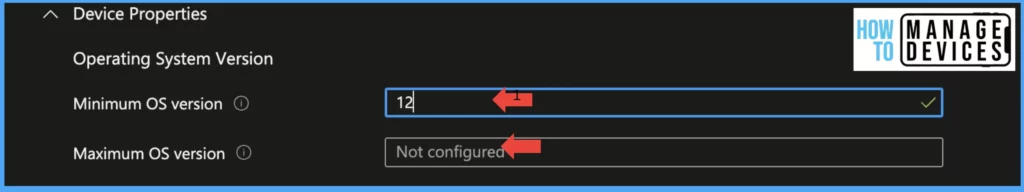
In this section, we must determine the minimum and maximum OS requirements to access corporate data. This guarantees that all devices used to access the data are current and safeguarded. It’s important to be meticulous when setting these values to uphold the highest level of security for our corporate information. Always use N-1 OS as Minimum OS required
System Security
In this section, we define values for Encryption, Device Security like blocking USB debugging mode, installing apps from Unknown resources, etc., and Device passcode values. Let’s see how we can configure it.
Encryption: If you want to enable devices to be encrypted for accessing Corporate data set value Require encryption of data storage on the device to Required, this will make Intune Company portal check for device encryption. By default, Android Enterprise devices enforce Device Encryption.
Device Security: Under the device Security section, we validate device features and force them to comply with our configurations.
Block apps from unknown sources: This feature applies to devices running on Android 4.0 to Android 7.0. When we set the value to Block, if we enable Install apps from unknown sources (which is required for side loading the apps), the device will be treated as non-compliant.
Company Portal app runtime integrity: When the value is set to Required, Intune checks if the Company Portal app has default runtime without debugging mode enabled for it and installed from Google PlayStore.
Block USB debugging on the device: USB debugging mode is required for testing apps and a few Android features that are required for developers. Enabling this feature, devices are prone to threats. So it is always good to Block the feature.
Minimum security patch level: If you want to block devices based on security patch level, use this feature ad define the oldest security patch required to access the corporate data. The value should be in YYYY-MM-DD format.
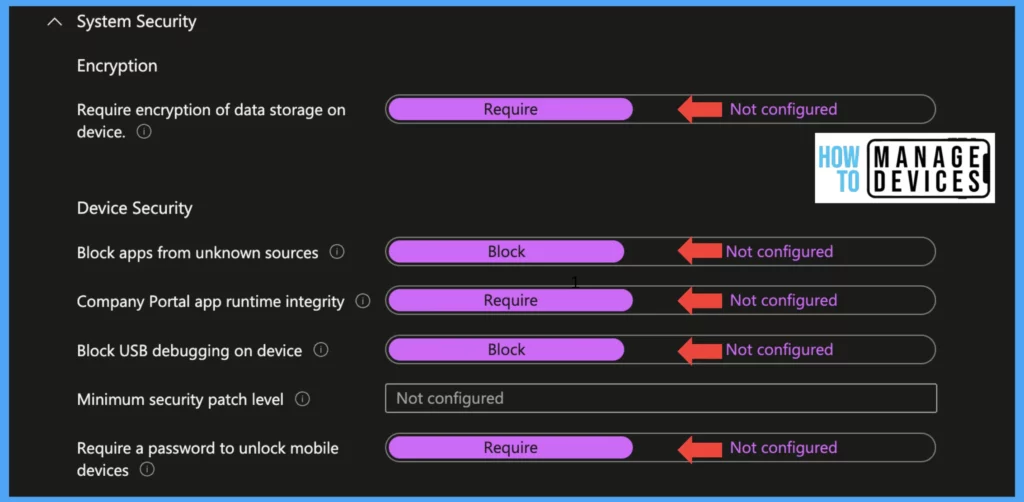
Require a password to unlock mobile device: These settings check if the device has a Passcode to unlock the device. Set the value to Required to validate compliance. When we enable the above settings, this will enable a few other settings for the Password.
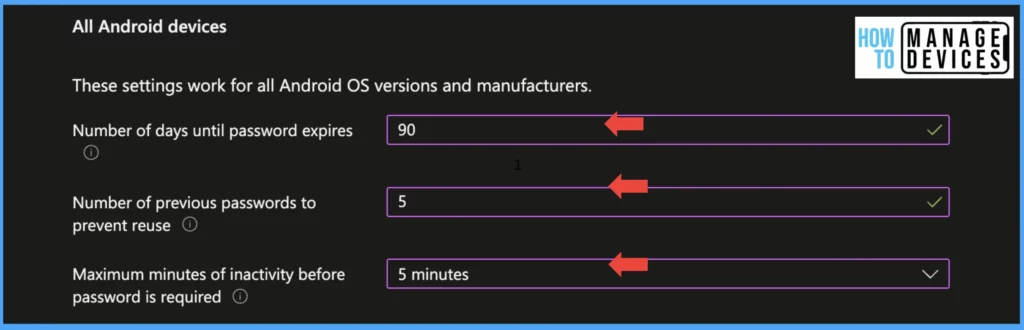
Note: The above settings are applied for all Android devices and manufacturers. From November 2022, Google made some changes to how we define password complexity for devices. The new settings will be applied for Android 12 ad above devices.
| Settings | Setting values |
|---|---|
| Number of days until the password expires | When we set the value setting will define the expiry of the device passocde and force users to change the device passcode (ideal value is 90 days) |
| Number of previous passwords to prevent reuse | This setting will prevent the user from using the same password until the defined number of times. For example, if we define it as 5, the user cannot use the same password for the next 5 times after the password expiry |
| The number of days until the Password expires | After setting the value, users will need to input their device password once the designated time interval to unlock the device |
We have explained more about new settings in our previous blog Enforcing Screen Lock for Android Devices in Intune as per CIS Benchmarks. I’m adding the complexity that can be applied for Android 12 and above devices in the below table
| Password Complexity | Type of Password Enforced |
|---|---|
| None | Intune does not look for a device lock for compliance check |
| Low | A Simple Password like (000, 1234, 1111) or A Pattern to unlock devices is allowed |
| Medium | The device should have the below type of passcode to be compliant At least a four-digit PIN or At least four letters of the Alphabetic Password or At least four digit Alphanumeric Password |
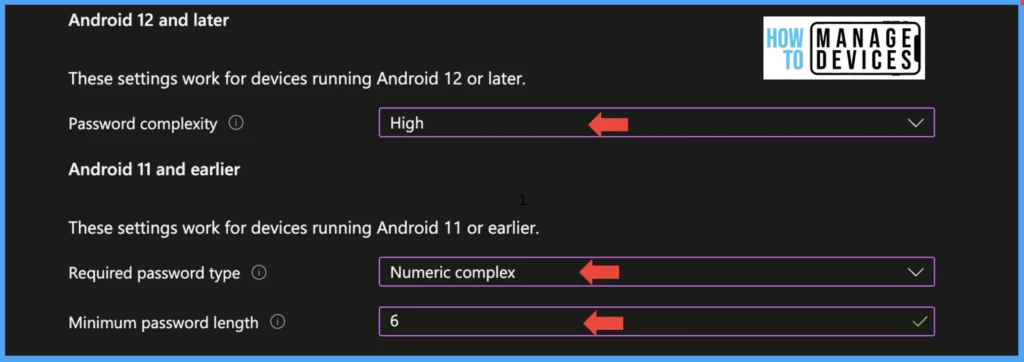
| High | The numeric Passcode length allowed is 8 Alphanumeric or alphabetic password length allowed is 6 |
If you have devices that are running on Android 11 or below OS versions, we need to configure the password type and password length under Android 11 and the earlier section
Select the Required Password type to specify the type of Password required for devices to unlock and set the minimum length of Password for the device. It is always good to have lengthy passwords like 6 and above
Now click on Next to move to Action for the Non-compliance screen, here, we define certain actions when the device becomes non-compliant. We can delay the device from becoming non-compliant immediately to give users a grace period to become compliant as per our settings
We can send emails to users if the device becomes non-compliant immediately or after some days. This feature is useful when you want to send alerts multiple times before blocking access to corporate data via a Conditional access policy. This is the section where we use the Notification template which we created at the beginning of the post
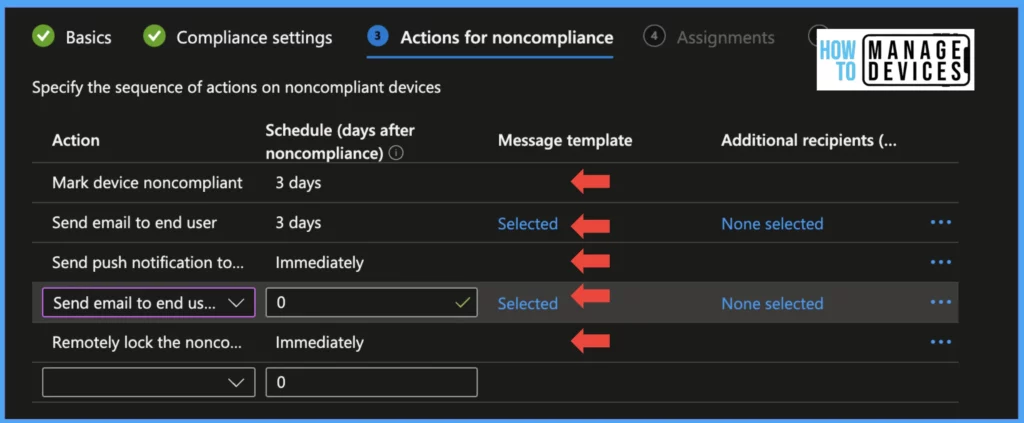
We can also Send Push Notifications, Remotely Lock the non-compliant device, and Add devices to the Retire device list either immediately or after certain days. All the values defined for these actions are in the number of days.
We can use the same action to inform users multiple times before marking the device as non-compliant. Click on Next to Scope tags and add scope tags if you have any, and click on Next to Assignment tab and assign the policies to user groups. Click on Next to review and create the Compliance Policy.
End-User Experience
Now we have successfully created a Compliance Policy. Let’s enroll a device and see what happens if the device does not satisfy the compliance rules we create. For this testing, I’m not setting the device Passcode and enabling USB debugging. Due to this, the user’s Mobile device will become non-compliant and prompted to make the device compliant before finalizing the device enrolment.
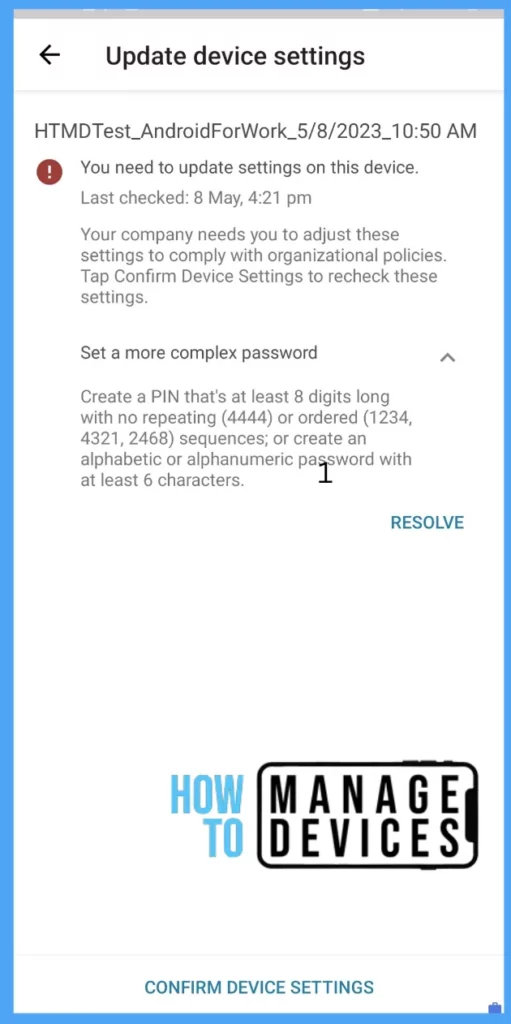
If the users already enrolled the devices and the compliance policy applied after, they are prompted with a message in the Company Portal app as soon as the device syncs with Intune. Company Portal also shows how to resolve the issue. When users click Resolve, they will take to the respective device screen to fix the issue. Once the user fixes all compliance issues, they can click confirm device settings to validate compliance.
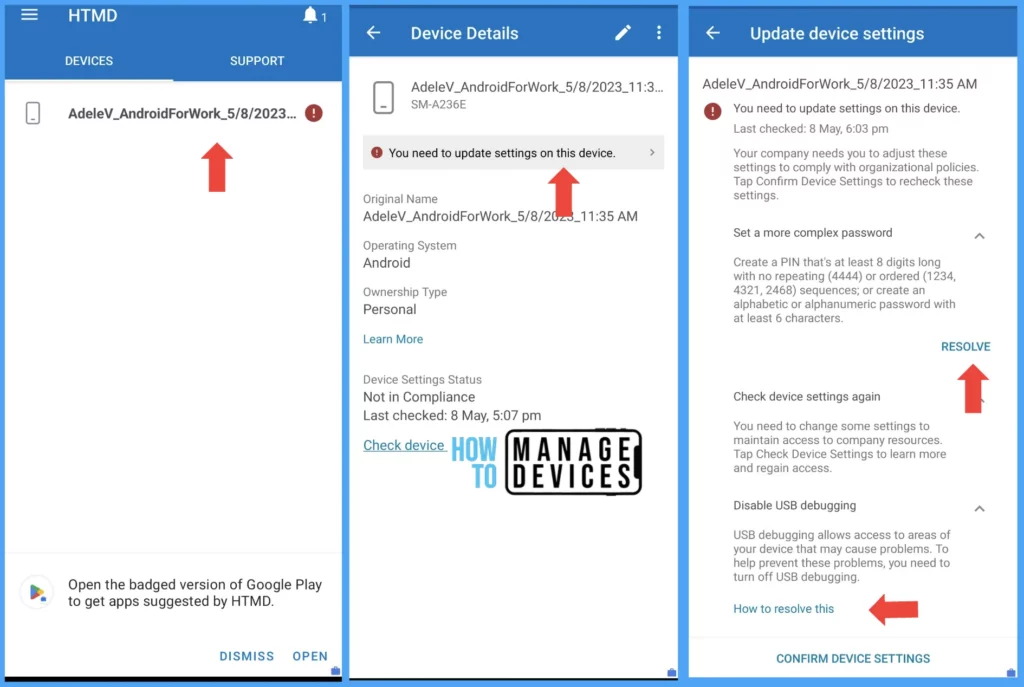
In Intune console, the admin can view the device compliance by navigating Devices > Search for the user device and clicking on the device. Under the compliance section admin can view whether the device is compliant or non-compliant
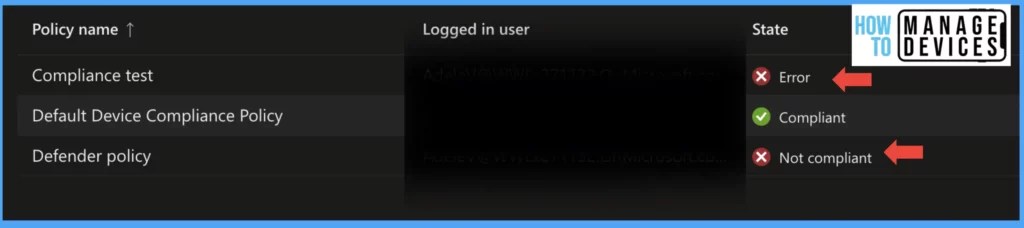
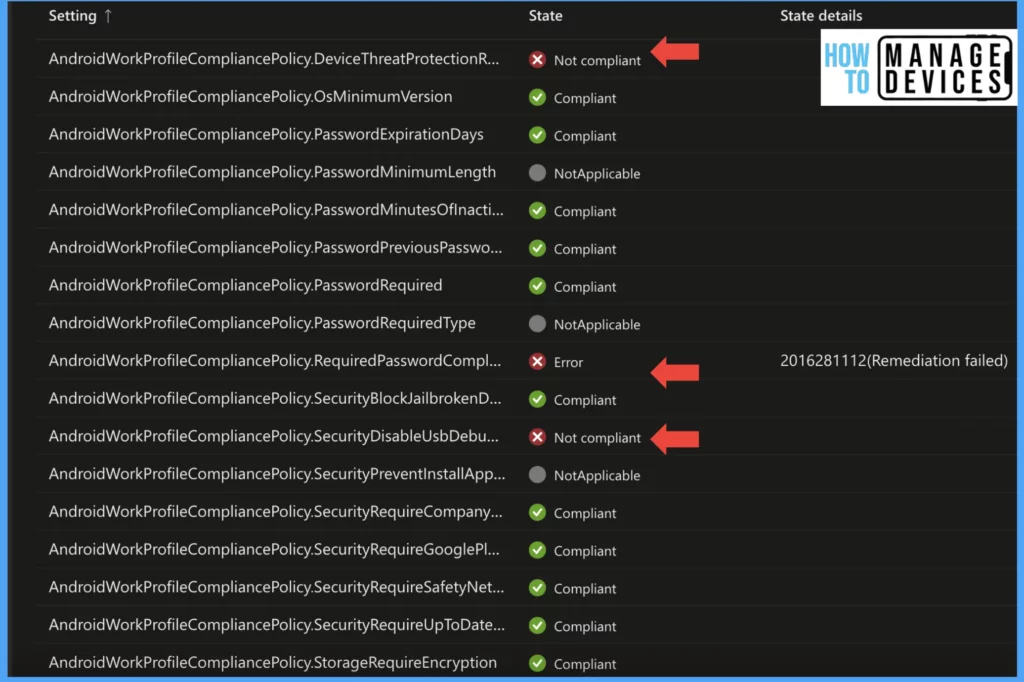
Intune also provided a detailed view of Compliance settings, which have passed the device compliance and have not met the compliance requirement. This can be viewed by clicking on the compliance policy in the above screenshot. As our device does not meet Password complexity and we have enabled USB debugging, the compliance rules became non-compliant.
As we set the Action for Non-Compliant Devices, the user will receive emails from Microsoft with the Notification Template created. Intune also captures the device details in the Email as well.
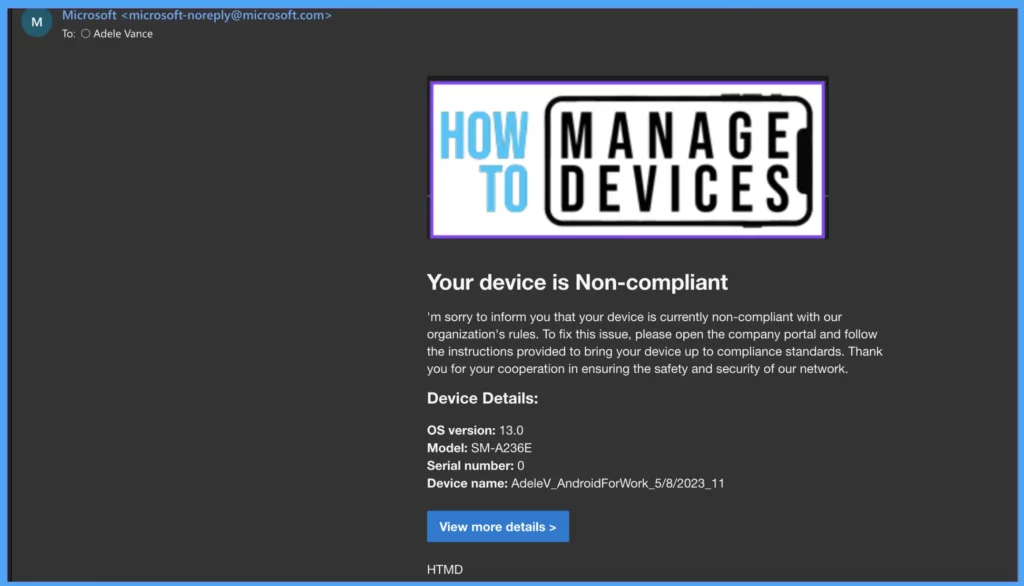
This is the first Email that users receive, and users will get an email after three days as per our configuration in non-compliance Action configured. We also configured Push Notification immediately, the user will receive Push Notification by clicking on Notification user is taken to the company portal app. Microsoft sends this Push Notification, and we cannot modify the message.

So this is how we can create Compliance policies for Android for Work devices. It is the same for Corporate devices that are enrolling using Fully managed, Corporate Dedicated devices and Corporate owned devices with Work profiles. We must select fully managed, dedicated, and corporate-owned with work profile under profile type while creating the Compliance Policy.
I hope this article has provided valuable insights and guidance on planning and creating a Compliance Policy for your organization. It’s crucial to configure your Compliance Policy according to your organization’s specific requirements to ensure its effectiveness and relevance. Best of luck!
Author
About Author – Narendra Kumar Malepati (Naren) has 11+ years of experience in IT, working on different MDM tools. Over the last seven years, Naren has been working on various features of Intune, including migration from different MDMs to Intune. Naren mainly focuses on Android, iOS, and MacOS.

How to trigger non complaince notification to mobile devices using intune till user is change his password?