In this article, let us discuss how to easily Disable Local Drive Redirection with Microsoft Intune. Local drive redirection is a Remote Desktop Services (RDS) feature that allows users to access files and folders on their local computer from within a remote desktop session.
When local drive redirection is enabled, users can access files stored on their local drives (such as C:\ or D:\) directly from within applications running on the remote desktop session.
However, there are security concerns associated with local drive redirection, as it can potentially expose sensitive data from the local computer to the remote session. For example, if a user inadvertently copies confidential files from their local drive to the remote session, those files could be accessed by other users who have access to the remote session.
Disabling local drive redirection prevents users from accessing files and folders on their local computer from within a remote desktop session. This can be useful in environments with strict security policies are in place or where there are concerns about data leakage.
In summary, disabling local drive redirection prevents users from accessing files and folders on their local computer within a remote desktop session, enhancing security and reducing the risk of data exposure.
- Quick and Easy way to Turn on PowerShell Audit using Intune Policy
- Best Guide to Enable WinSCP Win32 App Supersedence and Auto-Update with Intune
- Complete Guide Enable Copilot in Managed Microsoft Edge Browser with Intune
- Best Guide to Remove Windows Update Features Access with Intune

What are the Advantages of Disable Local Drive Redirection?
Disabling local drive redirection in Remote Desktop Services (RDS) environments like Windows 365 Cloud PCs can offer several advantages. The table below shows these advantages.
| Category | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Security | By preventing users from accessing their local drives within a remote desktop session, organizations can mitigate the risk of data leakage or exposure of sensitive information to unauthorized users. This helps to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of data. |
| Data Loss Prevention | Disabling local drive redirection helps prevent accidental data loss or theft by restricting the movement of files between local and remote environments. This reduces the likelihood of sensitive data being inadvertently copied or transferred to unauthorized locations. |
| Compliance | Organizations operating in regulated industries, such as healthcare or finance, may be subject to industry-specific regulations and data protection standards. Disabling local drive redirection can help organizations comply with these regulations by minimizing the risk of unauthorized data access or transfer. |
| Protection Against Malware | Local drive redirection can potentially expose remote desktop sessions to malware or malicious files stored on users’ local drives. Disabling this feature helps protect the remote desktop environment from such security threats and reduces the risk of malware propagation. |
| Resource Optimization | Disabling local drive redirection can help optimize network bandwidth and server resources by reducing the amount of data transferred between local and remote environments. This is especially beneficial in scenarios where large files are frequently accessed or transferred. |
| Improved Performance | By reducing the volume of data transferred between local and remote environments, disabling local drive redirection can contribute to improved performance and responsiveness of remote desktop sessions, particularly in bandwidth-constrained or high-latency network environments. |
| Simplified Management | Disabling local drive redirection simplifies the management and administration of the remote desktop environment by reducing the complexity associated with monitoring and controlling access to local drives within remote sessions. This can lead to lower administrative overhead and streamlined IT operations. |
Disabling local drive redirection helps organizations enhance security, prevent data loss, achieve compliance with regulatory requirements, optimize resource utilization, improve performance, and simplify management within their Remote Desktop Services environment.
Create Configuration Profile to Disable Local Drive Redirection with Intune
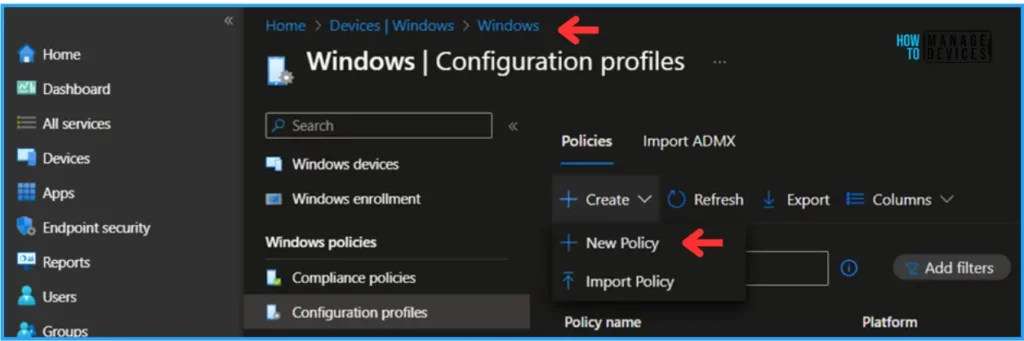
Follow the below-mentioned steps to create a configuration policy to Disable Local Drive Redirection with Intune. Log In to the Microsoft Intune Admin Center using your administrator credentials.
- Navigate to Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles
- Click on +Create > +New Policy
In the next step, we can create a new Configuration Profile starting from scratch. For that, give the below options as mentioned.
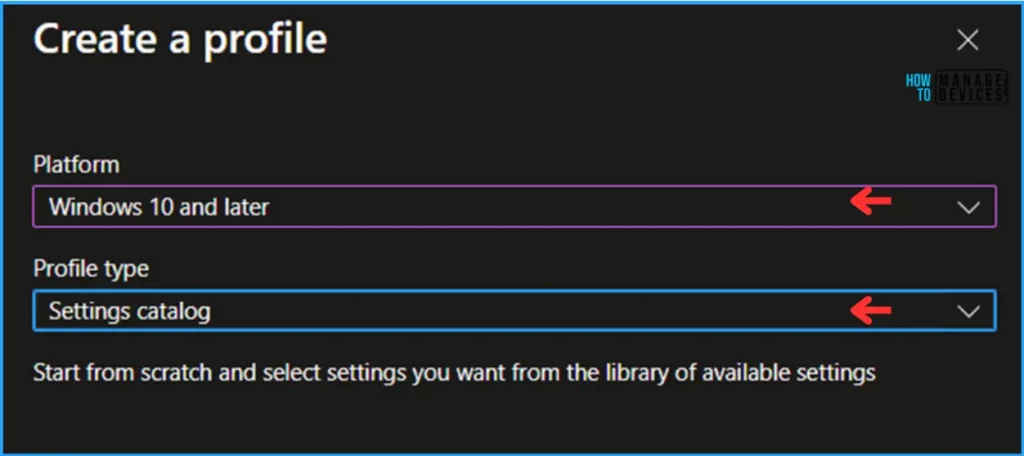
- Platform: Windows 10 and later
- Profile type: Settings catalog
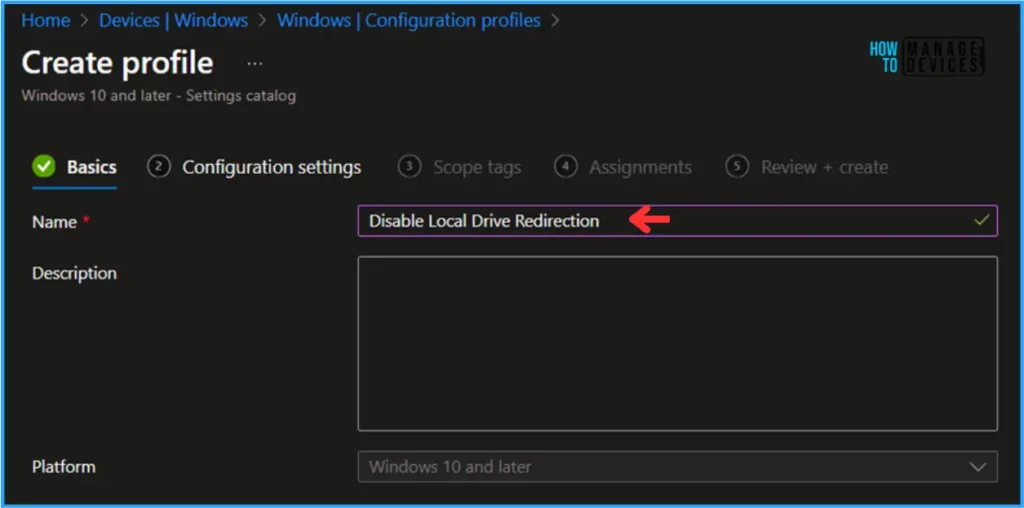
In the Basics details pane, we can give the Configuration profile name “Disable Local Drive Redirection.” If needed, provide a brief policy description and click Next.
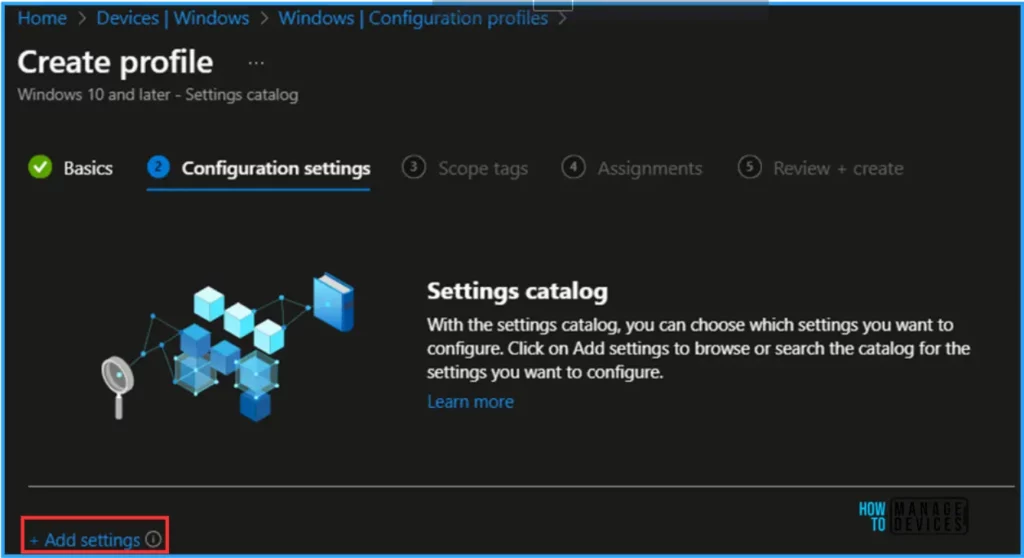
We can now add the required settings to the Configuration Settings pane. To do so, click on +Add settings in the bottom left corner of the page.
Note! With the Settings catalog, you can choose which settings you want to configure. Click on Add Settings to browse or search the catalog for the settings you want to configure.
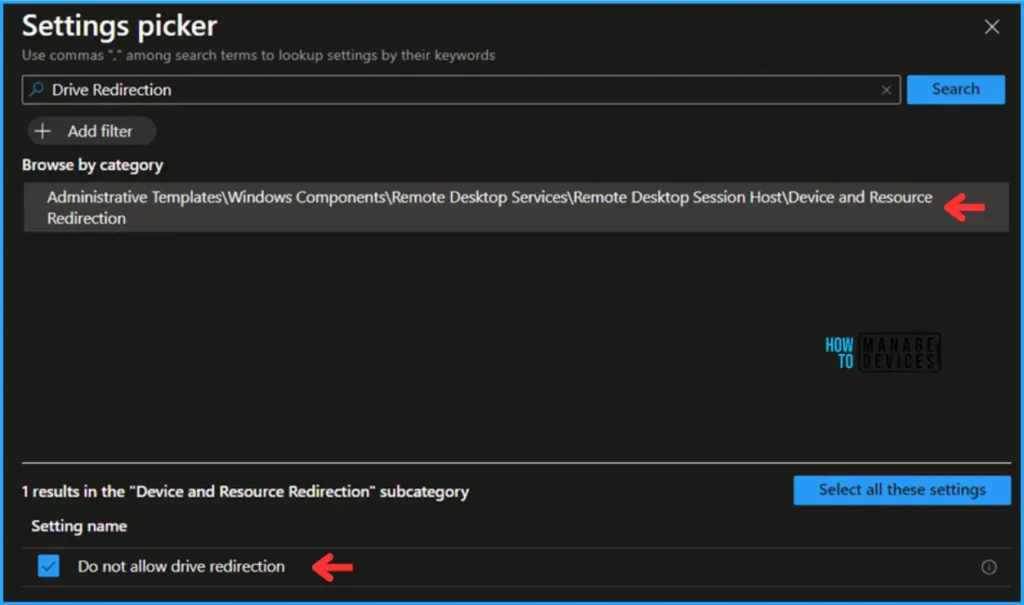
Search for “Drive Redirection” as a keyword. This will help you find the correct policy based on our current needs. Now you can see the “Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Device and Resources Redirection” under the Browse by category. Click on that and pick the settings below.
- Do not allow drive redirection
Note! This policy setting specifies whether to prevent the mapping of client drives in a Remote Desktop Services session (drive redirection). An RD Session Host server maps client drives automatically upon connection by default. Mapped drives appear in the session folder tree in File Explorer or Computer in the format <driveletter> on <computername>. You can use this policy setting to override this behaviour. If you enable this policy setting, client drive redirection is not allowed in Remote Desktop Services sessions, and Clipboard file copy redirection is not allowed on computers running Windows Server 2003, Windows 8, and Windows XP. If you disable this policy setting, client drive redirection is always allowed. In addition, Clipboard file copy redirection is always allowed if Clipboard redirection is allowed. If you do not configure this policy setting, client drive redirection and Clipboard file copy redirection are not specified at the Group Policy level.
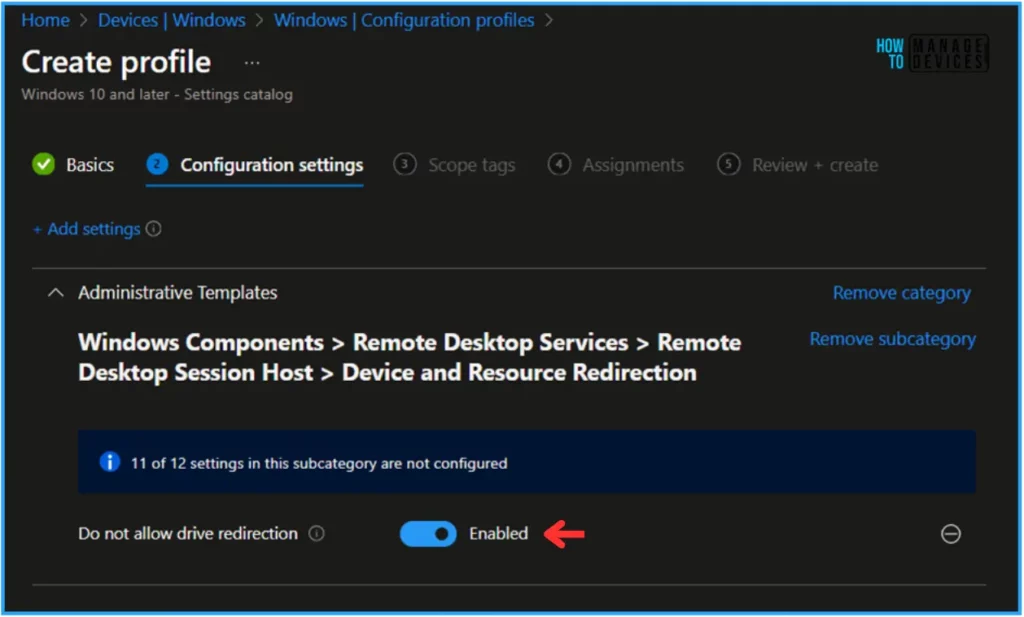
Close the Settings picker window and toggle the “Do not allow drive redirection” option as Enabled. Click on Next
On the next page, Leave the Scope tags as Default. If you have any custom scope tags available, you can also select that for this deployment.
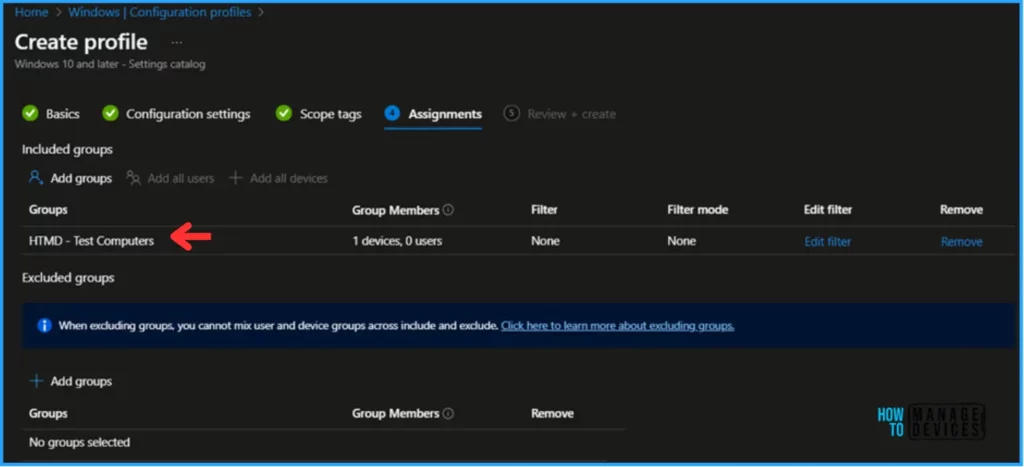
Click on Next and assign the configured policy to HTMD – Test Computers. In the Included Groups option, click on Add groups and select the required device group.
On the Review + Create page, carefully review all the settings you’ve defined for the Disable Local Drive Redirection policy. Select Create to implement the changes once you’ve confirmed everything is correct.
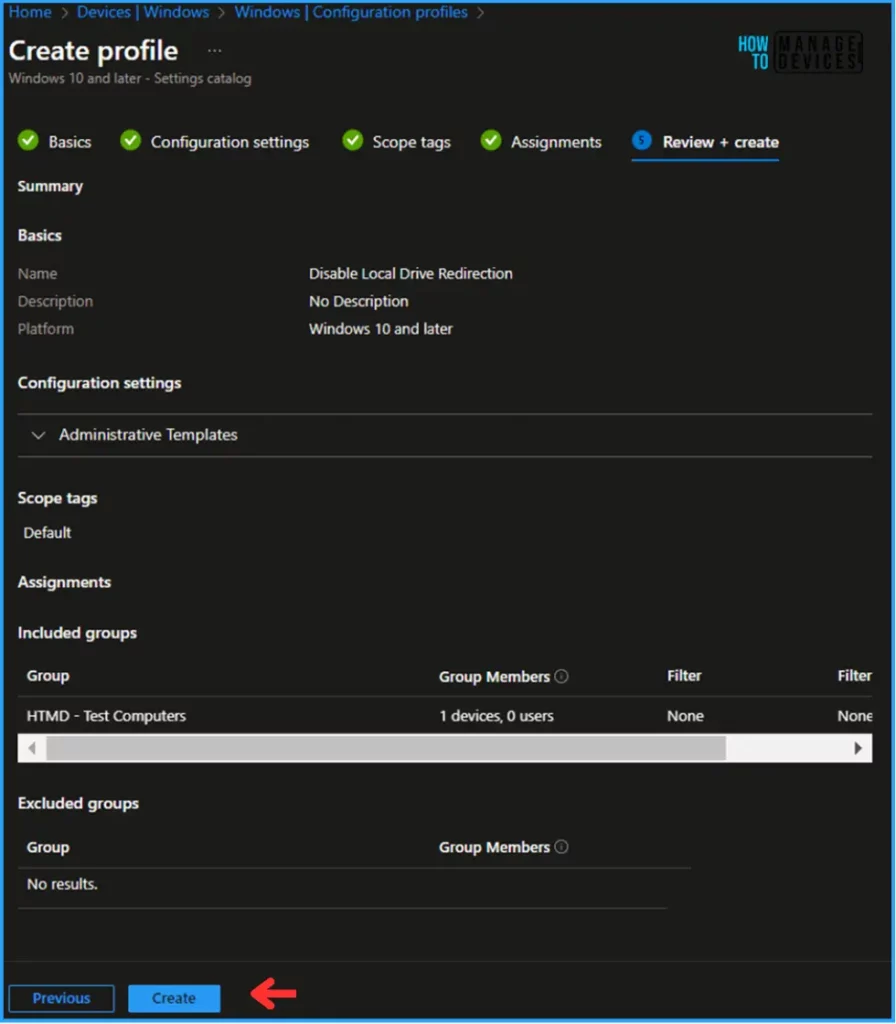
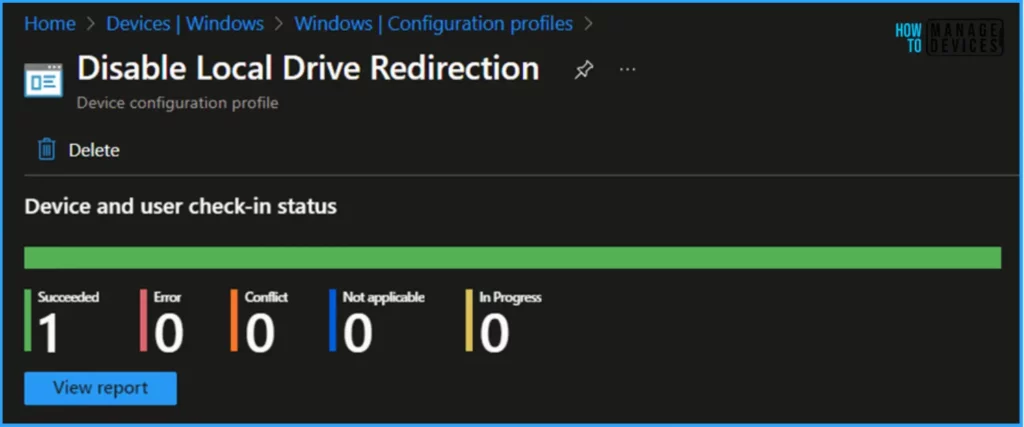
Monitor the Disable Local Drive Redirection Policy in Intune
This particular policy has been deployed to the Microsoft Entra ID group (HTMD – Test Computers). The policy will take effect as soon as possible once the device is synced.
- To monitor the policy deployment status from the Intune Portal, follow the below-mentioned steps.
- Navigate to Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles > Search for the “Disable Local Drive Redirection” policy.
- Under the Device and user check-in status, you can see the deployment status for the same.
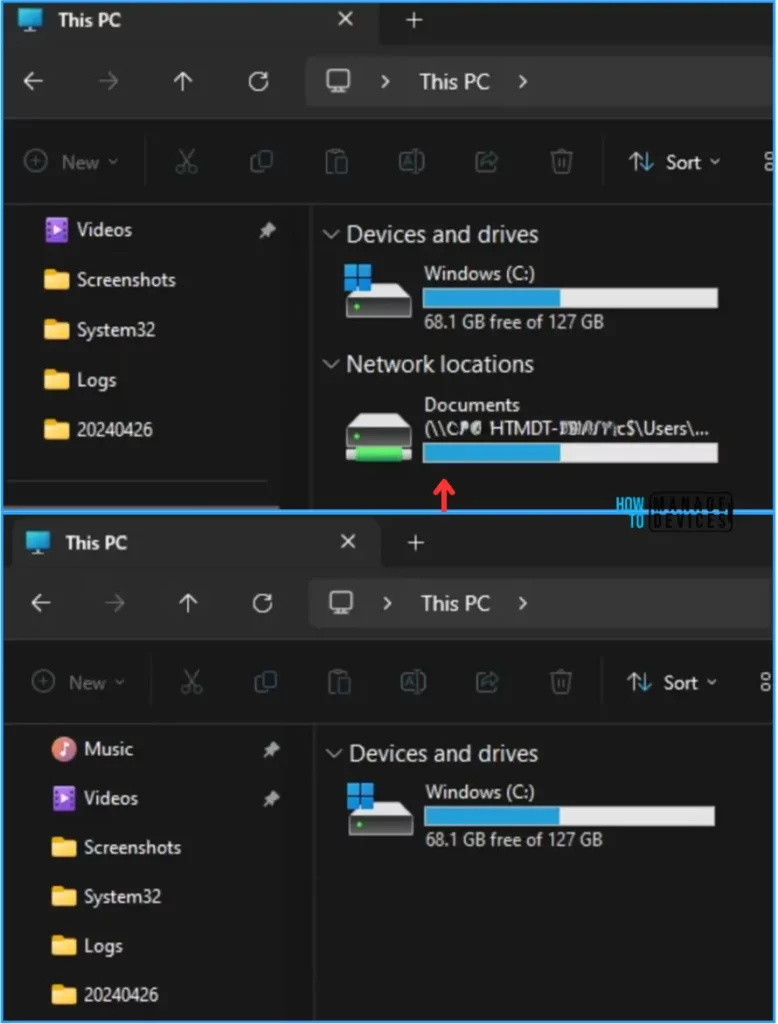
End User Experience – Disable Local Drive Redirection Policy
Now, we have to check whether the Disable Local Drive Redirection policy is working fine or not. Log in to one of the policy-targeted devices. In this example, mentioned in the first screenshot below, you can see the drive map and redirection is present before applying the policy.
The second screenshot shows after the policy was applied. The Redirected Drive is unavailable, and if we try to map it again, it won’t work due to the policy restriction.
I appreciate you taking the time to read my article. I’m excited to see you in the upcoming post. Continue to support the HTMD Community.
We are on WhatsApp. To get the latest step-by-step guides and news updates, Join our Channel. Click here –HTMD WhatsApp.
Vaishnav K has over 10+ years of experience in SCCM, Device Management, and Automation Solutions. He writes and imparts his knowledge about Microsoft Intune, Azure, PowerShell scripting, and automation. Check out his profile on LinkedIn.
