In this post, you will learn how to manage Intune Compliance Policy Settings. The compliance policies protect organizational data by requiring users and devices to meet some requirements.
Intune Compliance Policy for device help to protect company data; the organization needs to ensure that the devices used to access company apps and data comply with certain rules. By default, when Intune detects a device that isn’t compliant, Intune immediately marks the device as non-compliant.
When a device isn’t compliant, Intune allows you to add actions for noncompliance, which gives you the flexibility to decide what to do. One action to take when a device doesn’t meet compliance is to send an email to the user of the device, here’s how you can Send Notifications For Noncompliant Devices In Intune.
Compliance policy settings are tenant-wide settings that determine how Intune’s compliance service interacts with your devices. These settings are distinct from those you configure in a device compliance policy.
You can start creating compliance policies from the Intune admin center. The Devices Node and from the Endpoint Security node. The following steps will Create Intune Compliance Policy for Windows.
- Create Intune Compliance Policy For Windows 365 Cloud PC And AVD
- Easiest Method to Enable MFA for Admins using Azure AD Conditional Access
Manage Intune Compliance Policy Settings
To manage the compliance policy settings, The following steps provide you with details on how to configure compliance policy settings in Intune.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center https://endpoint.microsoft.com/.
- Navigate to Endpoint security > Device compliance.
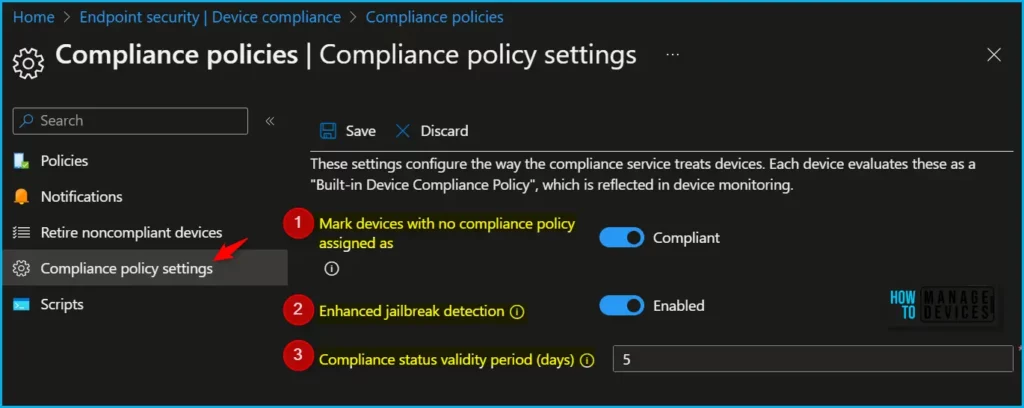
Compliance policy settings include the following settings, These settings configure how the compliance service treats devices. Each device evaluates these as a “Built-in Device Compliance Policy”, which is reflected in device monitoring.
- Mark devices with no compliance policy assigned as This setting determines how Intune treats devices that haven’t been assigned a device compliance policy.
- Enhanced jailbreak detection (applies only to iOS/iPadOS) This setting works only with devices that you target with a device compliance policy that blocks jailbroken devices.
- Compliance status validity period (days) Specify a period in which devices must successfully report on all their received compliance policies.
It is important to understand how it works and the available options to configure before you proceed to set it up. Here’s a detailed overview of the available compliance settings:
- Mark devices with no compliance policy assigned as This setting has two values:
- Compliant (default): This security feature is off. Devices that aren’t sent a device compliance policy are considered compliant.
- Not compliant: This security feature is on. Devices that haven’t received a device compliance policy are considered non-compliant.
- Enhanced jailbreak detection This setting has two values:
- Disabled (default): This security feature is off. This setting has no effect on your devices that receive device compliance policy that blocks jailbroken devices.
- Enabled: This security feature is on. Devices that receive device compliance policy to block jailbroken devices use the Enhanced jailbreak detection. When enabled on an applicable iOS/iPadOS device, the device: Enables location services at the OS level.
- Compliance status validity period (days) Specify when devices must successfully report on all their received compliance policies. If a device fails to report its compliance status for a policy before the validity period expires, it is treated as noncompliant. By default, the period is set to 30 days. You can configure a period from 1 to 120 days.
Monitor Device Compliance Policies Setting
In Intune portal, You can view details about devices compliance with the validity period setting. By Navigating to the Devices > Monitor > Setting compliance. This setting has a name of Is active in the Setting column.
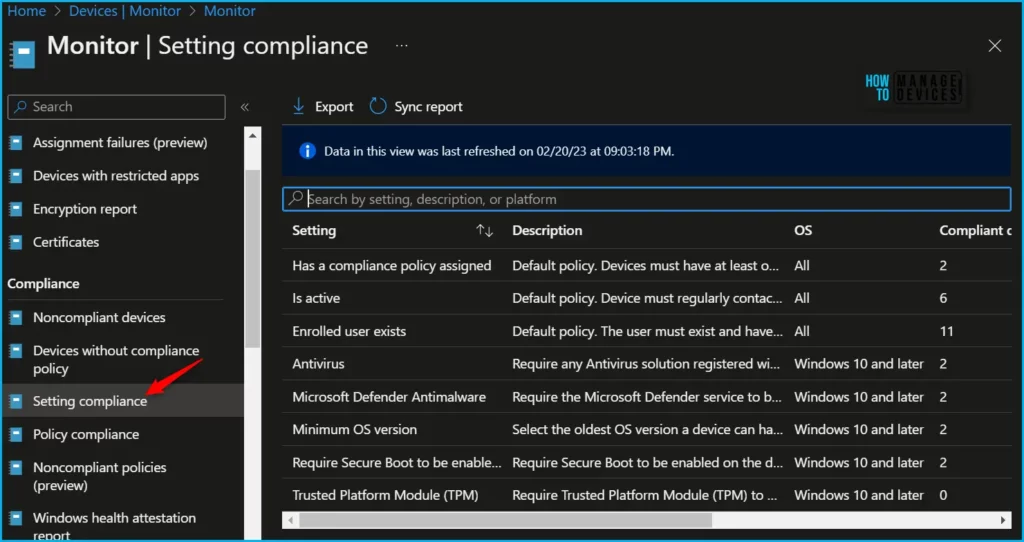
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Has a compliance policy assigned | Default policy. Devices must have at least one compliance policy assigned to be compliant. |
| Is active | Default policy. Device must regularly contact Intune to be considered compliant. |
| Enrolled user exists | Default policy. The user must exist and have a valid Intune license. |
| Antivirus | Require any Antivirus solution registered with Windows Security Center to be on and monitoring (e.g DigiCert, Microsoft Defender) |
| Microsoft Defender Antimalware | Require the Microsoft Defender service to be enabled. |
| Minimum OS version | Select the oldest OS version a device can have. The operating system version is defined as major.minor.build.revision. |
| Require Secure Boot to be enabled on the device | Require Secure Boot to be enabled on the device |
| Trusted Platform Module (TPM) | Require Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to be present |
Author
About Author – Jitesh, Microsoft MVP, has over six years of working experience in the IT Industry. He writes and shares his experiences related to Microsoft device management technologies and IT Infrastructure management. His primary focus is Windows 10/11 Deployment solution with Configuration Manager, Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT), and Microsoft Intune.

Sadly, because Microsoft can’t leave anything alone for five minutes, your instructions are already out of date.
I have many Entra-hybrid joined computers that refuse to go into Intune and I cannot figure out why.
Windows Automatic enrollment is set up. MDM User Scope is ALL and MAM is None. Of about 140 PCs, only 97 are showing in Intune.
Any ideas?
Hi Cathy,
This article isn’t regarding Hybrid joining endpoints though.
If devices fail to enroll into Intune after hybrid joining, it’s usually due to stale enrollments or user credential issues.