In this article, I will explain how to configure Windows Autopilot Next Generation Device Preparation Policies with Microsoft Intune.
Windows Autopilot simplifies the deployment of new devices by providing a streamlined, user-friendly setup process. With Windows Autopilot, devices are pre-configured and ready for use right out of the box. Understanding the preparation policies and best practices is essential to effectively managing and preparing Autopilot devices.
Organizations can streamline the device preparation by effectively implementing these components, reducing IT overhead, and enhancing the end-user experience.
To prepare new devices for productive use, Windows Autopilot device preparation is used to set them up and configure them. Windows Autopilot device preparation aims to simplify device deployment by providing consistent configurations, increasing setup speed overall, and strengthening troubleshooting functionality.
| Index |
|---|
| Key Components of Windows Autopilot V2 Device Preparation Policy |
| Create Windows Autopilot V2 Devices Preparation Policy |
| Configuration Settings of Windows Autopilot V2 Device Preparation Policy |

- How to Set App Defaults using Intune | Export the Default XML File & Encode it in Base64 format
- Best Guide to Deploy New Intune Company Portal App on Windows using Intune
- Easy Guide to Set Feature Updates for Windows 11 as Optional with Intune
- Intune Win32 App Supersedence and Auto App Update Explained
Key Components of Windows Autopilot Next Generation Device Preparation Policy
Windows Autopilot is a suite of tools to set up and pre-configure new devices, preparing them for productive use. The key components of a Windows Autopilot V2 Devices Preparation Policy include:
| Key Components | Details |
|---|---|
| Device Enrollment | Device Registration: Register devices with Windows Autopilot by uploading device information to the Microsoft Intune portal or using partner integrations. Profile Assignment: Assign Autopilot deployment profiles to the registered devices to define the setup experience. |
| Deployment Profiles | User-Driven Mode: Allows end-users to set up their devices with minimal IT intervention. Users sign in with their corporate credentials and the device is automatically enrolled in Intune and Azure AD. Self-Deploying Mode: Enables zero-touch deployments where the device sets up automatically without any user interaction, ideal for kiosks or shared devices. Pre-provisioning (White Glove) Mode: IT can pre-configure devices and install necessary applications before handing them over to the end-users, ensuring they are ready to use immediately. |
| Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE) Customization | Customize the OOBE to skip specific pages or display custom branding and messages. Configure language, locale, and keyboard settings. |
| Policies and Settings | Security Policies: Define security baselines, compliance policies, and conditional access rules to ensure devices meet organizational security standards. Configuration Profiles: Apply device configuration settings, such as Wi-Fi profiles, VPN settings, and other device-specific configurations. |
| Application Deployment | Pre-install critical applications using Microsoft Intune or other management tools during the setup process. Configure the Microsoft Store for Business to install required applications automatically. |
| Hybrid Azure AD Join | Configure devices to join both Azure Active Directory and on-premises Active Directory for hybrid identity management. |
| Telemetry and Diagnostics | Use Windows Analytics and other diagnostic tools to monitor device health and deployment progress. Collect feedback and troubleshoot deployment issues. |
| License Requirements: | Ensure that devices and users have the appropriate licenses for Windows Autopilot, such as Windows 10/11 Enterprise E3/E5, Microsoft 365 Business Premium, or higher. |
Create Windows Autopilot Next Generation Device Preparation Policy
Here are the steps to create the Windows Autopilot V2 device policy through Intune. Let’s discuss the step-by-step method to create this policy.
- Sign In to the Microsoft Intune admin center
- Navigate to Devices > Windows > Device onboarding > Enrollment
- Under Windows Autopilot device preparation, Click on > Device preparation policies
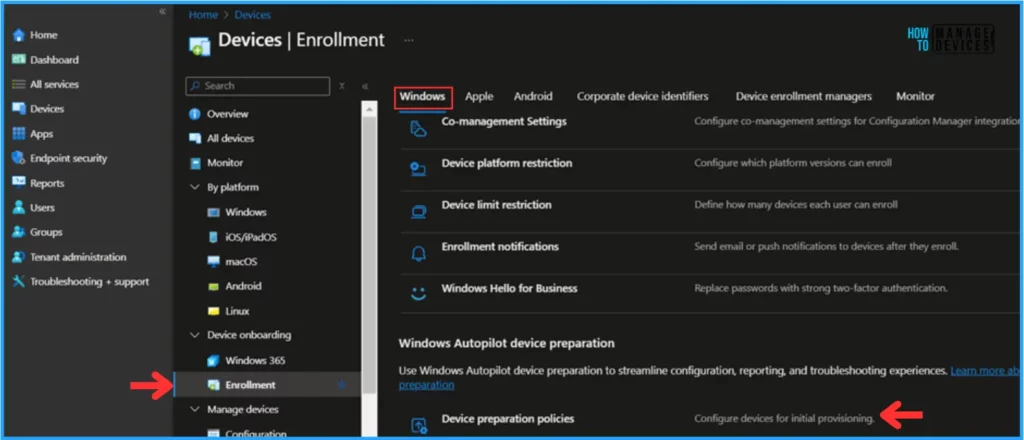
Click on the +Create option, read the details and Microsoft Official links in the Introduction pane, and click Next.
What’s new! Select a small number of policies, managed apps and scripts to reference in this policy. Windows Autopilot device preparation will report the installation status for these items in the Autopilot device preparation deployment report. Set up the Entra ID security group containing your Autopilot devices when they enroll. The policies and apps intended for these devices should target this group.
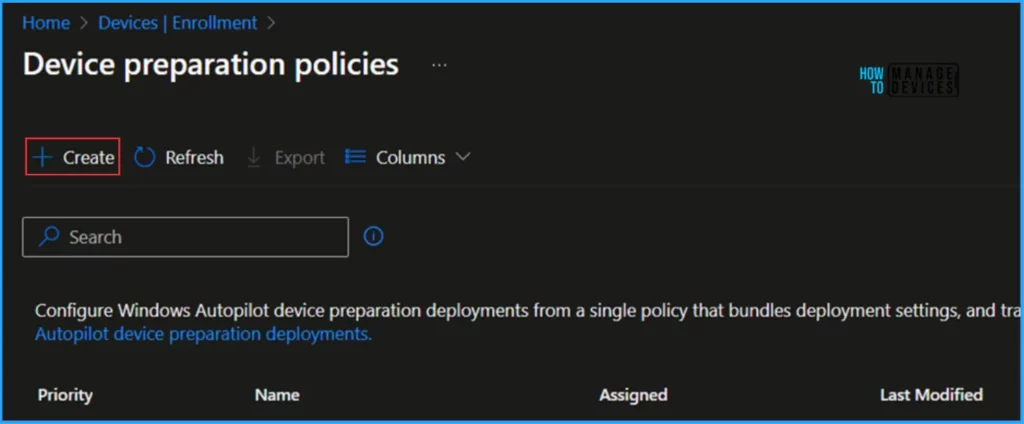
On the Basics pane, give the policy name “HTMD – Windows Autopilot V2 Device Preparation Policy” If needed, we can add a short description and hit Next.
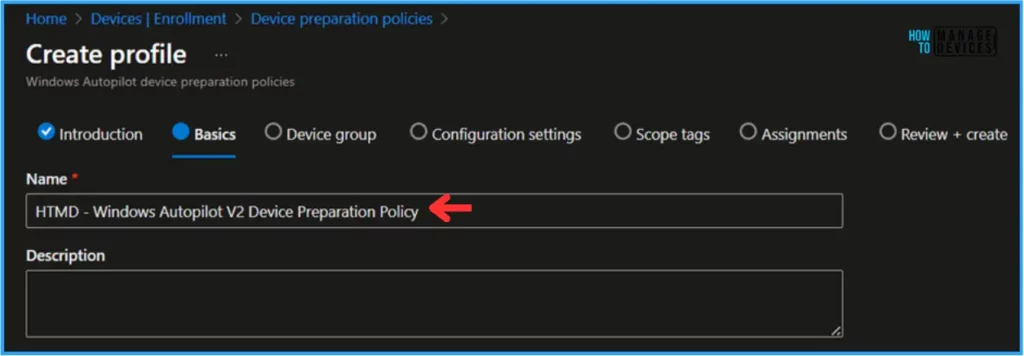
In the Device group section, you need to select the group predefined as “Windows Autopilot device preparation device group“
Note! Create a security group “Windows Autopilot device preparation device group” and add owner as Intune Autopilot ConfidentialClient Enterprise applications.
Configuration Settings of Windows Autopilot V2 Device Preparation Policy
In the Configuration settings, we have four significant sections: Apps, Deployment settings, Out-of-box experience settings and Scripts.
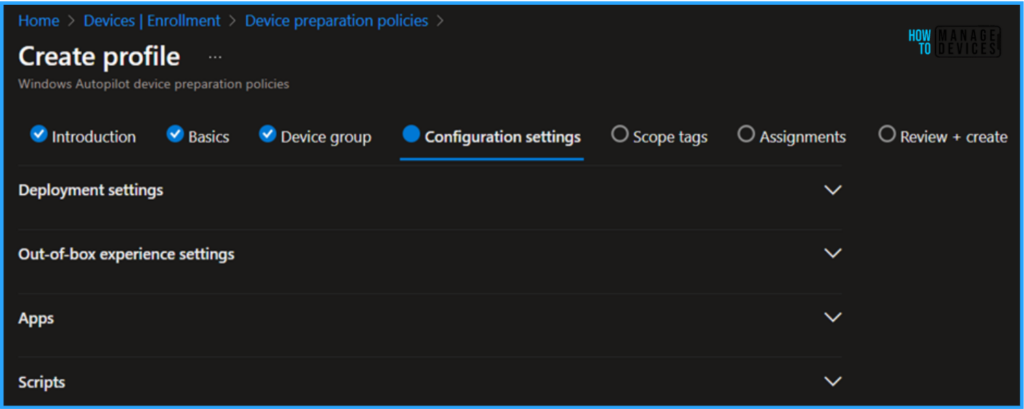
In the Deployment settings section, give the details below to configure them based on your needs.
- Deployment mode – User-driven –
Deployment mode controls if a user must provide credentials to provision the device. - Deployment type – Single user
- Join type – Microsoft Entra joined – (Specify how devices join an identity provider in your organization.)
- User account type – Standard user (
Specify whether users are administrators or standard users on the device. Note that this setting does not apply to Global Administrator or Company Administrator accounts. These accounts cannot be standard users because they have access to all administrative features in Microsoft Entra ID.)
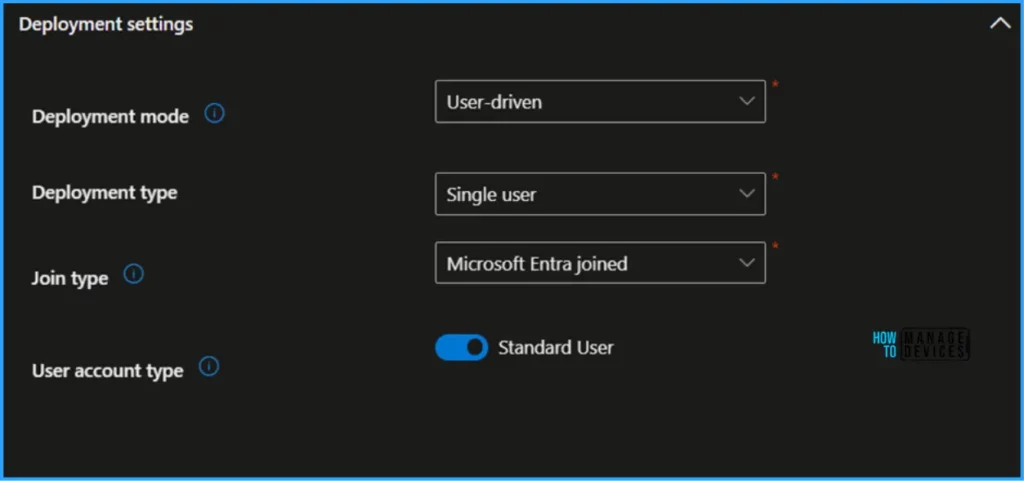
In the Out-of-box experience settings option, leave the values mentioned below. You can alter them based on your needs.
- Minutes allowed before showing installation error – 30
- Custom error message – Contact your organisation’s support person for help. (This message will be displayed if an error occurs during deployment.)
- Allow users to skip setup after multiple attempts – Yes (Allow users to continue to desktop if deployment fails.)
- Show link to diagnostics – Yes.
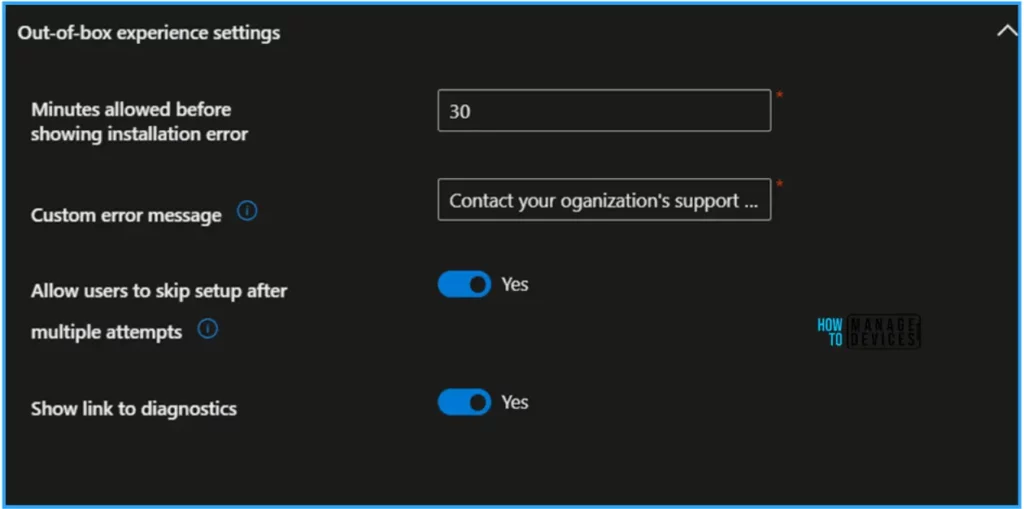
In the Apps section, click +Add and select up to 10 managed apps you want to reference for this deployment. These apps should be assigned to the device security group you selected earlier. You can check the installation status for these apps in the device details for devices in this deployment.
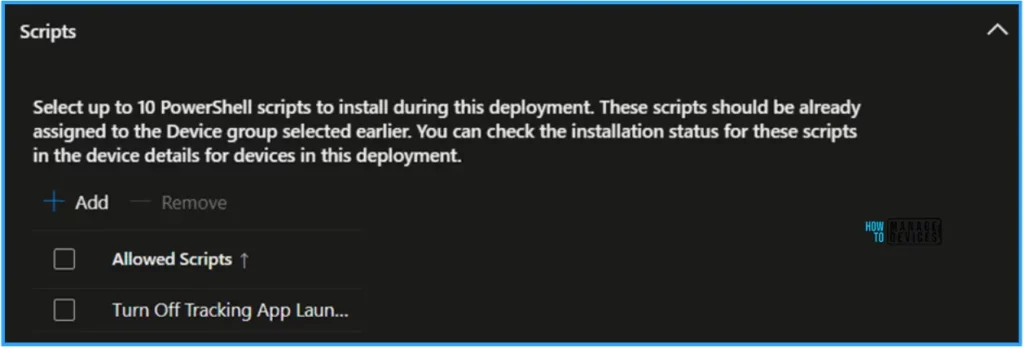
In the Script session, click +Add and Select up to 10 PowerShell scripts to install during this deployment. These scripts should have already been assigned to the Device group selected earlier. You can check the installation status for these scripts in the device details for devices in this deployment.
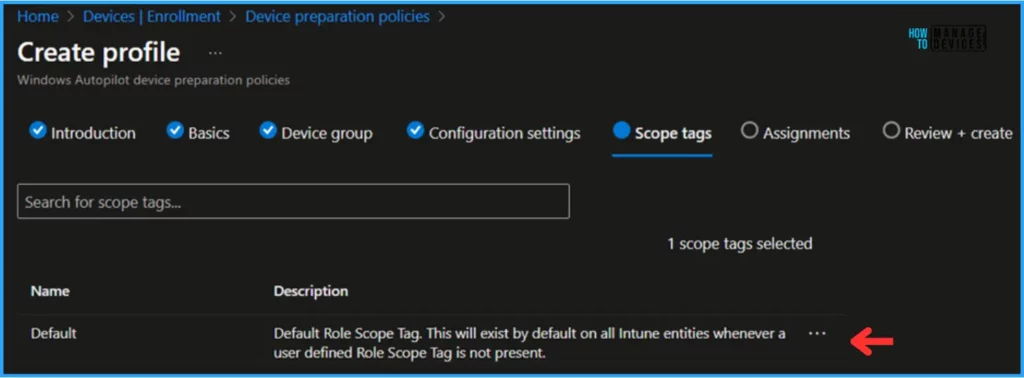
The following section is Scope tags, which will default on all Intune entities whenever a user-defined Role Scope Tag is absent.
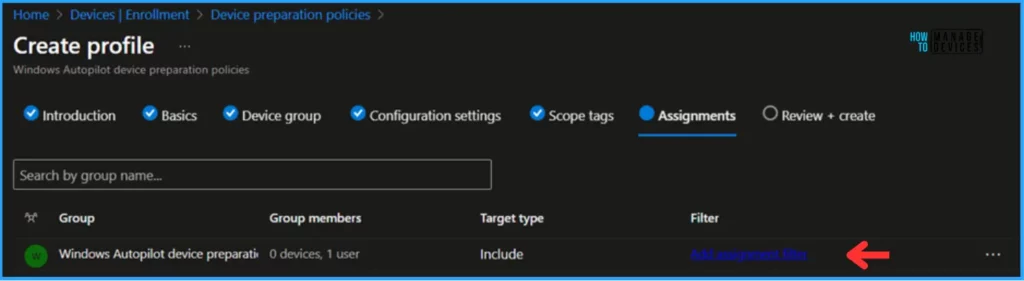
In the Assignment pane, search and select “Windows Autopilot device preparation user group.“
Note! Create a security group “Windows Autopilot user preparation device group” and add the Email IDs of the users who will going to use the device.
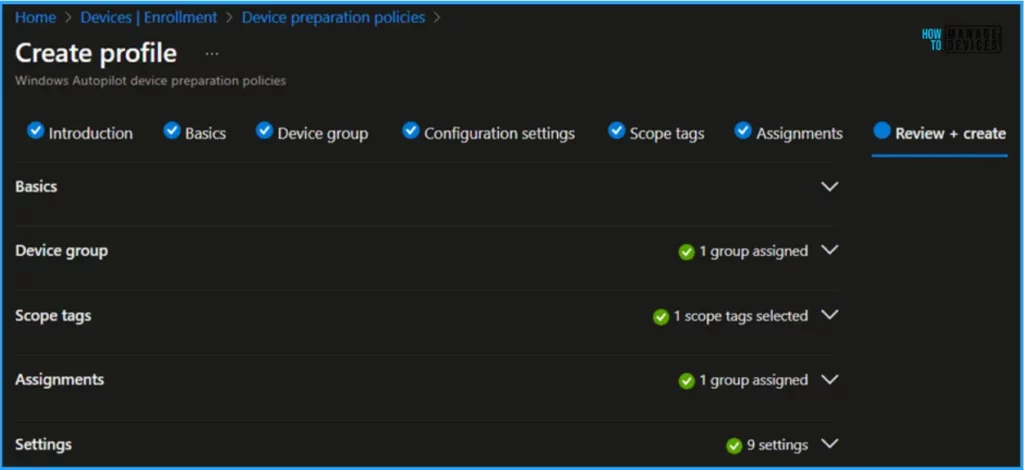
On the Review + Create page, carefully review all the settings you’ve defined for HTMD – Windows Autopilot V2 Device Preparation Policy. Once you’ve confirmed everything is correct, select Save to implement the changes.
I appreciate you taking the time to read my article. I’m excited to see you in the upcoming post. Continue to support the HTMD Community.
Author
Vaishnav K has over 10+ years of experience in SCCM, Device Management, and Automation Solutions. He writes and imparts knowledge about Microsoft Intune, Azure, PowerShell scripting, and automation. Check out his profile on LinkedIn.
