Let’s discuss the Top 5 Security Layers of Protection. Security and Protection are familiar words in the IT sector. Security is an essential factor in the Cyberworld, and all individuals value their security, and data protection every day.
There are different types of security solutions available in the IT sector. Have you ever heard about Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA)? ZTA is a security framework that helps to secure organizations. Its basic principle is maintaining strict access controls and not trusting anyone by default.
Different layers are introduced in Zero Trust Architecture. ZTA mandates rigorous authentication and authorization for any entity seeking access to resources, regardless of location or presumed trust level.
Different layers in Zero-Trust Architecture play a crucial role and offer specialized security controls. This blog post will help you understand the Top five Security Layers of Protection in Zero-Trust Architecture.
- Top 5 Data Security Challenges DLP Productivity eBook Download for Free
- Insights of How Copilot for Security Works
Top 5 Security Layers of Protection
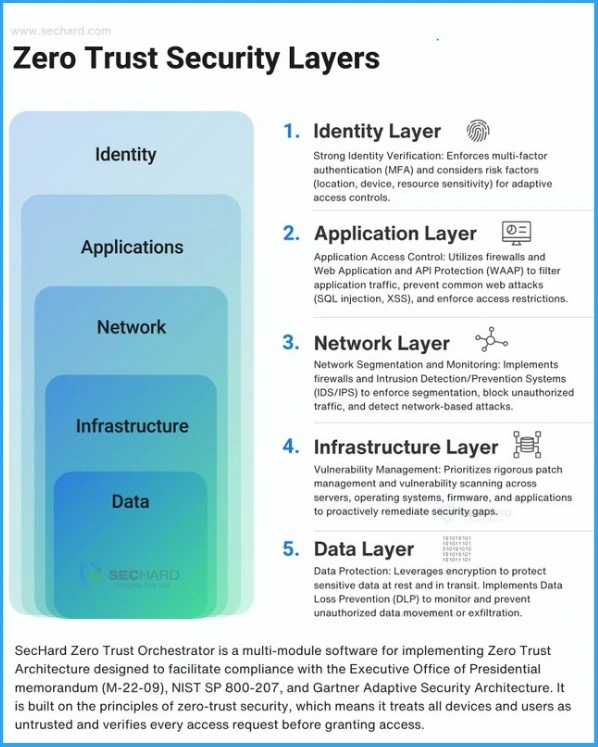
The five Security Layers of protection help users protect their organization. The multi-layered approach creates a huge defence-in-depth strategy that significantly reduces an organization’s overall attack surface. The following table shows the five layers of protection.
| Top 5 Security Layers of Protection |
|---|
| Identity Layer |
| Application Layer |
| Network Layer |
| Infrastructure Layer |
| Data Layer |
See More: 2024 Cybersecurity Certifications for IT Professionals
1. Identity Layer
The Identity layer is the first layer of Zero-Trust Architecture. In this layer, Strong identity verification occurs. The Identity Layer enforces multi-factor authentication (MFA) and considers risk factors for adaptive access control. Risk factors include location, device, and resource sensitivity.

2. Application Layer
Application Layer is the Second layer in Zero Trust Architecture. It includes application access control to utilise firewalls and Web Applications and API protection. It is used to filter application traffic, prevent common web attacks (SQL injection, XSS), and enforce access restrictions.

- What is the Security Compute Unit in MS Copilot for Security Context
- New Capabilities in Microsoft Copilot for Security
3. Network Layer
The Network layer implements firewalls and intrusion Detection/Prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to enforce segmentation, block unauthorized traffic, and detect network-based attacks.

4. Infrastructure Layer
The infrastructure layer is the 4th layer that includes vulnerability management. It prioritizes rigorous patch management and vulnerability scanning across servers, operating systems, firmware and applications.

5. Data Layer
Data Layer is the last layer in ZTA, that includes Data protection. It leverages encryption to protect sensitive data at rest and in transit. It implements data loss prevention (DLP) to monitor and prevent unauthorized data movement or exfiltration.

We are on WhatsApp. To get the latest step-by-step guides and news updates, Join our Channel. Click here –HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
Gopika S Nair is a computer enthusiast. She loves writing on Windows 11 and related technologies. She is here to share quick tips and tricks with Windows 11 or Windows 10 users. She is Post Graduate Diploma Holder in Computer Science.
