Let’s learn the Best Usage of Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool in Windows 11. Sometimes, you face some memory issues with your device. Then the Windows Memory Diagnostic (WMD) Tool is very helpful for testing your RAM (Random Access Memory) issues, if any.
If you are facing some problems using your Windows system, like random crashes, freezes, uncertain restarts, or not functioning well. The said problems may occur due to RAM or memory modules. There is nothing to worry about situation because now most of us use modern Windows devices that are equipped with the memory testing tool, which is used to test your RAM for any problems.
The Windows memory diagnostic tool is a free memory testing tool in the Windows system, that was introduced in Windows 7 and included in all later versions, and it performs a series of tests on your device’s RAM for any problems relating to memory.
In this guide, you will learn how to use the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool to rest your RAM. Also, here you can see the walkthrough to run the WMD tool and how to check the results of it and provide some possible solutions if any errors appear.

- 19 More Useful System Settings Run Commands for Windows
- Enable Windows Diagnostic Data and Licensing Usage from Intune
How to Run Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
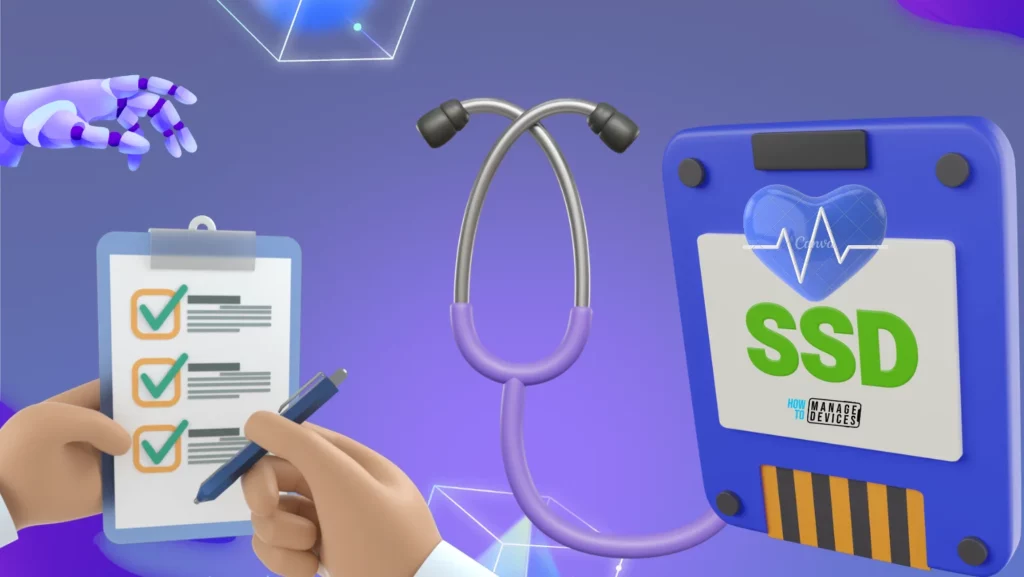
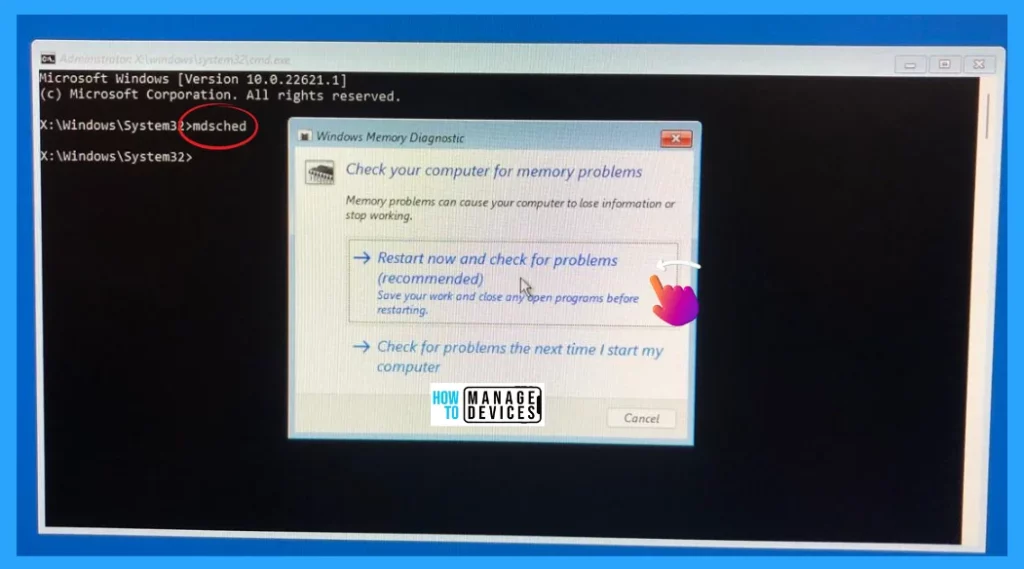
To run the Windows memory diagnostic tool, you can use the Run dialogue box. To do so, press the Win key + R to open the Run dialogue box, type mdsched.exe in the text field, and press the OK button or hit Enter.
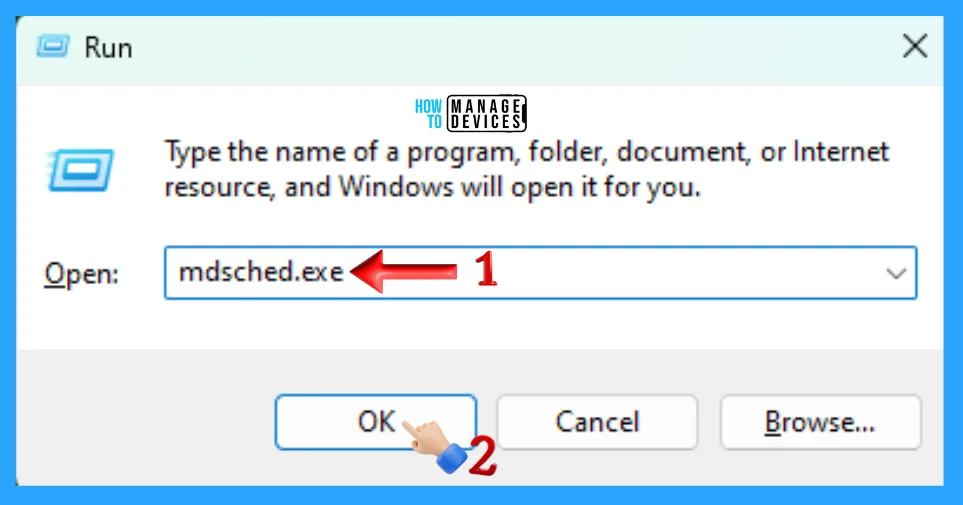
Windows Memory Diagnostic tool is an important built-in tool available on Windows 11 and its previous versions. You can use it to manage the memory testing. Type Windows Memory Diagnostic in the Search Box presented on the Taskbar, select, and click on the appropriate options shown in the list, illustrated in the image below.
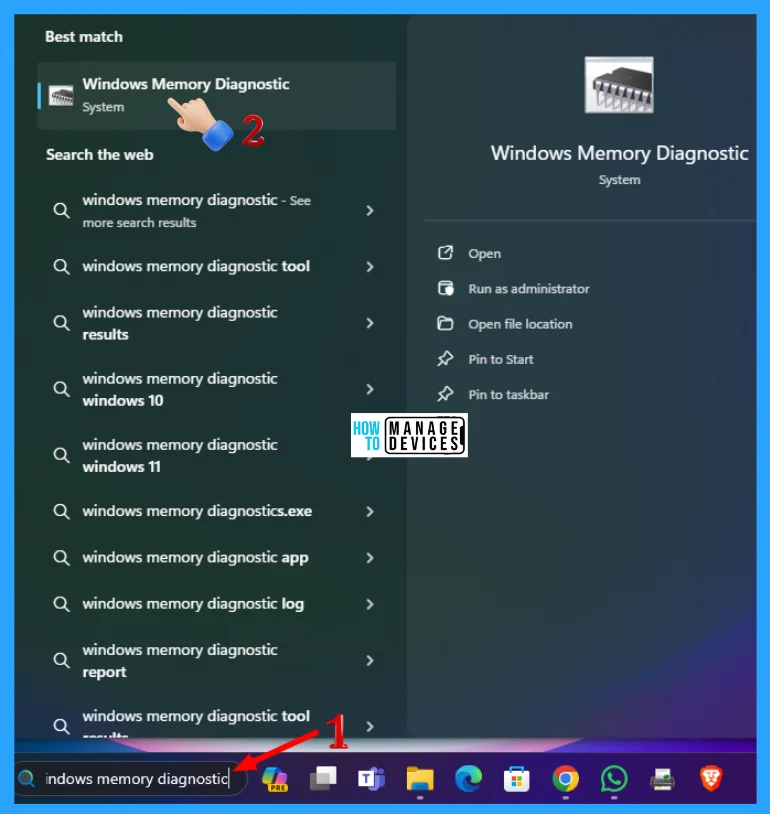
Now the WMD Tool window opens, which checks your computer for memory problems. Memory problems can cause your computer to lose information or stop working. It shows two options that are listed below.
- Restart now and check for problems (recommended)
- Check for problems the next time I start my computer
From the options, choose “Restart now and check for problems (recommended)“. But be sure to save all your work and close any open programs before restarting. If you do not want to do the operation right now then you can select “Check for problems the next time I start my computer” when you open your system next time it runs the WMD at the startup.
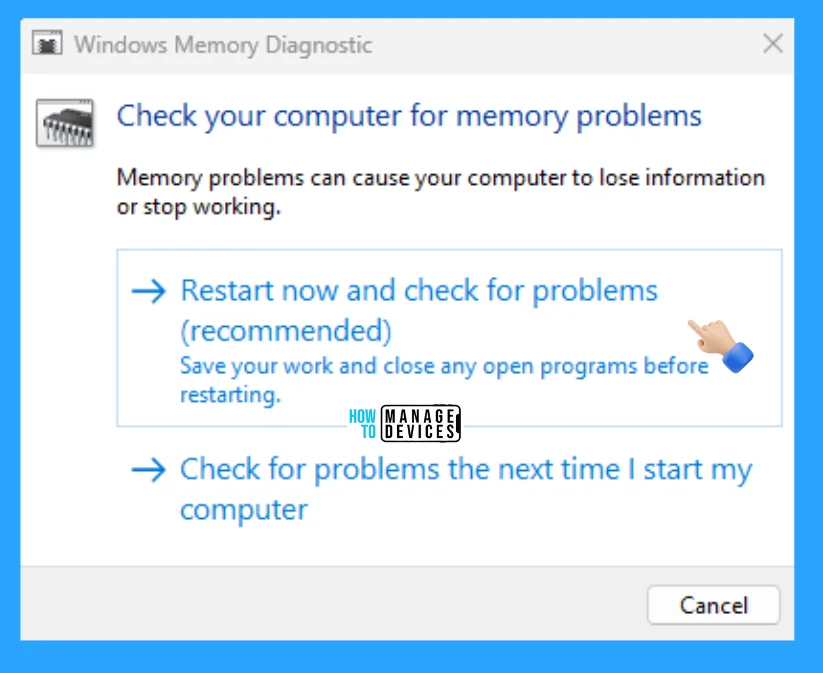
On restarting your PC, the WMD tool RAM test will run automatically, and you will see a blue screen with testing progress. Windows is checking for memory problems, and this might take several minutes whenever no problems have been detected yet.
Although the test may appear inactive at times, it is still running. Please wait until testing is completed. The window will restart the computer automatically. Test results will be displayed again after you log on. If you want to view more test options, then you can simply press the F1 key to open the options list and ESC to exit the current screen.
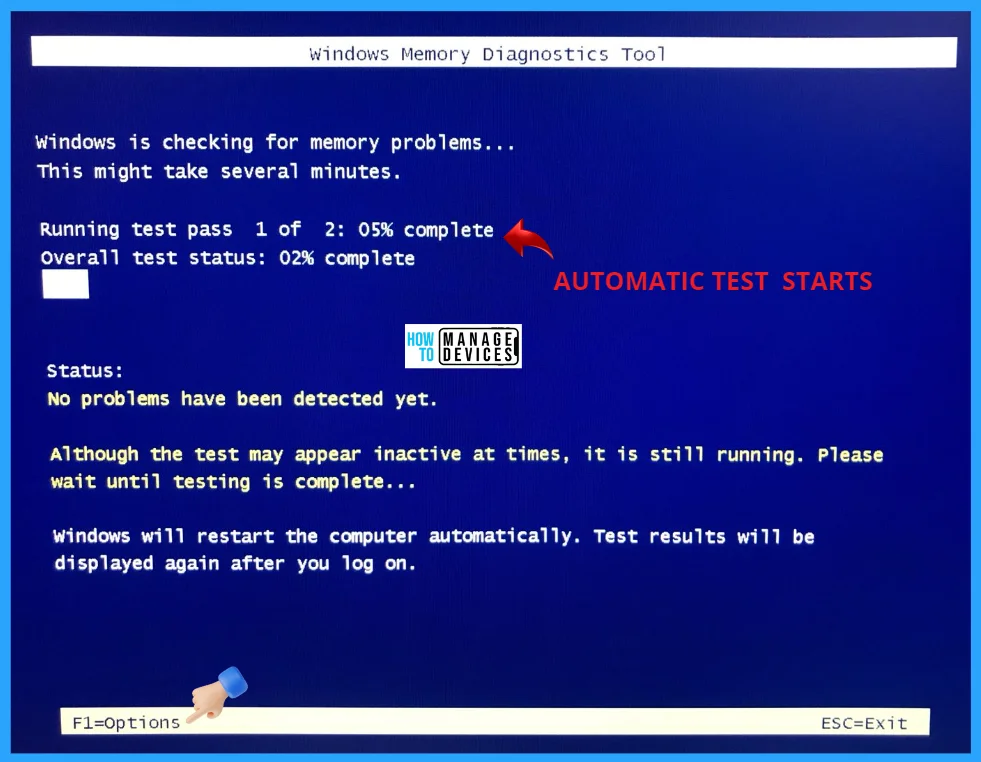
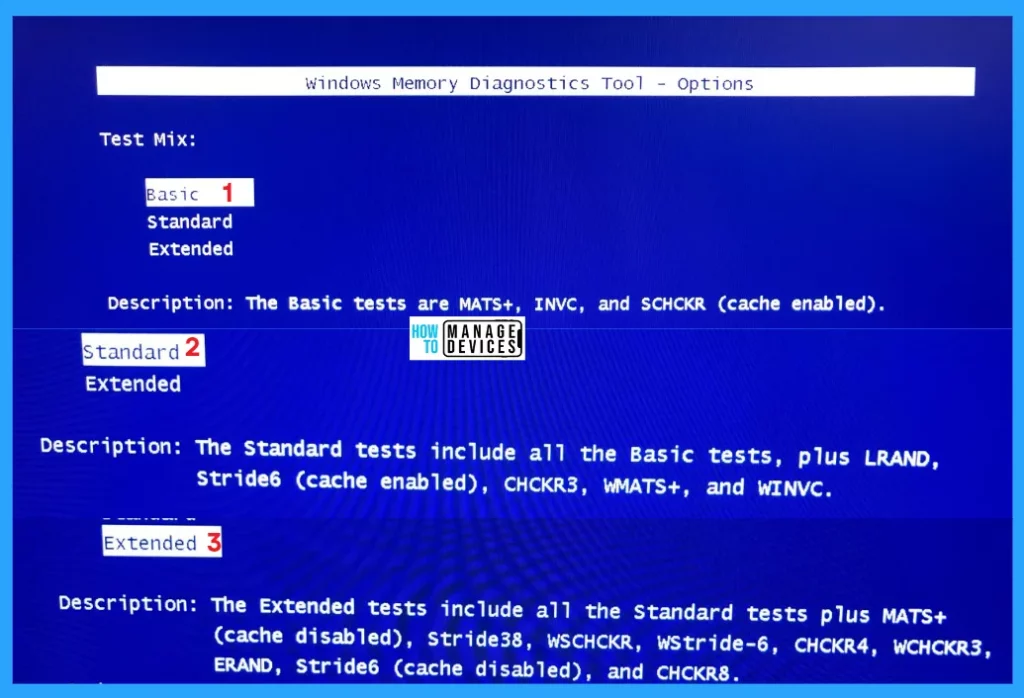
When you click the F1 button, then, more test options appear. Use arrow keys from your keyboard to highlight the desired setting, and press the Tab key from the keyboard to move between options. The WMD Tool has three different modes for testing for computers.
The Basic mode is the fastest way and runs only three tests. The Standard mode runs eight tests, and the Extended mode performs seventeen tests. But by default, the standard mode is used.
| Test Mix (Mode) | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic | The Basic tests are MATS+, INVC, and SCHCKR (cache enabled). |
| Standard | The Standard tests include all the Basic tests, plus LRAND, Stride6 (cache enabled), CKCKR3, WMATS+, and WINVC. |
| Extended | The Extended tests include all the Standard tests plus MATS+ (cache disabled), Stride38, WSCHCKR, WStride-6, CHCKR4, WCHCKR3, ERAND, Stride6 (cache disabled), and CHCKR8. |
On that screen, you can also use the CPU’s built-in cache settings. To reach there, press the TAB button, and you shift from the test mix to the cache option. Use the arrow key from the keyboard to move between options.
But, if you want to test more thoroughly, then you can try turning the cache Off, which forces the WMD tool to get data directly from RAM to test more effectively.
NOTE! It is better to leave it on Default cache settings.
| Cache | Description |
|---|---|
| Default | Use the default cache settings of each test. |
| On | Turn the cache on for all tests. |
| Off | Use the default cache settings of each test. |
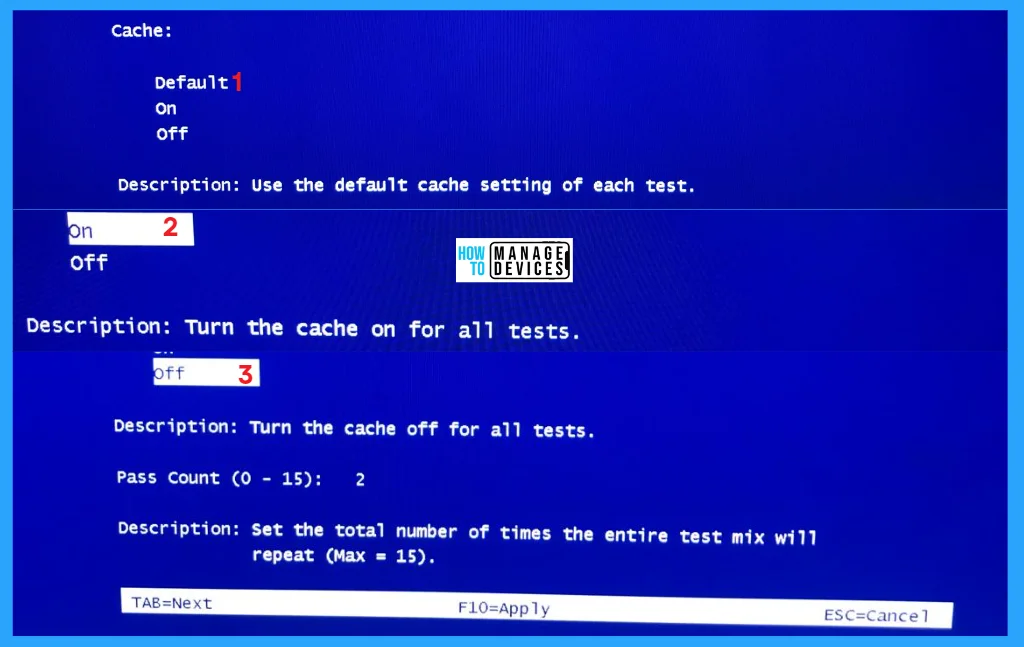
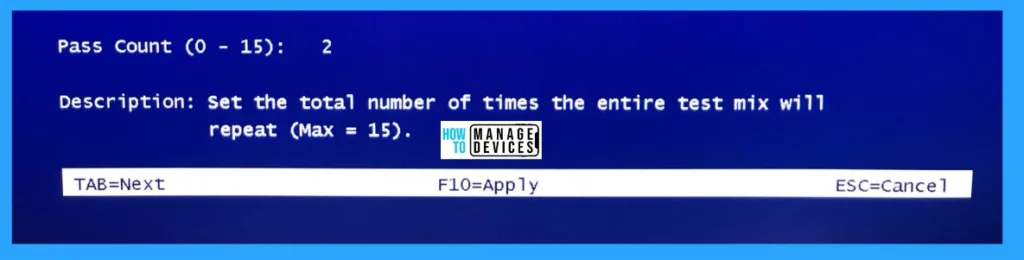
You can see the Pass Count option in the same window, it allows you to specify how many times the passes test to perform. Two is the default number of test count, but you can increase it as per your interest. The total number of times the entire test mix will repeat the number of times you set, i.e. Maximum Fifteen (15) times, not more than that.
Now you can press the F10 button to apply all the changes that you made, but it is recommended to many users that the default options are more sufficient to find memory-related issues. The more thorough tests you want to run, the more time it takes to complete. When the test is completed, the tool displays the results of the memory test.
NOTE! If memory problems are so severe that Standard mode is not eligible to find it, then you can choose Extended to do so, and it will take more time.
How to Run Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool in Safe Mode
The second method is to troubleshoot your Windows device, to do so open the Start Menu and click the power icon, then hold the Shift Key and click the Restart button.
The Startup setting is initiated, and the Choose an Option window opens, select the Troubleshoot from the options. When the Troubleshoot window opens, select Advanced Options. And from the Advanced Options window choose the option Command Prompt.
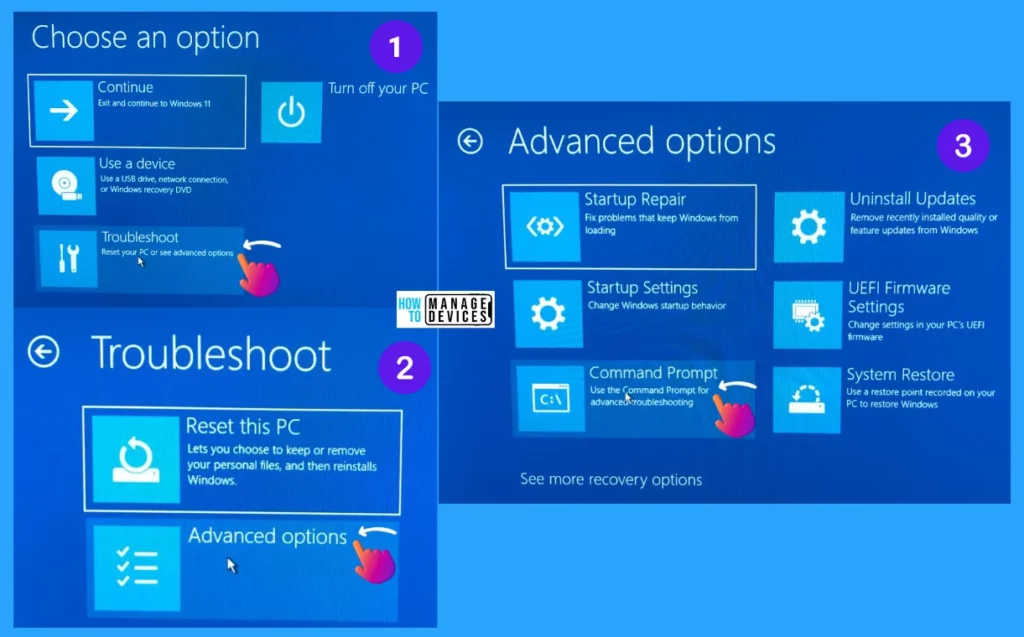
Now the Command prompt is open, type mdsched to launch the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool. Then, select the “Restart now and check for problems (recommended)” as shown earlier and follow the same process further.
Now your computer will start scanning your memory, and let you know if it finds any issues. When the test is completed, your device restarts and returns to the Windows desktop.
Check Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool Results
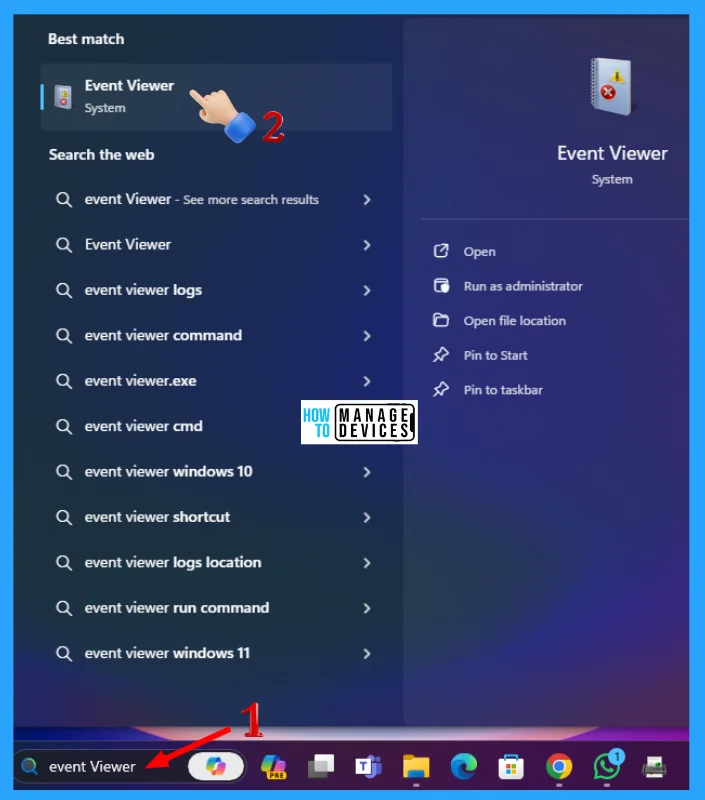
Event Viewer is an important built-in tool available on Windows 11 to get any test results stored in it. To open it, type Event Viewer in the Search Box presented on the Taskbar, select and click on the appropriate options shown in the list, illustrated in the image below.
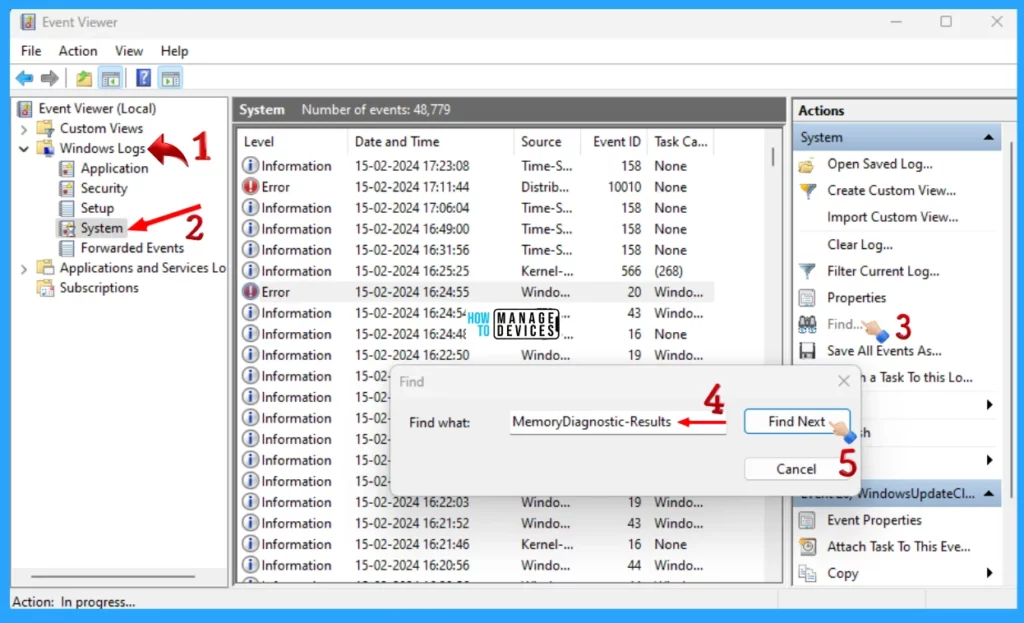
When the Event Viewer window launches, expand the Windows Logs option present in the left panel. Then select the System sub-option from it. Now click the Find button on the Right panel, or you can use the hotkey from the keyboard as Ctrl + F.
Type MemoryDiagnostic-Results in the box shown near the Find What, then click on the Find Next button to search for the result. It will show if any results are stored there. If any of the results appear, then double-click on the result, and it shows the General & Detailed information of the results.
If, any errors in the result, then you can run an Extended memory test and recheck the results. If you still see errors after that, then you need to change the RAM or any memory component.
Prevent Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool Finds Error
If you get any issue with your RAM, you get an error message. Common errors are “Hardware Problems were found” or “Physical Address Limit Exceeded”. This type of error indicates that there might be a fault in one or more of the memory modules installed on your device. There are some preventions are listed below.
- Remove & Reinstall Memory: If the memory sticks are not seated in their slots properly (Sometimes), turn off your device & unplug it. Carefully remove all the RAM and replace it properly.
- Swap Slots: If your device has multiple slots then Swap Slots for the RAM that prevents error.
- Replace Corrupt RAM: If you find any particular RAM that is not functioning well, then replace the current RAM.
- Check Each Memory Stick: If you have multiple RAMs then check one by one carefully to know which one is causing the error.
- Do not Overlock: Do not try to Overlock (Run the processer or any electronic logic device, at a speed higher than is recommended by the manufacturer) your GPU, CPU, or RAM to their maximum.
I hope the guide Best Usage of Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool in Windows 11 is helpful. Please follow us on the HTMD Community and visit our website HTMD Forum, if you like our content. Suggest improvements, if any, and we would love to know which topic you want us to explore next.
We are on WhatsApp. To get the latest step-by-step guides and news updates, Join our Channel. Click here –HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
Alok is a Master of Computer Applications (MCA) graduate. He loves writing on Windows 11 and related technologies. He likes to share his knowledge, quick tips, and tricks with Windows 11 or Windows 10 with the community.
