Let’s learn 23 System Settings Run Commands for Windows. These commands easily and quickly access the accessibility settings. The Windows Run command box is a built-in feature available in the Windows operating system since the release of Windows 95.
The Run command box is the quickest way to access various applications, system utilities, folders, settings, etc. Most of the run commands are discussed in our previous posts. Putting commands in the run box allows you to open or access any applications and tools quickly.
Execute the Run command quickly to open the required settings in two steps instead of the regular procedure to open or access any settings. Those commands help you be more productive in your daily use if you remember them.
You can use the run command dialog box to reach various system settings of Windows discussed below in this post. And our previous post, you can use personalization settings and configure Bluetooth settings and Network & internet settings.

- Best Network and Internet Run Commands for Windows
- Run Commands for Windows Update and Other Settings
System Settings Run Commands
Now let’s look at how we can quickly use the System Settings commands using the Run dialog box. The following Run commands are used to reach out to various Windows settings. The commands are shown in the table below for your reference, and the execution method is represented in this post.
| Sl. No. | Commands | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | control.exe /name Microsoft.Troubleshooting or ms-settings:troubleshoot | This command is used to open Windows Troubleshoot Settings |
| 2. | ms-settings:display | This command helps to adjust display settings |
| 3. | ms-settings: | This command is used to open the setting apps home page |
| 4. | ms-settings:about | This command is used to open the about settings page (Device and Windows specification, Related settings) |
| 5. | ms-settings:activation | This command is used to open Windows Activation settings |
| 6. | ms-settings:apps-volume | This command is used to open Sound Mixer settings |
| 7. | ms-settings:powersleep or ms-settings:batterysaver-settings | This command helps to Change Power & Battery settings |
| 8. | ms-settings:clipboard | This command is used to open Clipboard settings |
| 9. | ms-settings:crossdevice | This command is used to open Nearby Sharing options |
| 10. | ms-settings:display-advancedgraphics | This command helps to Adjust Graphics preference settings |
| 11. | ms-settings:multitasking | This command helps to Configure Multitasking |
| 12. | ms-settings:nightlight | This command helps to Change the Night light settings |
| 13. | ms-settings:notifications | This command helps to Configure Notifications settings |
| 14. | ms-settings:project | This command is used to open the About settings page (Device and Windows specification, Related settings) |
| 15. | ms-settings:quiethours | This command helps to Configure Focus assist settings |
| 16. | ms-settings:recovery | This command is used to open Recovery options – Reset/Go Back/Advanced startup |
| 17. | ms-settings:remotedesktop | This command is used to open Remote Desktop settings |
| 18. | ms-settings:savelocations | This command helps to Change where new content is saved |
| 19. | ms-settings:sound | This command is used to open Sound settings |
| 20. | ms-settings:sound-devices | This command helps to Manage Sound Devices (Input / Output Devices) |
| 21. | ms-settings:storagepolicies | This command helps to Configure Storage Sense |
| 22. | ms-settings:storagesense | This command is used to open Storage Settings |
| 23. | sndvol | This command is used to Control Volume Mixer |
To execute the above commands in the run dialog box, you need to open the Run dialog box quickly by pressing the Windows key + R. For more details, click here. The commands are discussed in detail below for better understanding.
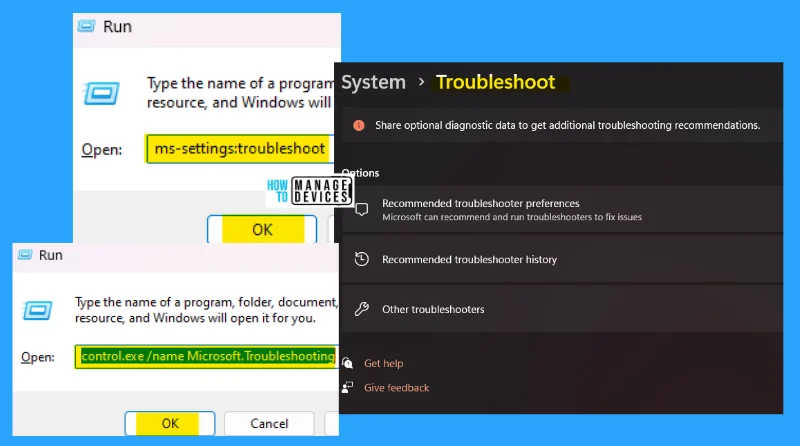
1. ms-settings:troubleshoot
The ms-settings:troubleshoot run command is used to share optional diagnostic data to get additional troubleshooting recommendations. Microsoft can recommend and run troubleshooters to fix issues.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:troubleshoot and press OK.
NOTE! You can also use control.exe /name Microsoft.Troubleshooting instead of ms-settings:troubleshoot to access the troubleshooting settings.
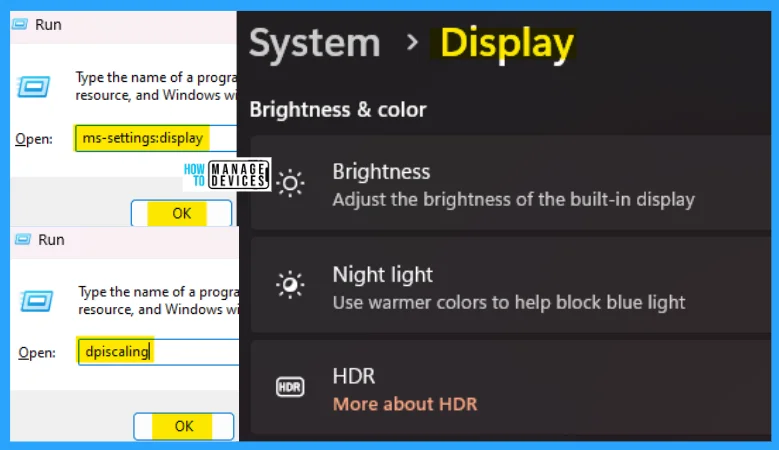
2. ms-settings:display
The ms-settings:display run command is used to enter your device’s display settings, where you can adjust the brightness of the built-in display. You can activate the warmer light to make a smooth impact on your eyesight.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:display and click OK.
NOTE! You can also use dpiscaling instead of ms-settings:display to access the display settings.
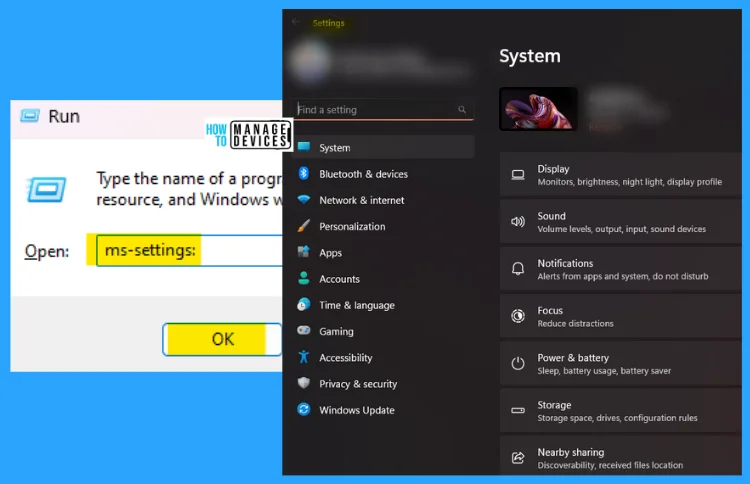
3. ms-settings:
The ms-settings: command is used to enter the settings menu, where all the settings are available to modify system settings. From here, you can access your computer to make any required changes.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings: and click OK.
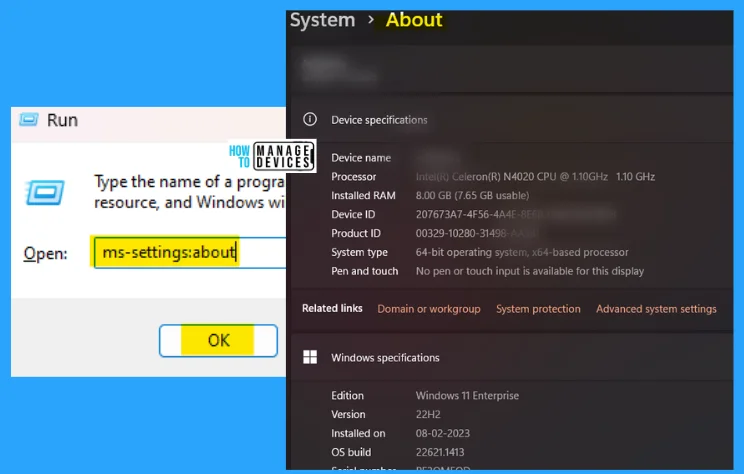
4. ms-settings:about
The ms-settings:about the run command is used to see the details about your device. In the About command, you can see the device all over specifications like device specifications, Windows specifications, etc.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:about and press OK.
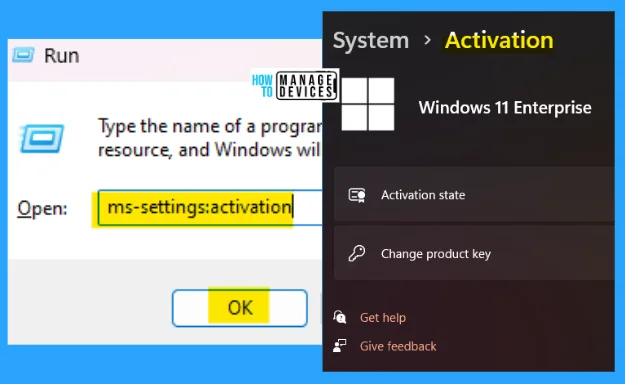
5. ms-settings:activation
The ms-settings:activation run command is used to access the Activation Windows. Here you can Activate the state and change the product key for Windows if required.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:activation and click OK.
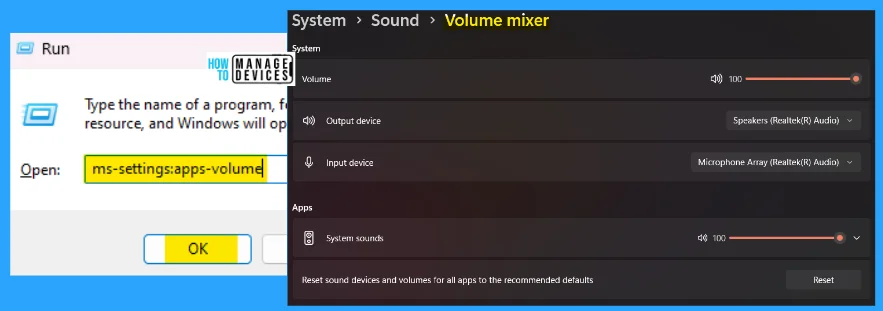
6. ms-settings:apps-volume
The ms-settings:apps-volume command is used to access the volume mixer under the sound option. Here you can adjust the Output device, Input device, manage system sounds, etc. Another option is resetting all apps’ sound devices and volumes to the recommended defaults.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:apps-volume and click OK.
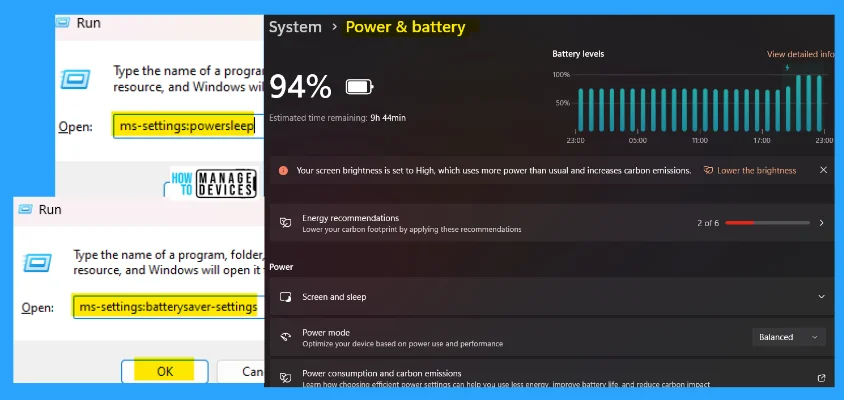
7. ms-settings:powersleep
The ms-settings:powersleep command redirects to Power & battery options. Here you can easily adjust the brightness as well as perfect colors.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:powersleep and click OK.
NOTE! You can also use ms-settings:batterysaver-settings instead of ms-settings:powersleep to access the display settings.
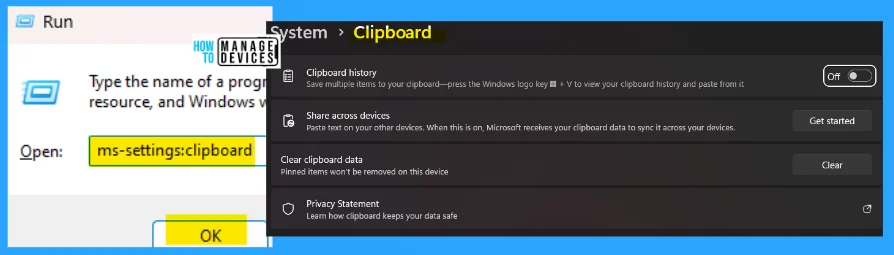
8. ms-settings:clipboard
The ms-settings:clipboard command is used to access the clipboard history, where you can save multiple items to your clipboard and find out the history from its history. This contains many options like clipboard history, sharing across devices, clear clipboard data, privacy statements, etc.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:clipboard and click OK.
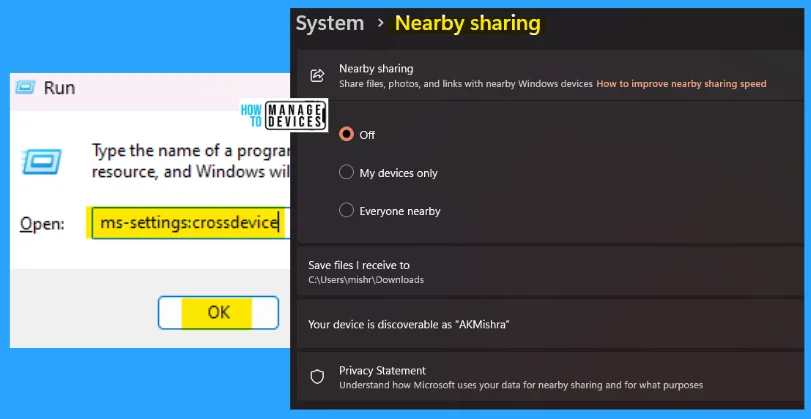
9. ms-settings:crossdevice
The ms-settings:crossdevice run command is used to find the nearby sharing device; you can share files, photos, and links with nearby Windows devices.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:crossdevice and press OK.
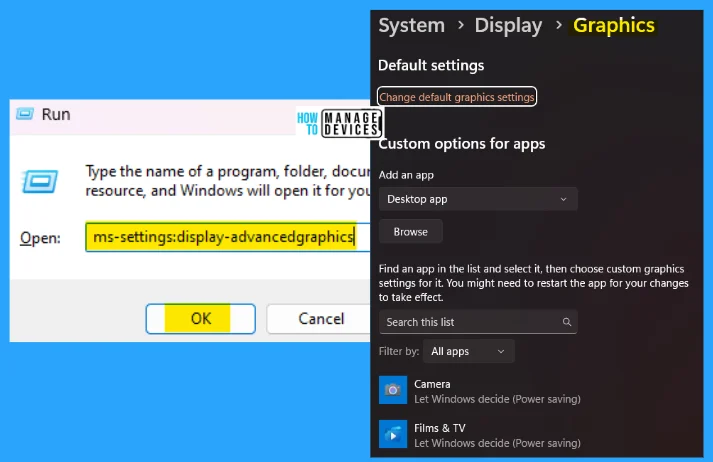
10. ms-settings:display-advancedgraphics
The ms-settings:display-advancedgraphics command is used to configure the graphics settings of the system. Here you can find an app (shown in the image) in the list and select it, then choose custom graphics settings. You might need to restart the app for your changes to take effect.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:display-advancedgraphics and press OK.
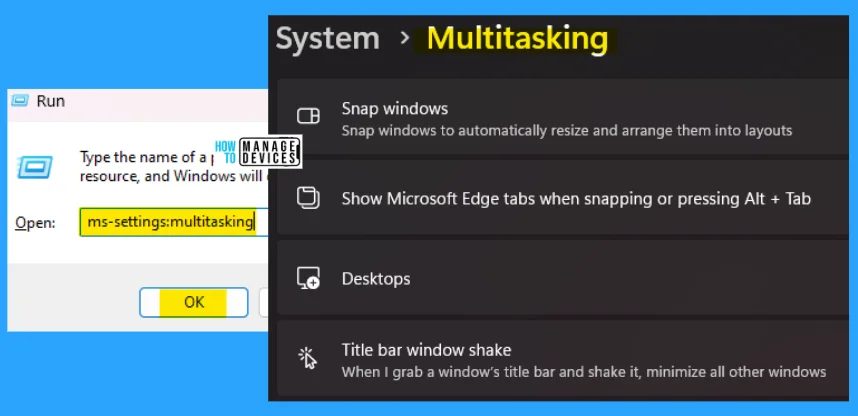
11. ms-settings:multitasking
The ms-settings:multitasking run command is used to automatically snap windows to resize and arrange them into layouts. Multitask is performed here to save time for the user.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:multitasking and press OK.
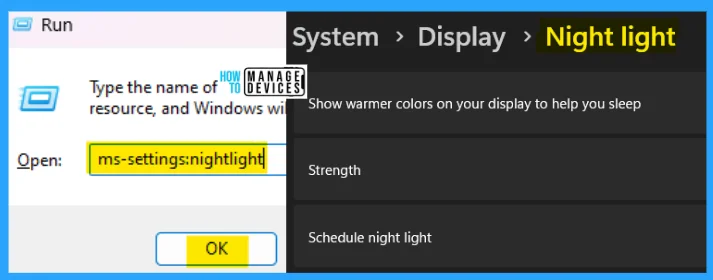
12. ms-settings:nightlight
The ms-settings:nightlight run command smooths the user’s night experience with the PC. You can use warmer colors on your display to help you sleep.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:nightlight and press OK.
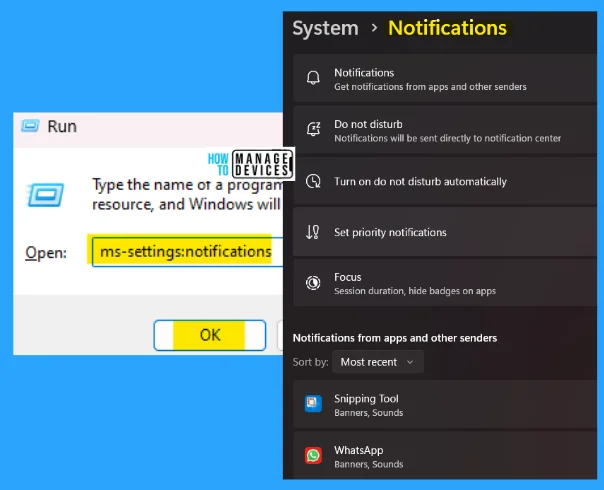
13. ms-settings:notifications
The ms-settings:notifications run command is used to get notifications from apps and other senders. Activating the do not disturb sends notifications directly to the notification center.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:nontifications and press OK.
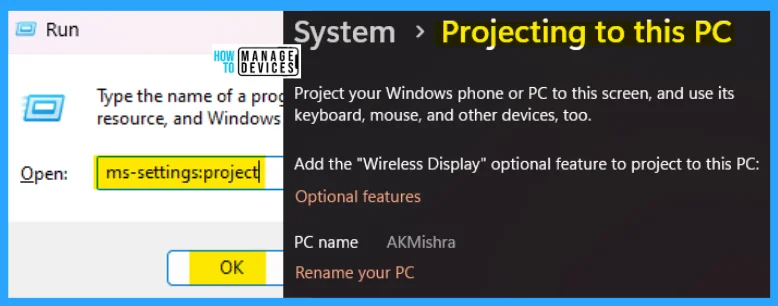
14. ms-settings:project
The ms-settings:project run command is used to project your Windows phone or PC to this screen and use its keyboard, mouse, and other devices. You can add any optional wireless display features to protect them to this PC.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:project and press OK.
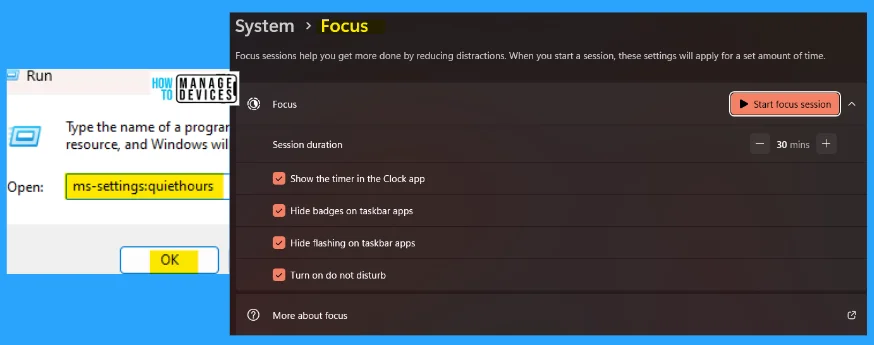
15. ms-settings:quiethours
The ms-settings:quiethours run commands are used to enter the focus option under system settings. Focus sessions help you get more done by reducing distractions. When you start a session, these settings will apply for a set amount of time.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:quiethours and press OK.
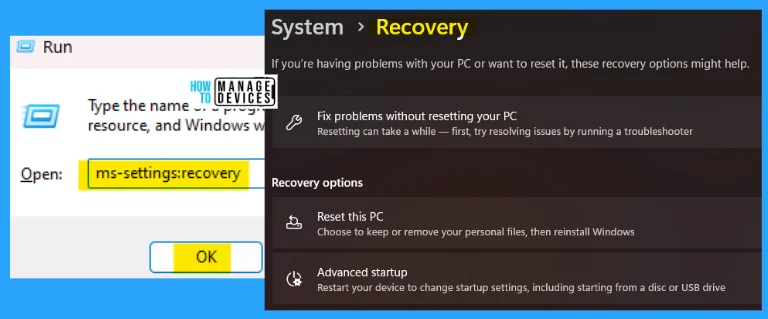
16. ms-settings:recovery
The ms-settings:recovery run commands are used to recover your PC if required. If you have problems with your PC or want to reset it, the recovery option might help.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:recovery and press OK.
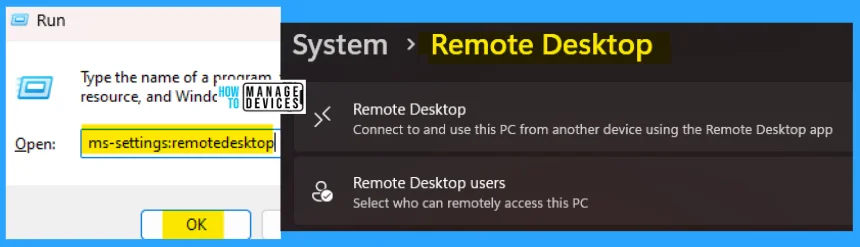
17. ms-settings:remotedesktop
The ms-settings:remotedesktop run command is used to connect to and use this PC from another device using the Remote desktop app. Using this command, you can limit who can access this PC with your permission.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:remotedesktop and press OK.
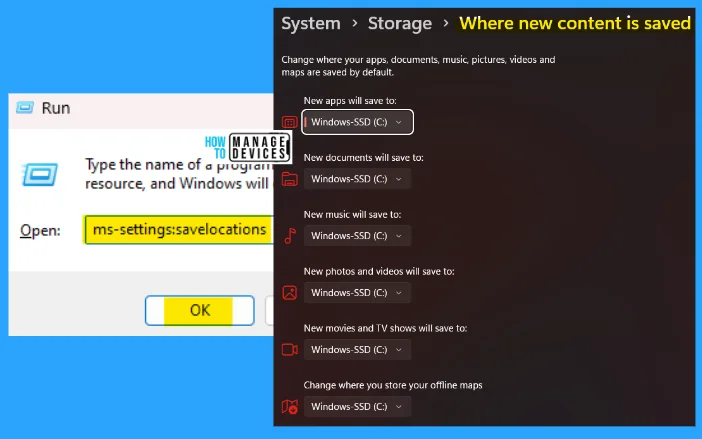
18. ms-settings:savelocations
The ms-settings:savelocations run command is used to save anything at the location selected by you. Change where your apps, documents, music, pictures, videos, and maps are protected by fault. You can set a separate location for each application in separate/same locations.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:savelocations and press OK.
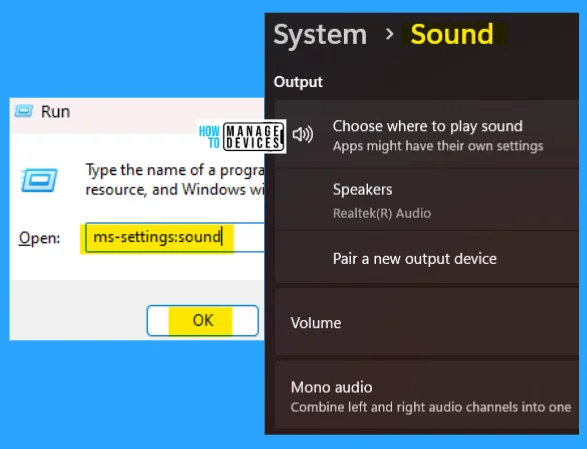
19. ms-settings:sound
The ms-settings:sound run commands are used to play sound. You can choose where to play sound, and the apps might have their settings. From here, you can change the audio-playing channels.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:sound and press OK.
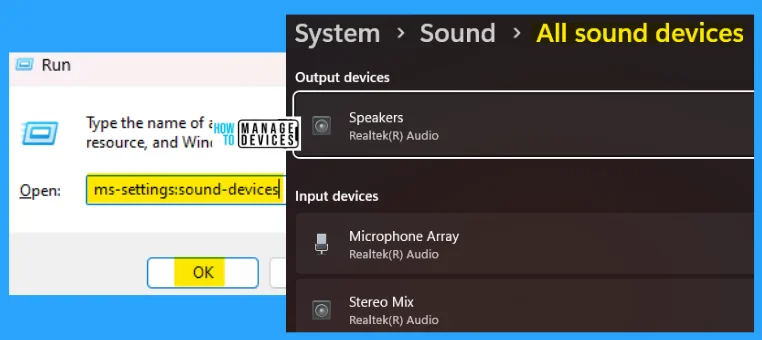
20. ms-settings:sound-devices
The ms-settings:sound-devices run command is used to locate all the sound devices connected to your PC. This shows the number of speakers working on your PC and the microphone working details.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:sound-devices and press OK.
21. ms-settings:storagepolicies
The ms-settings:storagepolicies run command is used to automate the system storage sense. This policy keeps Windows running smoothly by automatically cleaning up the temporary system and app files. Storage sense runs when disk space is low.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:storagepolicies and press OK.
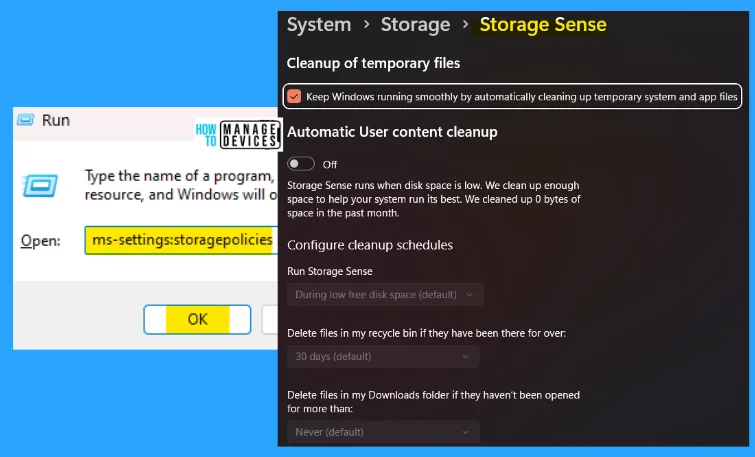
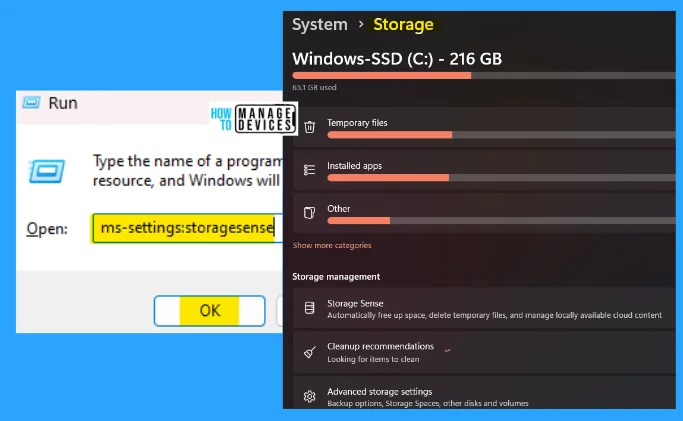
22. ms-settings:storagesense
The ms-settings:storagesense run command shows the storage and management details. Here automatically frees up space, deletes temporary files, and manages locally available cloud content.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type ms-settings:storagesense and press OK.
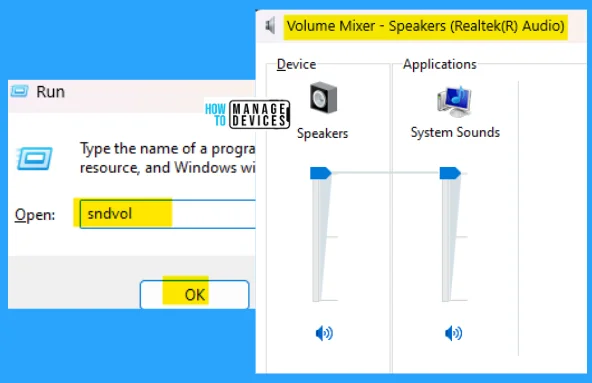
23. sndvol
The sndvol run command is used to enter into the volume mixer – speakers (Realtek(R) Audio). This shows the Device speakers and System Sounds; both are used to manage the sound system of your PC.
- Open the Run command dialog box.
- Type sndvol and press OK.
When you use too many commands in the Run dialog box, it is stored in the memory as history and looks like a mess. Click here to learn the process of deleting the history of the Run command dialog box.
The information on 23 System Settings Run Commands for Windows is helpful. Please follow us on HTMD Community and visit our website HTMD Forum if you like our content.
Author
Alok is a Master of Computer Applications (MCA) graduate. He loves writing on Windows 11 and related technologies. He likes to share his knowledge, quick tips, and tricks with Windows 11 or Windows 10 with the community.
