Learn how to configure Attack Surface Reduction ASR Rules in Intune. Attack surfaces are all the places where your organization is vulnerable to cyber threats and attacks. Defender for Endpoint includes several capabilities to help reduce your attack surfaces.
Attack surface reduction rules target behaviors that malware and malicious apps typically use to infect computers, including Executable files and scripts used in Office apps or webmail.
You can enable audit mode when testing how the attack surface reduction rules would affect your organization if enabled. Run all rules in audit mode first so you can also understand how they affect your line-of-business applications.
You can enable attack surface reduction rules by many methods, it is recommended to use Enterprise-level management such as Intune or Microsoft Endpoint Manager. Enterprise-level management will overwrite any conflicting Group Policy or PowerShell settings on startup.
- Block Vulnerable Signed Drivers Using Intune ASR Rules
- Microsoft Cloud LAPS Password Management Solution
Configure Attack Surface Reduction ASR Rules in Intune
Let’s follow the steps to configure attack surface reduction ASR rules in Intune Portal. Here are the processes for ASR rules deployment steps using Intune.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center https://endpoint.microsoft.com/.
- Select Endpoint security, Navigate to Attack Surface Reduction > Create Policy.
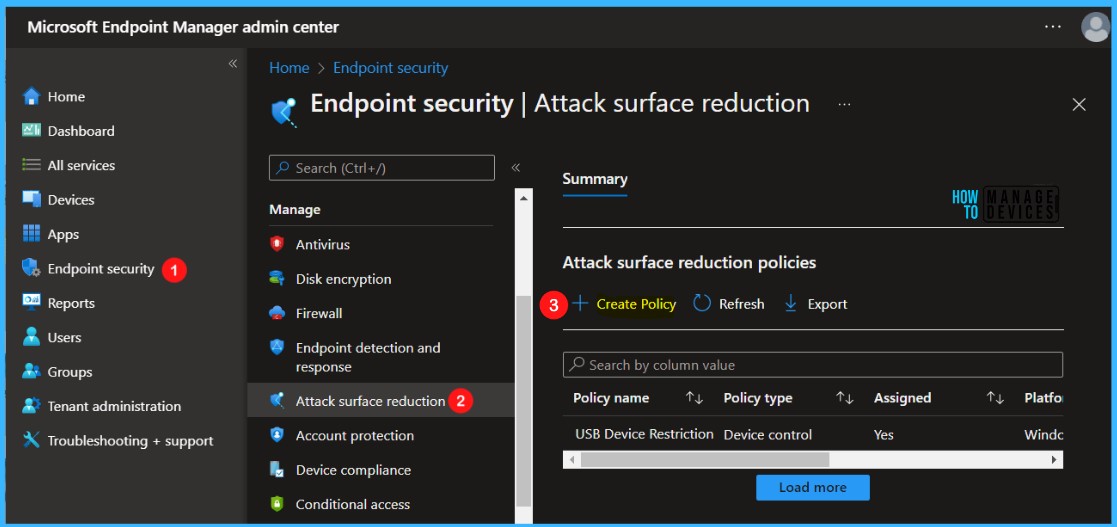
In Create Profile, Select Platform, Windows 10 and later, and Profile, Attack Surface Reduction Rules. Click on Create button.
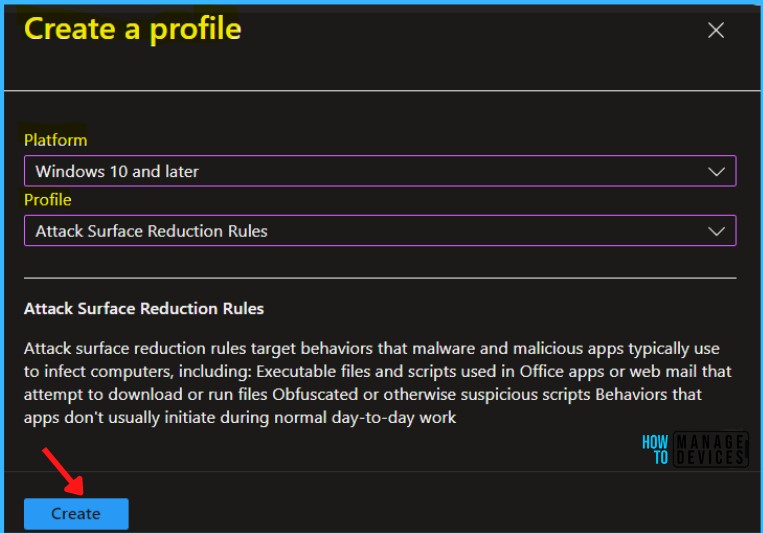
On the Basics tab, enter a descriptive name, such as Configure Attack surface reduction ASR Rules. Optionally, enter a Description for the policy, then select Next.
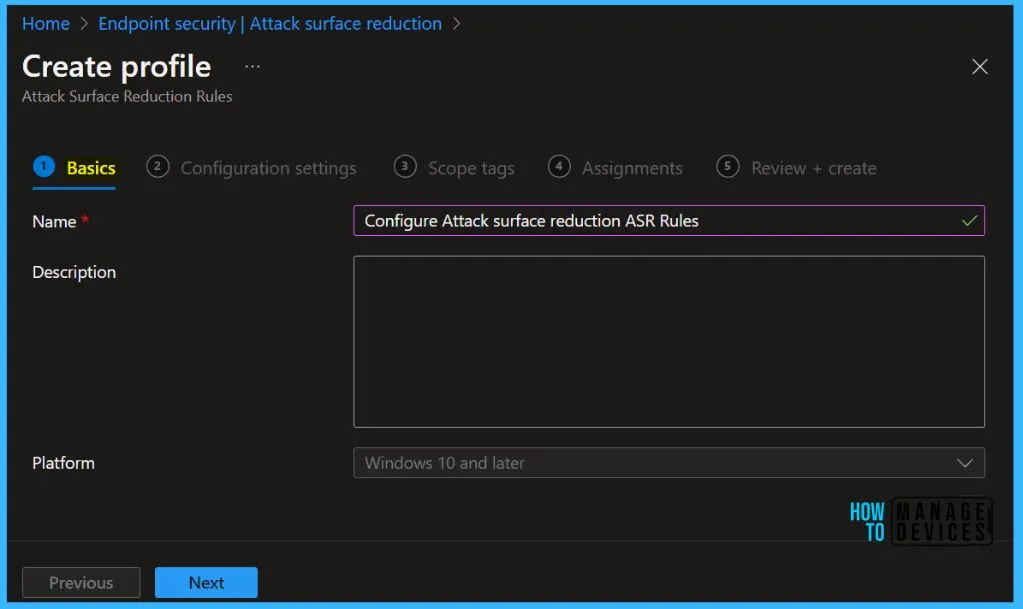
On the Configuration settings page, configure the following settings and click Next. By default, all rules are set to Not configured, Let’s check the ASR rule modes here before configuring each ASR rule containing one of four settings.
- Not configured or Disable: The state in which the ASR rule hasn’t been enabled or has been disabled. The code for this state = 0.
- Block: The state in which the ASR rule is enabled. The code for this state is 1.
- Audit: The state in which the ASR rule is evaluated for the effect it would have on the organization or environment if enabled (set to block or warn). The code for this state is 2.
- Warn The state in which the ASR rule is enabled and presents a notification to the end-user, but permits the end-user to bypass the block. The code for this state is 6.
You can configure the following attack surface reduction rules in Intune, Here is the ASR rule and detailed descriptions.
| Rule Name | Rule Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Block abuse of exploited vulnerable signed drivers | The Block abuse of exploited vulnerable signed drivers rule does not block a driver already existing on the system from being loaded |
| Block Adobe Reader from creating child processes | This rule prevents attacks by blocking Adobe Reader from creating additional processes. |
| Block all Office applications from creating child processes | This rule blocks Office apps from creating child processes. This includes Word, Excel, PowerPoint, OneNote, and Access. |
| Block credential stealing from the Windows local security authority subsystem (lsass.exe) | This rule helps prevent credential stealing, by locking down Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS). |
| Block executable content from email client and webmail | This rule blocks the following file types from launching from email opened within the Microsoft Outlook application, or Outlook.com and other popular webmail providers: Executable files (such as .exe, .dll, or .scr), Script files (such as a PowerShell .ps, VisualBasic .vbs, or JavaScript) |
| Block executable files from running unless they meet a prevalence, age, or trusted list criterion | This rule blocks the following file types from launching unless they meet prevalence or age criteria, or they’re in a trusted list or an exclusion list: Executable files (such as .exe, .dll, or .scr). |
| Block execution of potentially obfuscated scripts | This rule detects suspicious properties within an obfuscated script. |
| Block JavaScript or VBScript from launching downloaded executable content | This rule prevents scripts from launching potentially malicious downloaded content. Malware written in JavaScript or VBScript often acts as a downloader to fetch and launch other malware from the Internet. |
| Block Office applications from creating executable content | This rule prevents Office apps, including Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, from creating potentially malicious executable content, by blocking malicious code from being written to disk. |
| Block Office applications from injecting code into other processes | This rule blocks code injection attempts from Office apps into other processes. |
| Block Office communication application from creating child processes | This rule prevents Outlook from creating child processes, while till allowing legitimate Outlook functions. |
| Block persistence through WMI event subscription | This rule prevents malware from abusing WMI to attain persistence on a device. Fileless threats employ various tactics to stay hidden, to avoid being seen in the file system, and to gain periodic execution control. Some threats can abuse the WMI repository and event model to stay hidden. |
| Block process creations originating from PSExec and WMI commands | This rule blocks processes created through PsExec and WMI from running. Both PsExec and WMI can remotely execute code, so there is a risk of malware abusing this functionality for command and control purposes, or to spread infection throughout an organization’s network. |
| Block untrusted and unsigned processes that run from USB | With this rule, admins can prevent unsigned or untrusted scripts (such as VBScript, JavaScript) and executables (such as .exe, .dll, .scr files) from removable USB drives, including attached SD cards, from running. |
| Block Win32 API calls from Office macros | This rule prevents VBA macros from calling Win32 APIs. |
| Use advanced protection against ransomware | This rule provides an extra layer of protection against ransomware. It scans executable files entering the system to determine whether they’re trustworthy. If the files closely resemble ransomware, this rule blocks them from running, unless they’re in a trusted list or an exclusion list. |
Scope tags are filtering options provided in Intune to ease the admin jobs. In the scope tag section, you will get an option to configure scope tags for the rules. Click on Next.
Under Assignments, In Included groups, select Add groups and select groups to include one or more groups. Select Next to continue.
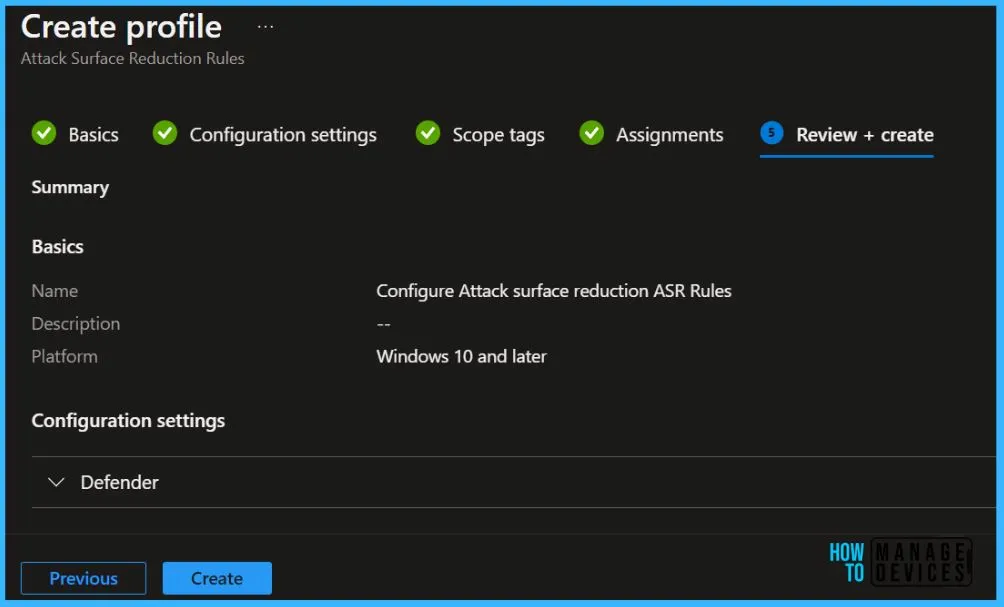
In Review + create, review your settings. When you select Create, your changes are saved, and the profile is assigned.
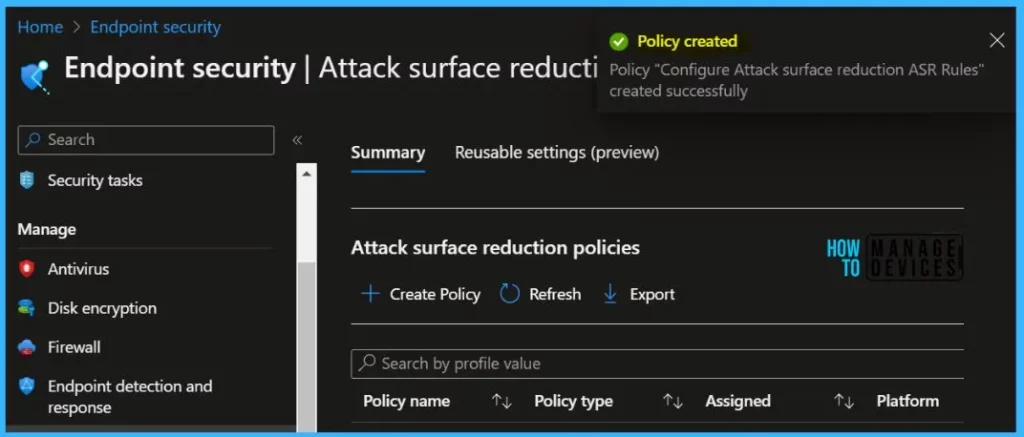
A notification will appear automatically in the top right-hand corner with a message. You can see that the Policy “Configure Attack surface reduction ASR Rules” created successfully. The policy is shown in the Endpoint security.
- 32 Privacy Settings for Windows 11 | 99 Intune Privacy Settings Policies
- Security Settings for Windows 11 Hardening options
Intune MDM Event Log
The Intune event ID 814 indicates that a string policy is applied on Windows 11 or 10 devices. You can also see the exact value of the policy being applied to those devices.
Your groups will receive your profile settings when the devices check in with the Intune service the policy applies to the device.
MDM PolicyManager: Set policy string, Policy: (AttackSurfaceReductionRules), Area: (Defender), EnrollmentID requesting merge: GUID
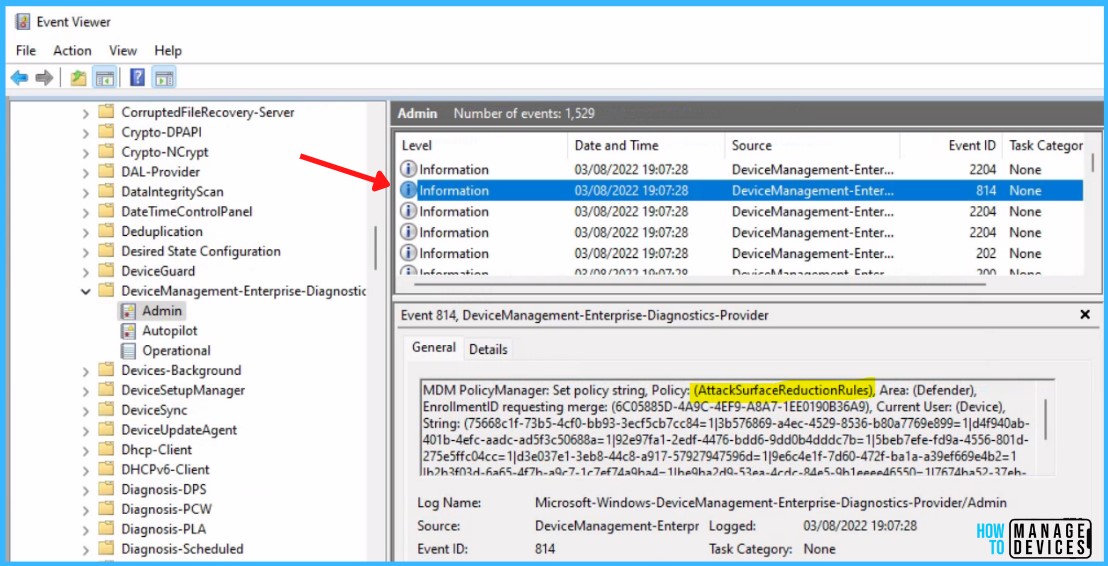
You can review the Windows event log to view events generated by attack surface reduction rules, details will be present in the Event Viewer, Windows Defender > Operational.
| Event ID | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| 5007 | Event when ASR settings are changed |
| 1121 | Event when ASR rule fires in block mode |
| 1122 | Event when ASR rule fires in audit mode |
