Let’s learn how you can configure Intune RBAC for Windows Autopilot Role. In this case, you will want to create a custom role that has the necessary permissions to manage Autopilot devices, such as the ability to reset, retire, or delete devices, as well as manage Autopilot profiles and settings.
You may need to perform the cleanup in several scenarios when you need to use devices for testing or assign to the users depending on the situation, whether you are deleting the device from Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) or need to keep it for other purposes.
Role-based access control (RBAC) helps Intune Admins to control who can perform various Intune tasks within your enterprise. There are twelve (12) built-in Intune roles (RBAC roles). You can create custom Intune roles if none of the provided roles supports your scenario.
RBAC allows you to assign specific permissions to users or groups within Intune, controlling who can access and manage specific features and settings. Without any additional configuration, it is possible to allocate built-in roles to groups. However, it is not feasible to modify the name, description, type, or permissions of a built-in role or remove it.
The addition of Duplicate Intune RBAC Roles will also be helpful for Intune admin in terms of time savior and effort to create a role from scratch.
- Assign Azure AD Roles Using Privileged Identity Management PIM
- New Built-in LAPs Client For Windows 11 And 10 | Conflict With Old Version Of LAPs
Configure Intune RBAC for Windows Autopilot Role
To create, edit, or assign roles, your account must have Global Administrator and Intune Service Administrator permissions in Azure AD.
It is important to properly configure RBAC to ensure that only authorized users have access to critical management functions, reducing the risk of accidental or malicious misuse of Intune features.
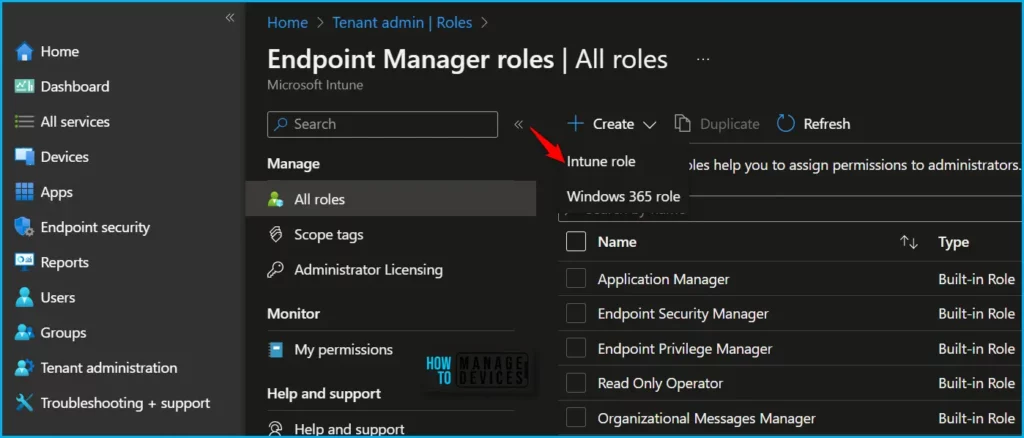
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center https://intune.microsoft.com/.
- Navigate to Tenant administration > Roles > All roles.
- Click on Create and select Intune role from the appeared options.
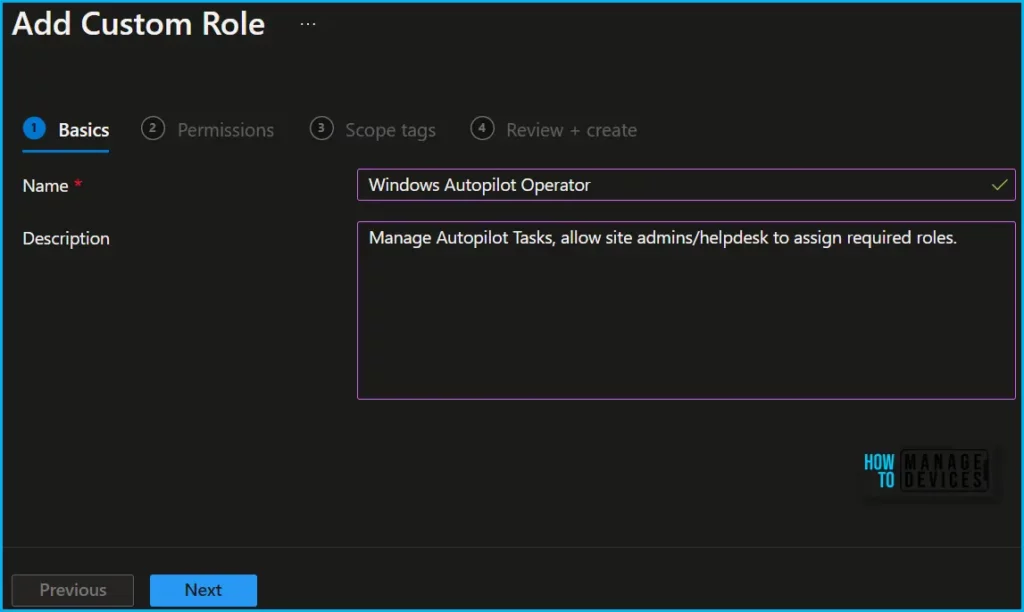
On the Basics page, enter a name and description for the custom role, then choose Next.
To modify the roles associated with a particular category, navigate to the “Permissions” page. When creating custom roles, you can enable the relevant permissions by selecting “Enrollment Programs” and toggling the switch to “Yes” to select the appropriate roles.
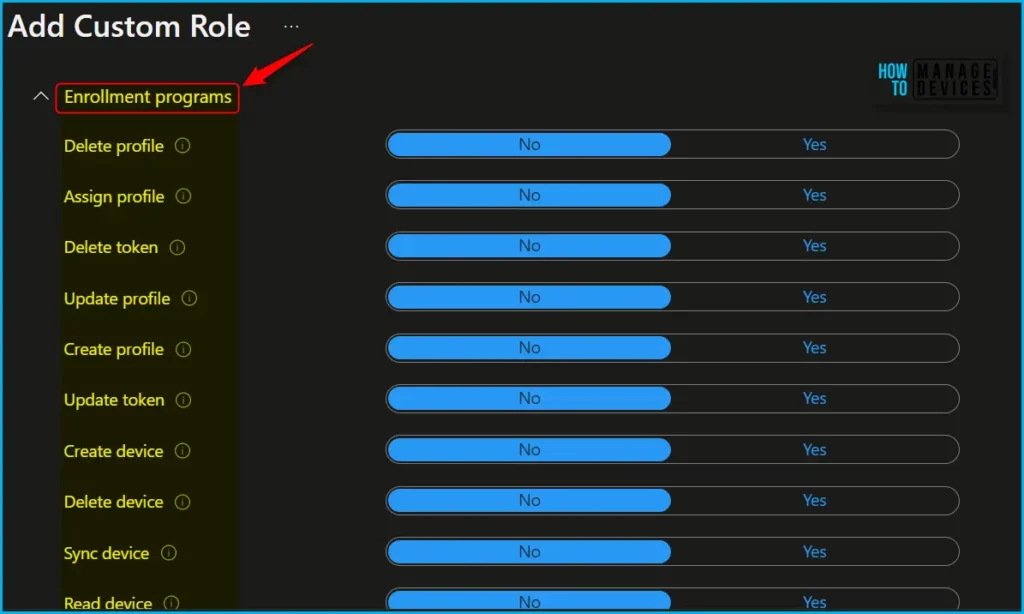
| Actions | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Delete profile | Delete profiles for the Automated Device Enrollment, Apple School Manager, Apple Configurator, or Windows Autopilot. |
| Assign profile | Assign profiles for Automated Device Enrollment, Apple School Manager, Apple Business Manager, Apple Configurator, or Windows Autopilot. |
| Update profile | Manage profiles for the Automated Device Enrollment, Apple School Manager, Apple Configurator, or Windows Autopilot. |
| Create profile | Create new profiles for the Automated Device Enrollment, Apple School Manager, Apple Configurator, or Windows Autopilot. |
| Delete device | Delete Apple devices for the Automated Device Enrollment, Apple School Manager, or Apple Configurator. |
| Sync device | Initiate the Sync command for Windows Autopilot devices. |
| Read device | View Apple devices for the Automated Device Enrollment, Apple School Manager, Apple Configurator, or Windows Autopilot devices. |
| Read profile | View profiles for the Automated Device Enrollment, Apple School Manager, Apple Configurator, or Windows Autopilot. |
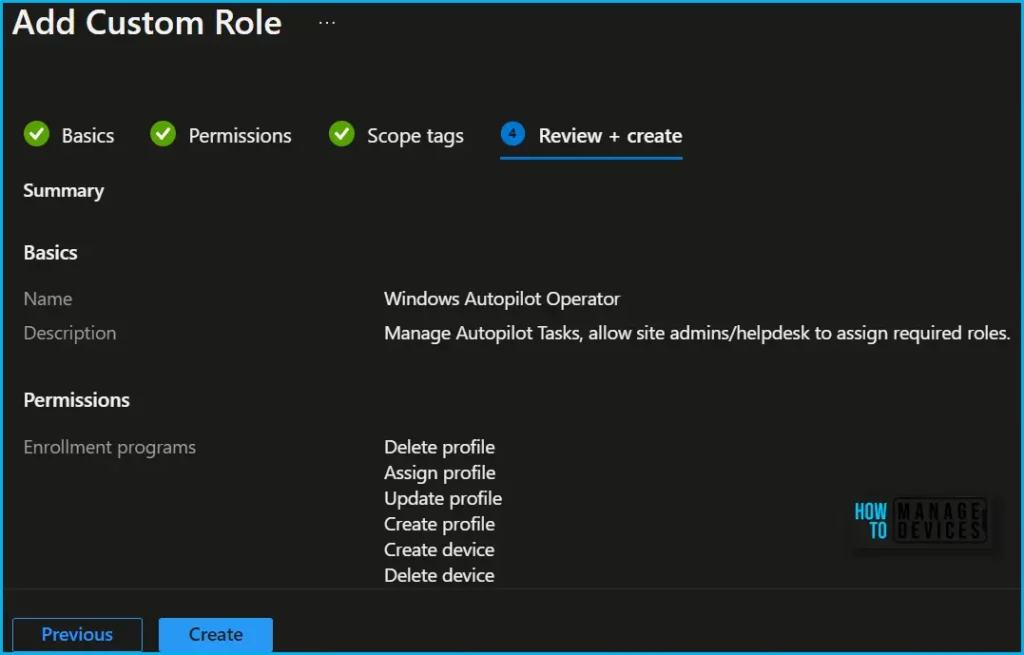
Choose the tags for this role on the Scope (Tags) page. When this role is assigned to a user, that user can access resources that also have these tags. Choose Next.
On the Review + create page, when you’re done, choose Create. The new role is displayed in the list on the Intune roles – All roles blade.
Upon successful role creation, a message with the “Windows Autopilot Operator” successfully created notification will automatically appear in the top-right corner.
Click the Refresh button at the top to quickly see the roles. You will be able to see the Custom Intune role “Windows Autopilot Operator” created in the All Roles list.
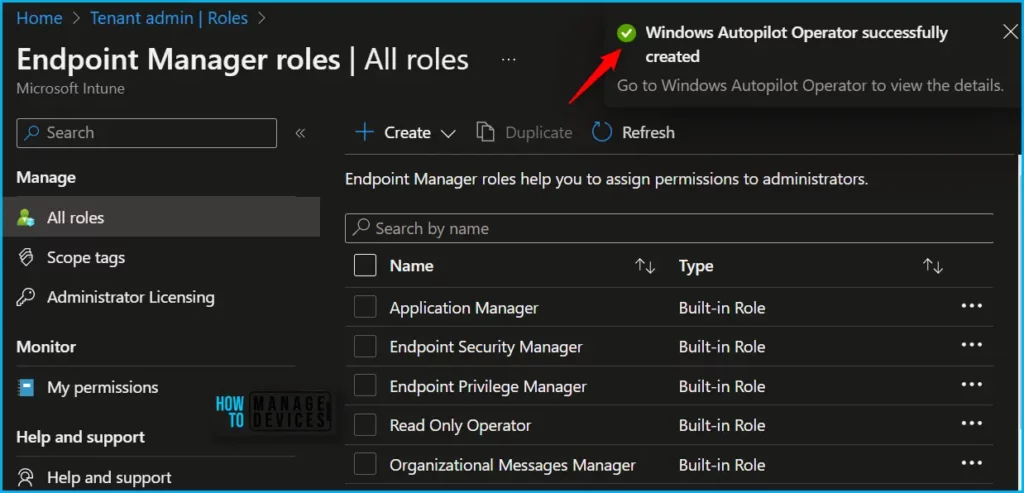
If you want, you can modify the permissions by navigating to the roles you created and clicking on Properties. Here you can also able to get the details of permissions added for the role.
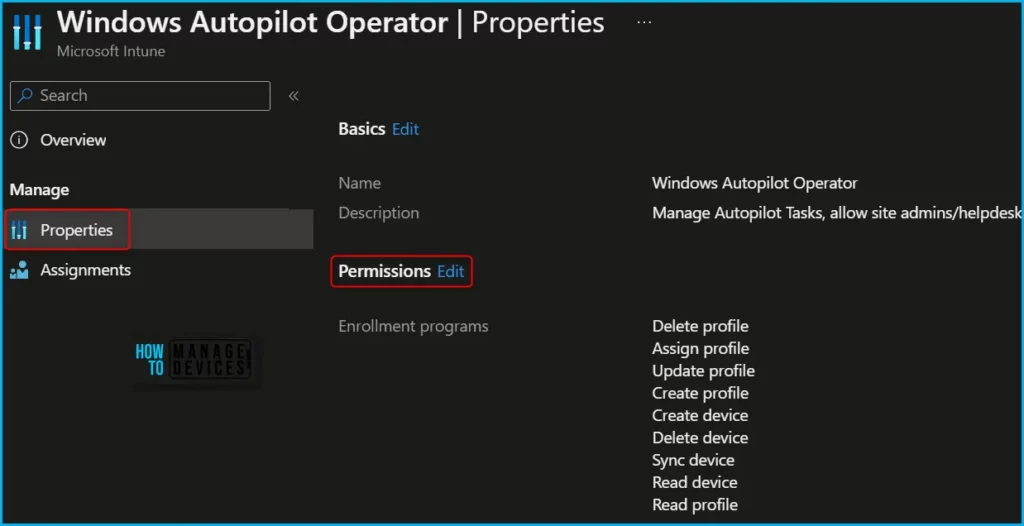
In Intune Portal, Navigate to Devices > Windows > Windows enrollment > Devices (under Windows Autopilot Deployment Program). Here you could perform multiple actions specific to the Windows Autopilot based on your assigned role.
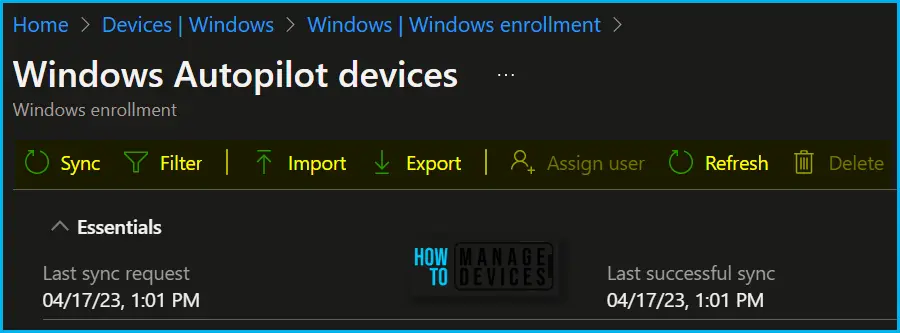
The most common tasks you would like to allow are importing autopilot devices in a few scenarios only as the process is taken care of by OEM and read, deleting autopilot devices. The device deletion process was a bit challenging, Once the device is provisioned and associated with Intune, Azure AD Object.
You need to first removed the associated Intune device then you will be able to delete the hardware hash. I have seen some weird behavior even if “Managed devices” delete permissions were assigned, ensuring the role is scoped in the correct group.
Starting in Intune Service Release 2307, Windows Autopilot is making it easier to manage devices by adding one step removal of a device in Autopilot devices in Intune. One step removal of a device means that you can now remove the Autopilot registration of a device without needing to delete the record in Intune.
Once you have the appropriate access, you can manage or delete autopilot devices. Let’s review the steps to clean up your Intune Windows Autopilot devices more quickly, Delete Windows Autopilot Device From Intune.
Video Guide – Intune RBAC Strategic Options
In this video, you will get to know more about Intune RBAC Strategic options, Role Based Access Controls, Scope Groups and Intune Objects, and Roles.
Author
About Author – Jitesh, Microsoft MVP, has over six years of working experience in the IT Industry. He writes and shares his experiences related to Microsoft device management technologies and IT Infrastructure management. His primary focus is Windows 10/11 Deployment solution with Configuration Manager, Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT), and Microsoft Intune.
