Let’s learn how you can enable Windows Autopilot Diagnostics Page. By enabling the Windows Autopilot Diagnostics Page, IT administrators can have a better visibility and control over their devices, and diagnose the issues more efficiently.
The Autopilot Diagnostics page is a tool that can be used to troubleshoot issues with the Autopilot process. This page displays information such as the device’s Autopilot profile, its enrollment status, and any errors that may have occurred during the Autopilot process.
This feature can save IT administrators valuable time and effort in resolving issues with Autopilot deployment, including devices that are not properly enrolling or issues with Autopilot profile configurations.
When you deploy Windows 11 with Autopilot, you can enable users to view detailed troubleshooting information about the Autopilot provisioning process. A new Windows Autopilot diagnostics page is available, which provides a user-friendly view to troubleshoot Windows Autopilot failures.
If you are looking for a simple way to export and import your Windows Autopilot devices, there are multiple methods available, and Intune has a built-in option. Learn how to export the windows autopilot devices in Intune.
- Delete Windows Autopilot Device From Intune
- PS Script To Add Or Modify Group Tag Of Autopilot Devices In Intune
Enable Windows Autopilot Diagnostics Page
To deploy the ESP to devices, you have to create an ESP profile in Microsoft Intune. Within the profile, you can configure the ESP settings that control. Here’s how you can enable Windows Autopilot Diagnostics Page.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center https://endpoint.microsoft.com/.
- Navigate to Devices > Windows.
- Select Windows enrollment > Enrollment Status Page.
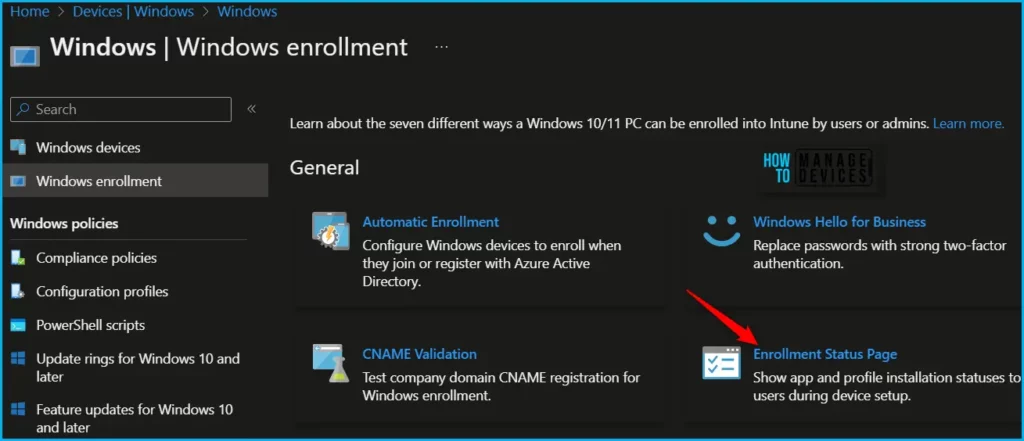
Select the existing ESP from the list, On the Properties. Click Edit to modify the settings.
To enable the diagnostics page, Make sure Show app and profile configuration progress is selected to Yes, and then select Yes next to Turn on log collection and diagnostics page for end users.
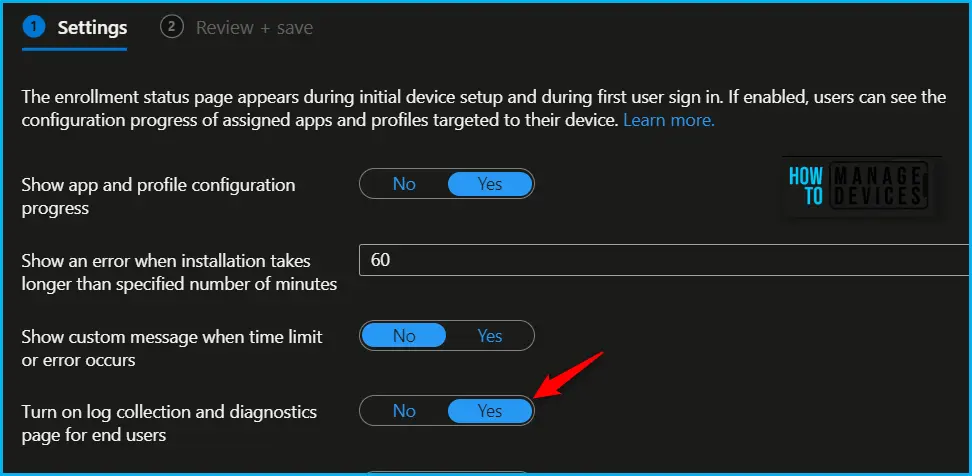
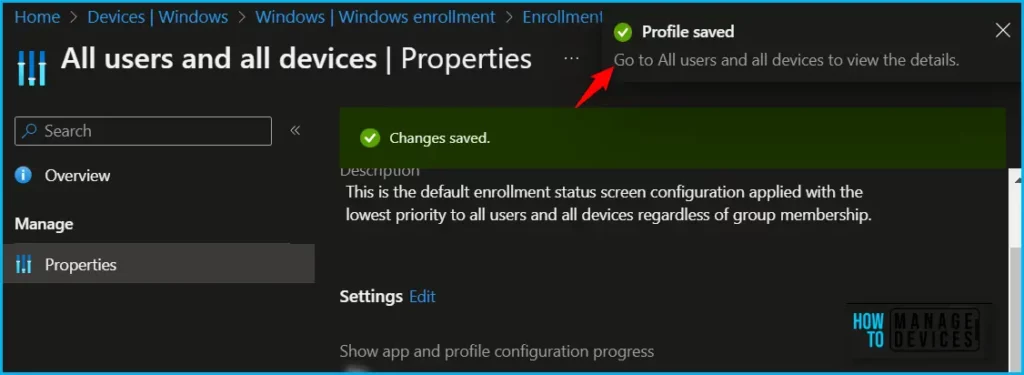
The next screen will appear with the Summary, Review the selection and click Save. A notification will appear automatically in the top right-hand corner with a message. Here you can see, Profile saved successfully.
The diagnostics page is currently supported for commercial OOBE, and Autopilot user-driven mode. It’s currently available on Windows 11. Windows 10 users can still collect and export diagnostic logs when this setting is enabled in Intune.
The following example shows details for Deployment info, which includes Network Connectivity, Autopilot Settings, and Enrollment Status. You can also Export logs for detailed troubleshooting analysis.
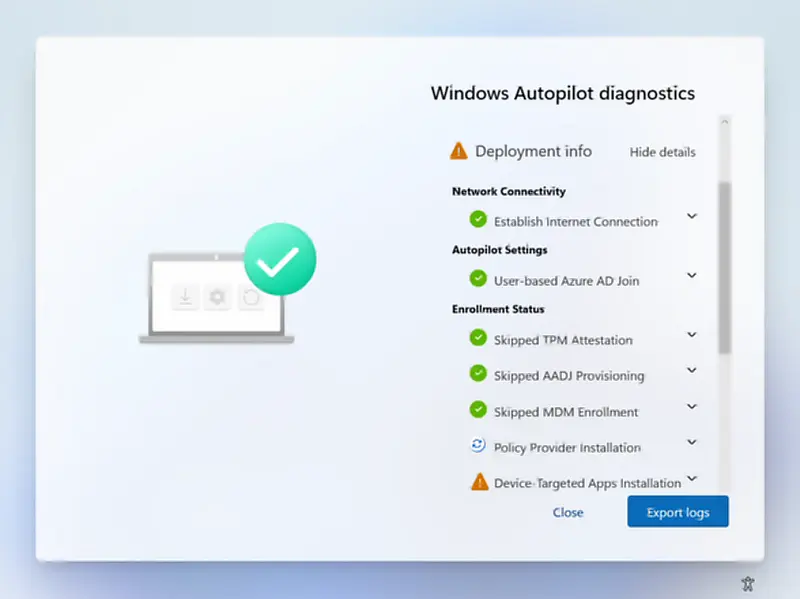
The best way to troubleshoot Windows autopilot deployment is from the Windows Enrollment status screen. Recommend reading post about Windows Enrollment Status Screen Troubleshooting.
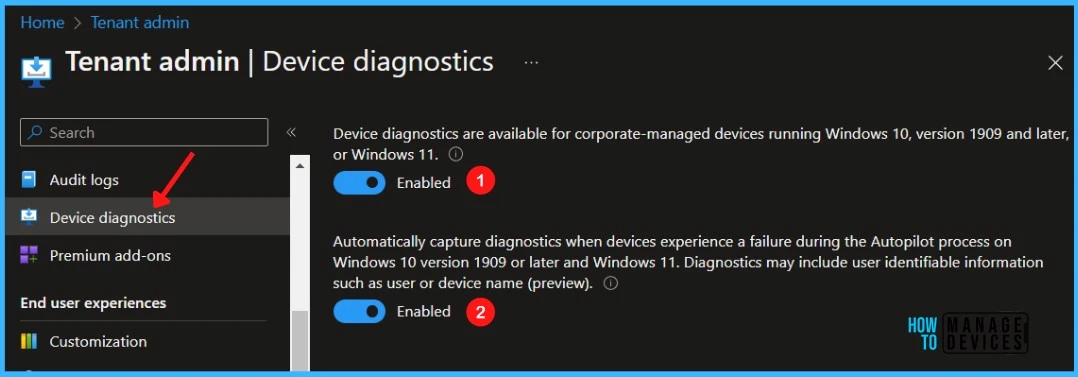
Microsoft has enabled the Windows 10 Device diagnostics to feature Collect Diagnostics from Windows devices with Remote Action. Windows Autopilot diagnostics will automatically capture diagnostics about Windows Autopilot failures that occur on the Enrollment Status Page (ESP).
In this post, you will learn more details about how to collect Intune logs using the Intune portal. This is helpful to collect Intune logs from Windows 10 and Windows 11. All the troubleshooting related to Intune and MDM can be done using these diagnostic logs.
First, you need to enable the device diagnostic settings from the Tenant Admin blade of Intune MEM Portal as shown in the screenshot below.
Automatically capture diagnostics when devices experience a failure during the Autopilot process on Windows 10 version 1909 or later and Windows 11. Diagnostics may include user identifiable information such as user or device name – Enabled
Author
About Author – Jitesh, Microsoft MVP, has over five years of working experience in the IT Industry. He writes and shares his experiences related to Microsoft device management technologies and IT Infrastructure management. His primary focus is Windows 10/11 Deployment solution with Configuration Manager, Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT), and Microsoft Intune.
