Let’s learn how to Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune. You can utilize the powerful security features provided by Microsoft Defender to implement security policies. Integrating Microsoft Defender Security Baseline policies within Intune enables you to establish a standardized set of security configurations across your device.
We covered integration between Intune and Microsoft Defender for the endpoint. And we explained the step-by-step onboarding process of Windows devices under the protective umbrella of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
We also shared a quick walkthrough guide of the Microsoft Defender portal. The Microsoft 365 Defender portal is a comprehensive command center, providing the tools and insights needed to proactively defend against threats and secure your organization’s digital assets.
Deploying Microsoft Defender for Endpoint policies using Intune refers to configuring and distributing security policies within the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint solution through the Intune management platform.
- Latest Microsoft Defender Antivirus Configuration Policy Settings in Intune
- Secure Android Devices using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint in Intune
What are the Options for Deploying Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies?
In Intune, multiple ways are there to deploy Security policies for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE). You can Deploy it using a security baseline from Intune, or else we can use individual profiles to deploy security baseline policies for MDE.
What are Intune Security Policies?
Intune Security Policies help you to secure the managed devices; you need to apply the security policies to the devices. Organizations follow various security standards – the CIS benchmark is the most common.
1. Group Policies settings are the most popular method to implement security policies.
2. More organizations are moving to Intune-based security policies to implement the security baseline.
What are the Advantages of using Security Baseline Templates?
You can implement it very quickly. Use security baselines to apply Microsoft-recommended security configuration settings to your enrolled devices quickly. This is not a CIS Benchmark recommended policy.
1. Customizable Templates
2. Only for the Windows platform
What are the Gotchas / Catches with Defender Security Baseline Templates?
The following are the gotchas and security Baseline related issues. Intune Baseline Templates are not updated regularly. Settings Catalog is the most up-to-date configuration available in Intune.
1. Not allowed to make any changes on Deprecated versions of baseline profiles.
2. Intune security baselines CIS or NIST compliant? – NO
3. User Vs. Device-based policy deployment – Yes, it’s limited, but you can create different Profiles with different configs
5. Intune Filter Rules are NOT Supported for OLD security baseline templates
Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune – Video 1
Welcome to our video series on deploying Microsoft Defender for Endpoint policies using Intune.
In this video, we will walk you through, How to deploy to Windows devices, the characteristics of Security Baseline policies for Microsoft Defender, and what you can learn from those policies that Microsoft recommends, etc.
How to Create and Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune
Log in to the Microsoft Intune admin center for Deploying Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. Enable, configure, and deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to help prevent security breaches and gain visibility into your organization’s security posture.
- Select the Endpoint security tab on the left side of Intune Admin Center.
- Select Security Baselines from Endpoint Security.
After selecting the Security Baseline, you can see the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Baseline option below. The Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Baseline is updated very long back. This is not acceptable for most of the security teams in the organization.
You can easily create a new Security Baseline policy profile. You can create and manage profiles to configure and assign your custom settings to groups within your organization. Click the Create Profile button from the below window.

Select the Name and Description on the Basic tab as the Security baseline for MS Defender. Select the platform as Windows 10 and later. Select the Baseline Version as Version 6. After entering all the details, click the Next button.
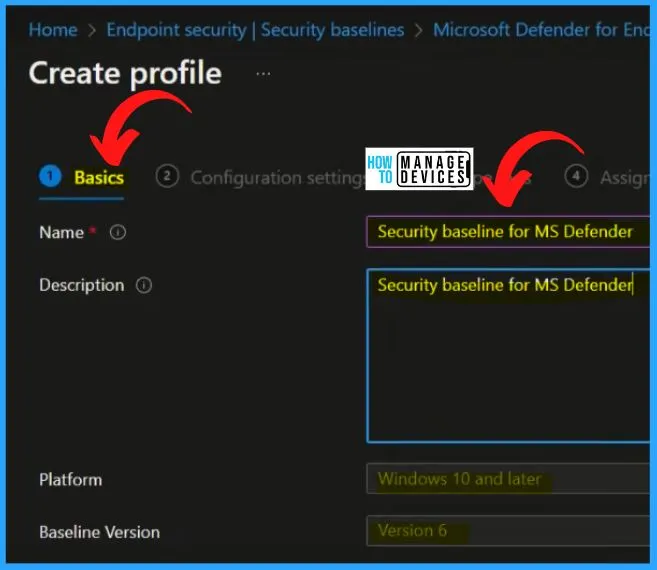
MDE Security Baseline Configuration Settings Categories
The MDE Security Baseline Configuration Settings Categories are important. Here You can see what are the policies covered in all the categories. All these are recommended policies and configurations from Microsoft. In the Configuration settings, you can see different categories as follows.
- Attack Surface Reduction Rules
- BitLocker
- Device Guard
- Device Installation
- DMA Guard
- Firewall
- Microsoft Defender
- Smart Screen
1. Attack Surface Reduction Rules
Using Intune, let’s check the Attack Surface Reduction Rules configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. The below table shows the Attack Surface Reduction Rules configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune.
| Attack Surface Reduction Rules Configuration Settings | Enabled/Disabled |
|---|---|
| Block Office communication apps from creating child processes | Warn |
| Block Adobe Reader from creating child processes | Block |
| Block Office applications from injecting code into other processes | Warn |
| Block Office applications from creating executable content | Audit mode |
| Block JavaScript or VBScript from launching downloaded executable content | Audit mode |
| Enable network protection | Block |
| Block untrusted and unsigned processes that run from USB | Block |
| Block credential stealing from the Windows local security authority subsystem (lsass.exe) | Not configured |
| Block executable content download from email and webmail clients | Audit mode |
| Block all Office applications from creating child processes | Block |
| Block execution of potentially obfuscated scripts (js/vbs/ps) | Block |
| Block Win32 API calls from Office macro | Not configured |
2. BitLocker
Using Intune, let’s check the BitLocker configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. The below table shows the BitLocker configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune.
| BitLocker Configuration Settings | Enabled/Disabled |
|---|---|
| BitLocker system drive policy | Configure/Not configured |
| Startup authentication required | Yes/Not configured |
| Compatible TPM startup PIN | Configure |
| Compatible TPM startup key | |
| Disable BitLocker on devices where TPM is incompatible | Yes/Not configured |
| Configure encryption method for Operating System drives | Configure/ |
| Standby states when sleeping while on battery | Yes |
| Standby states when sleeping while plugged in | Configure/ |
| Enable Full disk or Used Space only encryption for OS and fixed data drives | Yes/Not configured |
| BitLocker fixed drive policy | Configure/Not configured |
| Block write access to fixed data drives not protected by BitLocker | Yes/Not configured |
| Configure encryption method for fixed data-drives | Yes |
| BitLocker removable drive policy | Configure/Not configured |
| Configure encryption method for removable data-drives | Yes |
| Block write access to removable data drives not protected by BitLocker | Yes |
3. Device Guard
Using Intune, let’s check the Device Guard configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. The below table shows the Device Guard configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune.
| Device Guard Configuration Settings | Enabled/Disabled | Used to |
|---|---|---|
| Turn on Credential Guard | Enabled with UEFI lock | Turn on Credential Guard Setting this No will disable the use of Credential Guard, which is the Windows default. Setting this to Yes with UEFI lock will enable Credential Guard and not allow it to be disabled remotely, as the UEFI persisted configuration must be manually cleared. Setting this to Yes without UEFI lock will enable Credential Guard and allow it to be turned off without physical access to the machine. Credential Guard uses Windows Hypervisor to provide protections, which requires Secure Boot and DMA protections to function, which require hardware support. This setting will only successfully enable if the hardware requirements are met. |
4. Device Installation
Using Intune, let’s check the Device Installation configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. The below table shows the Device Installation configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune.
| Device Installation configuration settings | Enabled/Disabled |
|---|---|
| Block hardware device installation by setup classes | Yes |
| Remove matching hardware devices | Not configured |
5. DMA Guard
Using Intune, let’s check the DMA Guard configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. The below table shows the DMA Guard configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune.
| DMA Guard configuration settings | Enabled/Disabled | Used to |
|---|---|---|
| Enumeration of external devices incompatible with Kernel DMA Protection | Allow all | Enumeration of external devices incompatible with Kernel DMA Protection This policy is intended to provide additional security against external DMA capable devices. It allows for more control over the enumeration of external DMA capable devices incompatible with DMA Remapping/device memory isolation and sandboxing. This policy only takes effect when Kernel DMA Protection is supported and enabled by the system firmware. Kernel DMA Protection is a platform feature that cannot be controlled via policy or by end user. It has to be supported by the system at the time of manufacturing. To check if the system supports Kernel DMA Protection, please check the Kernel DMA Protection field in the Summary page of MSINFO32.exe. |
6. Firewall
Using Intune, let’s check the Firewall configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. The below table shows the Firewall configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune.
| Firewall Configuration Settings | Enable/Disabled |
|---|---|
| Stateful File Transfer Protocol (FTP) | Configure |
| Number of seconds a security association can be idle before it’s deleted | 300 |
| Preshared key encoding | Configure |
| Certificate revocation list (CRL) verification | Yes |
| Packet queuing | Yes |
| Firewall profile private | Configure |
| Firewall profile public | Not configured |
| Firewall profile domain | Configure |
7. Microsoft Defender
Using Intune, let’s check the Microsoft Defender configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. The below table shows the Microsoft Defender configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune.
| Microsoft Defender Configuration Settings | Enabled/Disabled |
|---|---|
| Turn on real-time protection | Yes |
| Additional amount of time (0-50 seconds) to extend cloud | Configure |
| protection timeout | Yes |
| Scan all downloaded files and attachments | Not Configure |
| Defender schedule scan day | Configure |
| Scheduled scan start time | Yes |
| Defender sample submission consent | Not Configure |
| Cloud-delivered protection level | Configure |
| Scan removable drives during full scan | Yes |
| Defender potentially unwanted app action | Not Configure |
| Turn on cloud-delivered protection | Configure |
8. Smart Screen
Using Intune, let’s check the Smart Screen configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies. The below table shows the Smart Screen configuration settings for Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Policies using Intune.
| Smart Screen configuration settings | Enabled/Disabled |
|---|---|
| Block users from ignoring SmartScreen warnings | Configure |
| Turn on Windows SmartScreen | Yes |
| Require SmartScreen for Microsoft Edge Legacy | Yes |
| Block malicious site access | Yes |
| Block unverified file download | Yes |
| Configure Microsoft Defender SmartScreen | Configure |
| Prevent bypassing Microsoft Defender SmartScreen prompts for sites | Configure |
| Prevent bypassing of Microsoft Defender SmartScreen warnings about downloads | Not Configure |
| Configure Microsoft Defender SmartScreen to block potentially unwanted apps | Configure |
In Microsoft Intune, scope tags control access and visibility to resources and policies within an organization. They help define who can see and manage specific resources in Intune. Scope tags can be applied to various objects in Intune, such as policies, profiles, apps, and devices.
- By selecting the default scope tags, you can proceed to the next step by clicking the “Next” button in the window provided.
In the Assignments section of Intune, you can include or exclude specific groups for a policy or resource. Adding groups is a straightforward process. Click the “Add Groups” button below to add a specific group.
- Here we are adding HTMD Anoop Test Group.
- Click Create button and click Next.
The Review + Create tab helps you to show all the details, such as name, Description, configuration settings, scope tags, assignments, etc. Click the Create button from the below window.
Microsoft Defender Antivirus Configuration Policy Settings using Intune
Intune Security baseline policies are updated back in 2020. Hence I won’t recommend using these baseline policies blindly. Rather I would prefer to use other Endpoint Security Templates available in Intune portal, such as Antivirus, Bitlocker, etc…
Intune Endpoint security Antivirus policies provide a centralized approach for security administrators to manage antivirus settings across managed devices efficiently. These policies streamline the process, allowing admins to focus specifically on the discrete group of antivirus configurations.
- Click the Create Policy option below to create MS Defender in the endpoint security Antivirus Policy.
- Select the Platform as Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server
- Select the Profile as Microsoft Defender Antivirus
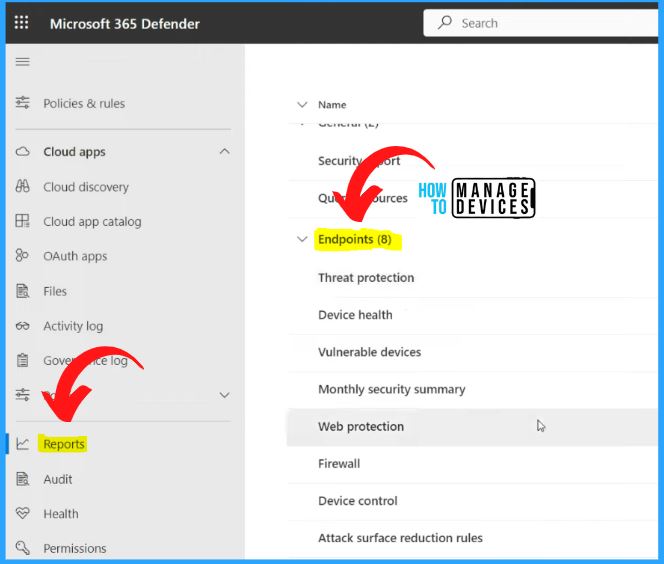
Reports from Microsoft 365 Defender and Intune Portal
You can get the default reports about policy deployment from Intune Default reports. The Reports are mainly available on security.microsoft.com, the Microsoft 365 Defender portal. Select the Reports tab on the Left side of the Microsoft 365 Defender portal. The Reports tab helps you to show all the reporting options. In the Endpoints section, you can see the reports related to the following.
- Threat protection
- Device health
- Vulnerable devices
- Monthly security summary
- Web protection
- Firewall
- Device control
- Attack surface reduction rules
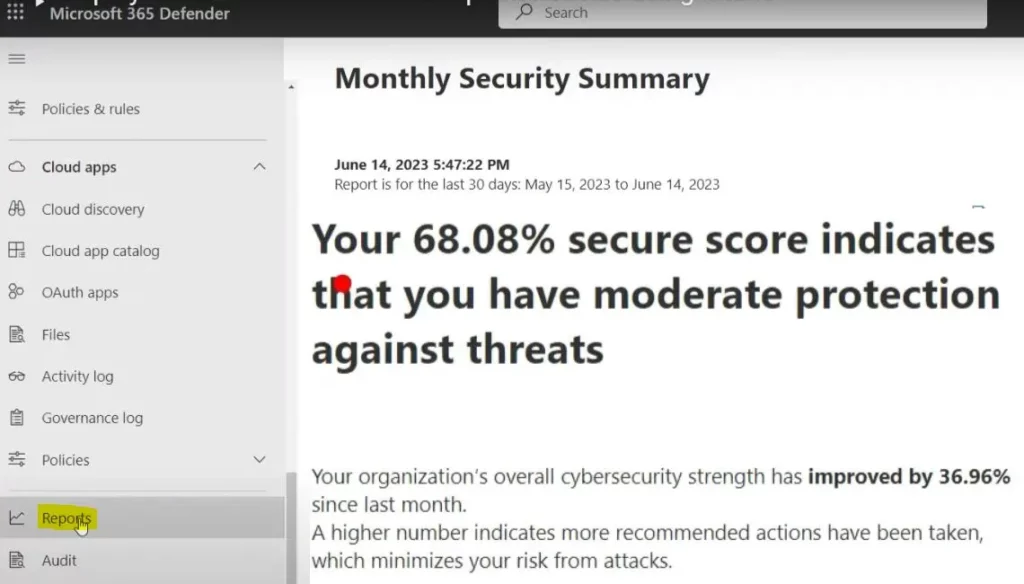
Monthly Security Summary Reports from Microsoft 365 Defender
The monthly security summary helps you to show the overall cybersecurity strength. A higher number indicates more recommended actions have been taken, which minimizes your risk from attacks.
Author
About Author – Vidya is a computer enthusiast. She is here to share quick tips and tricks with Windows 11 or Windows 10 users. She loves writing on Windows 11 and related technologies. She is also keen to find solutions and write about day-to-day tech problems.
