Let’s learn to Use the CHKDSK Tool to Fix Windows Issues. The chkdsk stands for Check Disk; it’s a command prompt used to check and repair or recover data on the drive if necessary; the user needs to use this command to improve the hard drive.
The chkdsk can mark any damage or malfunction on the hard drive or disk as bad sector and recover any information it contains. This Windows feature helps analyze hard drive errors and automatically runs repairs.
The chkdsk works for both HDD and SSD and takes care of your system. The damage made by any malware to the hard drive or disk can be rectified. However, it can not help with any physical damage to the hard drive.
In this post, I will explain various check disk operation types using the Elevated command prompt, PowerShell terminal, and the graphical user interface (GUI) of windows to perform the chkdsk operation.

- Windows 11 Account Lockout Policy Settings Group Policy and Intune options
- Configure Audit Policies for Windows 11 using GPO or Intune
- 4 Best Methods Enable Windows Sandbox | Configure Policies for Windows 11
Repair Hard Drive Using CHKDSK from File Explorer
Before the move to the command prompt to check the CHKDSK command, let’s review the other options for checking the disk and repairing it. From the file explorer, you can easily check and repair a disk. The process of checking the disk is discussed in it.
To check disk operation in GUI mode, open the file explorer window, then click This PC (you can use Window Key + E hotkey). Then select any drive and right-click on it, and click Properties.
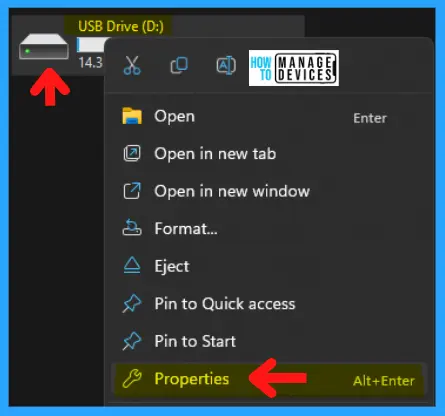
When you click on the Properties, the next window is the driver properties window; select the Tools tab. Under the tools tab, the Error Checking Section is there, and click on Check. This option will check the drive for system errors.
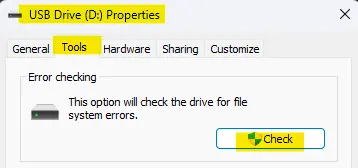
If the check disk operation finds your drive running smoothly, it shows a message that you don’t need to scan this drive. However, run the scan by clicking the Scan Drive option; it will not damage your hard drive.
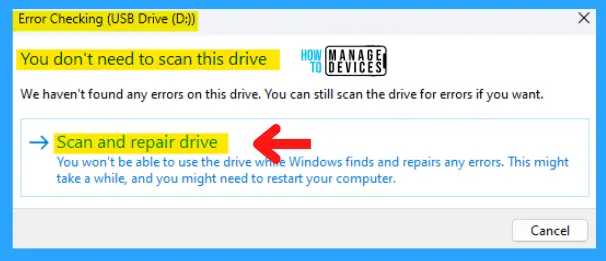
Clicking on the scan drive, the CHKDSK function starts its checking process. It takes some time, depending on the size of the drive and the amount of data stored in it. After completion, the success message will show up. Drive scanned successfully without any errors.
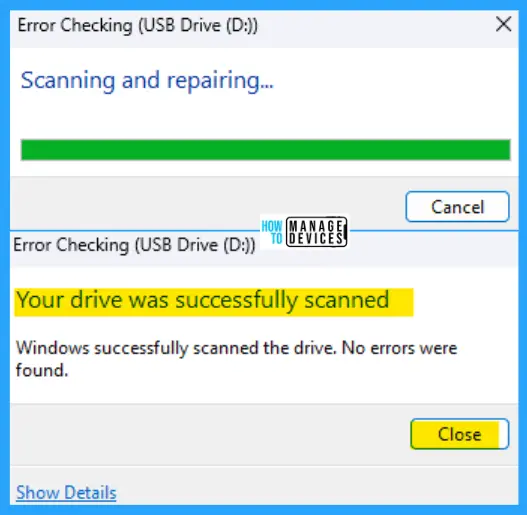
Repair Hard Drive Using CHKDSK from Elevated Command Prompt
This is the original or old command line area where the chkdsk command is run to check the drive. Open Elevated Command Prompt to perform the chkdsk operation.
Checks the file system and file system metadata of a volume for logical and physical errors. If used without parameters, chkdsk displays only the Volume’s status and does not fix any errors. It fixes errors in the Volume if used with the /f, /r, /x, or /b parameters.
NOTE! Interrupting chkdsk is not recommended. However, canceling or interrupting chkdsk should not leave the Volume more corrupt than before chkdsk was run. Running chkdsk again checks and should repair any remaining corruption on the Volume.
The syntax for the command is shown below for reference, where Volume defines the particular drive to scan.
chkdsk [<volume>[[<path>]<filename>]] [/f] [/v] [/r] [/x] [/i] [/c] [/l[:<size>]] [/b]
NOTE! Chkdsk can be used only for local disks. The command cannot be used with a local drive letter that has been redirected over the network.
Open an elevated command prompt, and after C:\Windows\System32> type chkdsk and press Enter. It will default check the C drive for errors and start repairing.
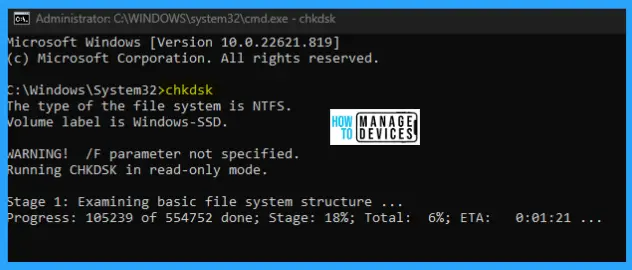
The syntax parameters shown above are explained in the table below with a description for better reference. Each parameter has its specific work to do. This is shown in the below table.
| Parameters | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| <volume> | Specifies the drive letter (followed by a colon), mount point, or volume name. |
[ [<path>]<filename> | Use with file allocation table (FAT) and FAT32 only. Specify the location and name of a file or set of files you want chkdsk to check for fragmentation. Can you use the? and * wildcard characters to specify multiple files. |
| /F | Fixes errors on the disk. The disk must be locked. If chkdsk cannot lock the drive, a message appears that asks you if you want to check the drive the next time you restart the computer. |
| /v | Displays the name of each file in every directory as the disk is checked |
| /r | Locates bad sectors and recovers readable information. The disk must be locked. /r includes the functionality of /f, with the additional analysis of physical disk errors. |
| /x | Forces the Volume to dismount first, if necessary. All open handles to the drive are invalidated. /x also includes the functionality of /f. |
| /i | Use NTFS only. Performs a less vigorous check of index entries, reducing the time required to run chkdsk. |
| /c | Use NTFS only. It does not check cycles within the folder structure, reducing the time required to run chkdsk. |
/l[:<size>] | Use NTFS only. Changes the log file size to the size you type if you omit the size parameter, /l displays the current size. |
| /b | Use NTFS only. Clears the list of bad clusters on the Volume and rescans all allocated and free clusters for errors. /b includes the functionality of /r. Use this parameter after imaging a volume to a new hard disk drive. |
| /scan | Use NTFS only. Runs an online scan on the Volume. |
| /forceofflinefix | Use with NTFS only (must be used with /scan). Bypass all online repairs; all defects found are queued for offline repair (for example, chkdsk /spotfix). |
| /perf | Use with NTFS only (must be used with /scan). It uses more system resources to complete a scan as fast as possible. This may have a negative performance impact on other tasks running on the system. |
| /spotfix | Use NTFS only. It runs spot-fixing on the Volume. |
| /sdcleanup | Use NTFS only. Garbage collects unneeded security descriptor data (implies /f). |
| /offlinescanandfix | Runs an offline scan and fix on the Volume. |
| /freeorphanedchains | Use with FAT/FAT32/exFAT only. Frees any orphaned cluster chains instead of recovering their contents. |
| /markclean | Use with FAT/FAT32/exFAT only. Marks the Volume clean if no corruption was detected, even if /f was not specified. |
| /? | Displays help at the command prompt. |
Let’s check how the /f, /r, /x, or /b parameters are working in the elevated command prompt below:
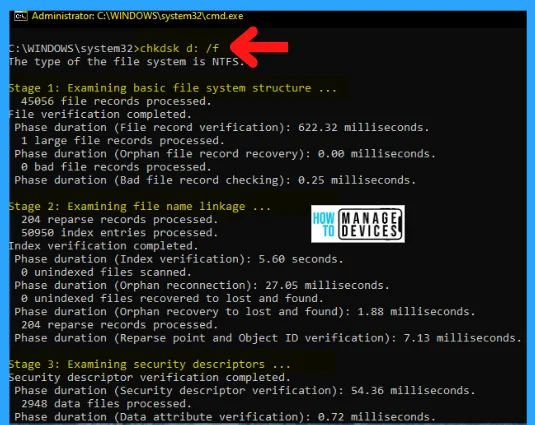
C:\Windows\System32>chkdsk d: /f
To check the disk in drive D and have Windows fix errors, type: C:\Windows\System32>chkdsk d: /f for further process. If it encounters errors, chkdsk pauses and displays messages. Chkdsk finishes by showing a report that lists the status of the disk. You cannot open any files on the specified drive until chkdsk finishes.
The type of file system is NTFS. There are 3 stages of checking the disk, as shown in the image and described below:
Stage 1 examines the basic file system structure and verifies the files and their records. The file verification duration and any bad file records are also checked.
Stage 1: Examining basic file system structure …
45056 file records processed.
File verification completed.
Phase duration (File record verification): 991.46 milliseconds.
1 large file record processed.
Phase duration (Orphan file record recovery): 0.00 milliseconds.
0 bad file records processed.
Phase duration (Bad file record checking): 0.92 milliseconds.
Stage 2 it is examining the file name linkage. The file details are indexed with proper entries. The duration of index verification and recovery of lost and found files be made here.
Stage 2: Examining file name linkage …
204 reparse records processed.
50950 index entries processed.
Index verification completed.
Phase duration (Index verification): 6.39 seconds.
0 unindexed files scanned.
Phase duration (Orphan reconnection): 5.29 milliseconds.
0 unindexed files recovered to lost and found.
Phase duration (Orphan recovery to lost and found): 1.25 milliseconds.
204 reparse records processed.
Phase duration (Reparse point and Object ID verification): 3.99 milliseconds.
Stage 3 is examining security descriptors verification. Data attributes verification and the CHKDSK is verifying the USN journal; then the process is complete.
Stage 3: Examining security descriptors …
Security descriptor verification completed.
Phase duration (Security descriptor verification): 39.91 milliseconds.
2948 data files processed.
Phase duration (Data attribute verification): 0.38 milliseconds.
CHKDSK is verifying Usn Journal…
9018040 USN bytes processed.
Usn Journal verification completed.
Phase duration (USN journal verification): 111.50 milliseconds.
The above image shows the process that starts after the execution of the command in the elevated command prompt. The result after scanning is shown below:
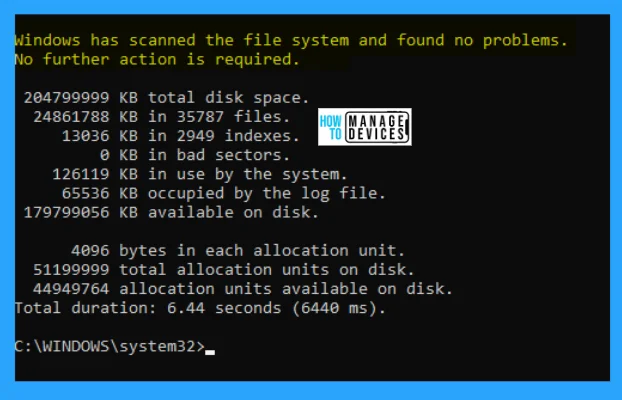
It shows, “Windows has scanned the file system and found no problems. No further action is required.” All the details scanned are shown below, which indicates all the details about that particular drive.
The final result shown in the image below is also represented in the table below:
| File Sizes | Descriptions of the Sizes |
|---|---|
| 204799999 KB | Total disk space |
| 24861796 KB | 35788 files |
| 13036 KB | 2949 indexes |
| 0 KB | Bad sectors |
| 126119 KB | Use by the system |
| 65536 KB | Occupied by the log file |
| 179799048 KB | Available on disk |
| 4096 bytes | Each allocation unit |
| 51199999 | Total allocation units on disk |
| 44949762 | Allocation units available on the disk |
| 7.55 seconds (7551 ms) | Total duration |
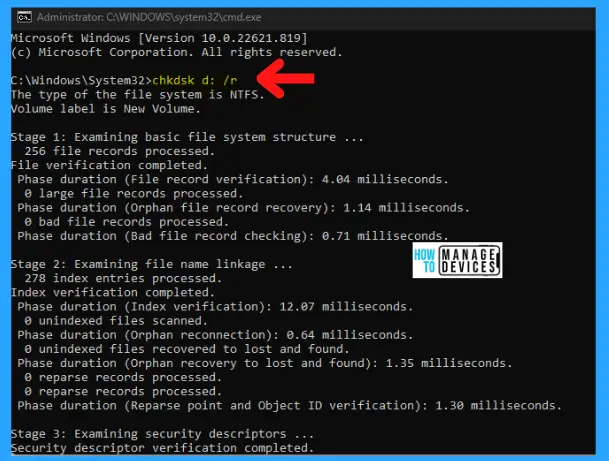
C:\Windows\System32>chkdsk d: /r
To check the disk in drive D and have Windows fix errors, type: C:\Windows\System32>chkdsk d: /r to encounter mistakes, chkdsk pauses, and displays messages. Chkdsk finishes by showing a report that lists the status of the disk. You cannot open any files on the specified drive until chkdsk finishes.
The type of file system is NTFS. There are 5 stages of checking the disk, as shown in the image and described below:
Stage 1 examines the basic file system structure and verifies the files and their records. The file verification duration and any bad file records are also checked.
Stage 1: Examining basic file system structure …
256 file records processed.
File verification completed.
Phase duration (File record verification): 4.04 milliseconds.
0 large file records processed.
Phase duration (Orphan file record recovery): 1.14 milliseconds.
0 bad file records processed.
Phase duration (Bad file record checking): 0.71 milliseconds.
Stage 2 it is examining the file name linkage. The file details are indexed with proper entries. The duration of index verification and recovery of lost and found files be made here.
Stage 2: Examining file name linkage …
278 index entries processed.
Index verification completed.
Phase duration (Index verification): 12.07 milliseconds.
0 unindexed files scanned.
Phase duration (Orphan reconnection): 0.64 milliseconds.
0 unindexed files recovered to lost and found.
Phase duration (Orphan recovery to lost and found): 1.35 milliseconds.
0 reparse records processed.
0 reparse records processed.
Phase duration (Reparse point and Object ID verification): 1.30 milliseconds.
Stage 3 is examining security descriptors verification. Data attributes verification and the CHKDSK is verifying the USN journal.
Stage 3: Examining security descriptors …
Security descriptor verification completed.
Phase duration (Security descriptor verification): 1.20 milliseconds.
11 data files were processed.
Phase duration (Data attribute verification): 5.10 milliseconds.
Stage 4 is looking for bad clusters in user file data. Data attributes verification and file data verification completed.
Stage 4: Looking for bad clusters in user file data …
240 files processed.
File data verification completed.
Phase duration (User file recovery): 36.63 milliseconds.
Stage 5 is looking for bad, free clusters in user file data. Data attributes verification and free space verification are completed then the process is complete.
Stage 5: Looking for bad, free clusters …
5106713 free clusters processed.
Free space verification is complete.
Phase duration (Free space recovery): 8.36 seconds.
The result shows, “Windows has scanned the file system and found no problems. No further action is required.” All the details scanned are shown below, which indicates all the details about that particular drive.
The final result shown in the image below is also represented in the table below:
| File Sizes | Descriptions of the Sizes |
|---|---|
| 20478975 KB | Total disk space |
| 21568 KB | In 6 files |
| 72 KB | In 13 indexes |
| 0 KB | In bad sectors |
| 30479 KB | In use by the system |
| 29184 KB | Occupied by the log file |
| 20426856 KB | Available on disk |
| 4096 bytes | in each allocation unit |
| 5119743 | total allocation units on disk |
| 5106714 | allocation units available on the disk |
| 8.43 seconds (8435 ms) | Total duration |
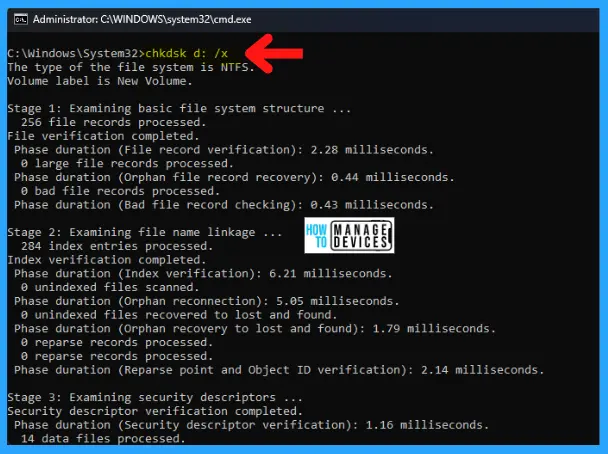
C:\Windows\System32>chkdsk d: /x
To check the disk in drive D and have Windows fix errors, type: C:\Windows\System32>chkdsk d: /x to encounter mistakes, chkdsk pauses, and displays messages. Chkdsk finishes by showing a report that lists the status of the disk. You cannot open any files on the specified drive until chkdsk finishes.
The type of file system is NTFS. There are 3 stages of checking the disk, as shown in the image and described below:
Stage 1 examines the basic file system structure and verifies the files and their records. The file verification duration and any bad file records are also checked.
Stage 1: Examining basic file system structure …
45056 file records processed.
File verification completed.
Phase duration (File record verification): 1.05 seconds.
1 large file record processed.
Phase duration (Orphan file record recovery): 0.00 milliseconds.
0 bad file records processed.
Phase duration (Bad file record checking): 2.52 milliseconds.
Stage 2 it is examining the file name linkage. The file details are indexed with proper entries. The duration of index verification and recovery of lost and found files be made here.
Stage 2: Examining file name linkage …
204 reparse records processed.
50950 index entries processed.
Index verification completed.
Phase duration (Index verification): 7.24 seconds.
0 unindexed files scanned.
Phase duration (Orphan reconnection): 37.41 milliseconds.
0 unindexed files recovered to lost and found.
Phase duration (Orphan recovery to lost and found): 1.18 milliseconds.
204 reparse records processed.
Phase duration (Reparse point and Object ID verification): 2.22 milliseconds.
Stage 3 is examining security descriptors verification. Data attributes verification and the CHKDSK is verifying the USN journal; then the process is complete.
Stage 3: Examining security descriptors …
Security descriptor verification completed.
Phase duration (Security descriptor verification): 27.12 milliseconds.
2948 data files processed.
Phase duration (Data attribute verification): 0.64 milliseconds.
CHKDSK is verifying Usn Journal…
9032128 USN bytes processed.
Usn Journal verification completed.
Phase duration (USN journal verification): 161.63 milliseconds.
The result shows, “Windows has scanned the file system and found no problems. No further action is required.” All the details scanned are shown below, which indicates all the details about that particular drive.
The final result shown in the image below is also represented in the table below:
| Free Sizes | Descriptions of the Sizes |
|---|---|
| 204799999 KB | Total disk space |
| 24861804 KB | In 35807 files |
| 13044 KB | In 2949 indexes |
| 0 KB | In bad sectors |
| 126119 KB | In use by the system |
| 65536 KB | Occupied by the log file |
| 179799032 KB | Available on disk |
| 4096 bytes | In each allocation unit |
| 51199999 | Total allocation units on disk |
| 44949758 | Allocation units available on disk |
| 8.53 seconds (8536 ms) | Total duration |
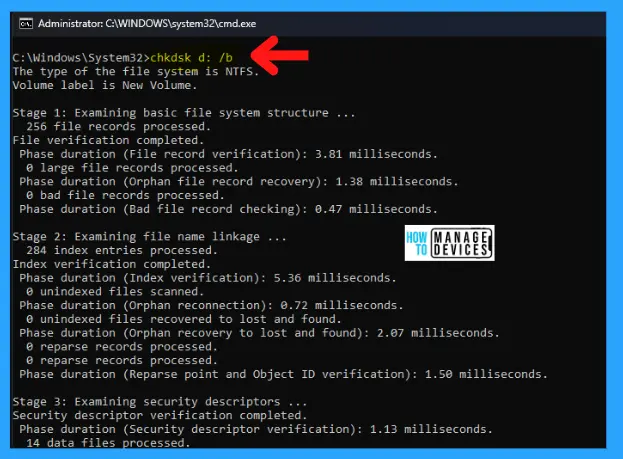
C:\Windows\System32>chkdsk d: /b
To check the disk in drive D and have Windows fix errors, type: C:\Windows\System32>chkdsk d: /b to encounter errors, chkdsk pauses, and displays messages. Chkdsk finishes by showing a report that lists the status of the disk. You cannot open any files on the specified drive until chkdsk finishes.
The type of file system is NTFS. There are 5 stages of checking the disk, as shown in the image and described below:
Stage 1 examines the basic file system structure and verifies the files and their records. The file verification duration and any bad file records are also checked.
Stage 1: Examining basic file system structure …
256 file records processed.
File verification completed.
Phase duration (File record verification): 3.81 milliseconds.
0 large file records processed.
Phase duration (Orphan file record recovery): 1.38 milliseconds.
0 bad file records processed.
Phase duration (Bad file record checking): 0.47 milliseconds.
Stage 2 it is examining the file name linkage. The file details are indexed with proper entries. The duration of index verification and recovery of lost and found files be made here.
Stage 2: Examining file name linkage …
284 index entries processed.
Index verification completed.
Phase duration (Index verification): 5.36 milliseconds.
0 unindexed files scanned.
Phase duration (Orphan reconnection): 0.72 milliseconds.
0 unindexed files recovered to lost and found.
Phase duration (Orphan recovery to lost and found): 2.07 milliseconds.
0 reparse records processed.
0 reparse records processed.
Phase duration (Reparse point and Object ID verification): 1.50 milliseconds.
Stage 3 is examining security descriptors verification. Data attributes verification and the CHKDSK is verifying the USN journal.
Stage 3: Examining security descriptors …
Security descriptor verification completed.
Phase duration (Security descriptor verification): 1.13 milliseconds.
14 data files were processed.
Phase duration (Data attribute verification): 0.73 milliseconds.
Stage 4 is looking for bad clusters in user file data. Data attributes verification and file data verification completed.
Stage 4: Looking for bad clusters in user file data …
240 files processed.
File data verification completed.
Phase duration (User file recovery): 43.98 milliseconds.
Stage 5 is looking for bad, free clusters in user file data. Data attributes verification and free space verification are completed then the process is complete.
Stage 5: Looking for bad, free clusters …
5106712 free clusters processed.
Free space verification is complete.
Phase duration (Free space recovery): 8.74 seconds.
The result shows, “Windows has scanned the file system and found no problems. No further action is required.” All the details scanned are shown below, which indicates all the details about that particular drive.
The final result shown in the image below is also represented in the table below:
| Free Sizes | Descriptions of the Sizes |
|---|---|
| 20478975 KB | Total disk space |
| 21576 KB | In 7 files |
| 72 KB | In 16 indexes |
| 0 KB | In bad sectors |
| 30479 KB | In use by the system |
| 29184 KB | Occupied by the log file |
| 20426848 KB | Available on disk |
| 4096 bytes | In each allocation unit |
| 5119743 | Total allocation units on disk |
| 5106712 | Allocation units available on the disk |
| 8.80 seconds (8803 ms) | Total duration |
How to View CHKDSK Logs in Windows 11
Two methods can be used to retrieve chkdsk log file(s) in Windows. The below list and screenshot show the 2 methods used to retrieve the chkdsk log file.
- Event Viewer
- PowerShell
1. Event Viewer for CHKDSK Logs
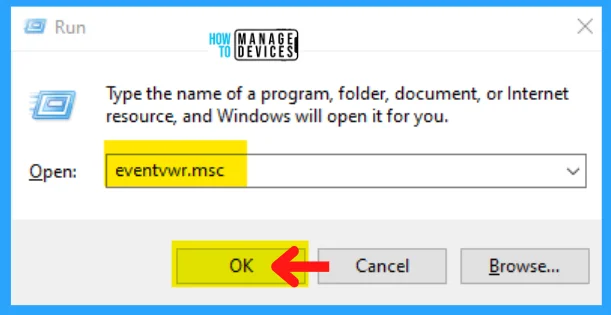
To view logs with Event Viewer, you’ll need to follow the process described. Open the run dialog box by pressing Windows Key + R, type eventvwr.msc, and press OK.
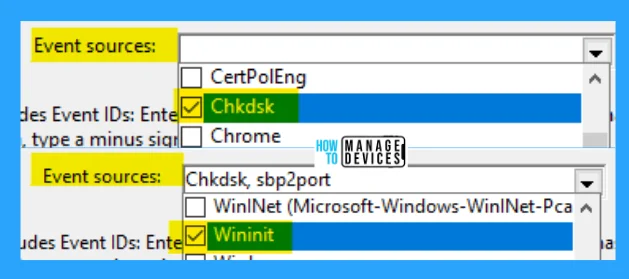
When the event viewer window opens, expand Windows Logs under it, then right-click on Application and select Filter Current Log.
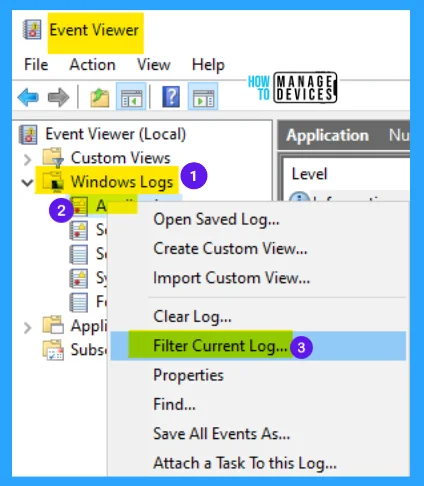
When entering the Filter Current Log window, there is an option named Event Sources available; select Chkdsk and Wininit from its drop-down menu and press OK to finish filtering for these two sources.
2. PowerShell for CHKDSK Logs
There are two source types when retrieving logs in PowerShell: chkdsk and wininit. Run one of the two commands in PowerShell to view the most current chkdsk log. The following commands for a PowerShell script to chkdsk log and wininit log.
- chkdsk
- wininit
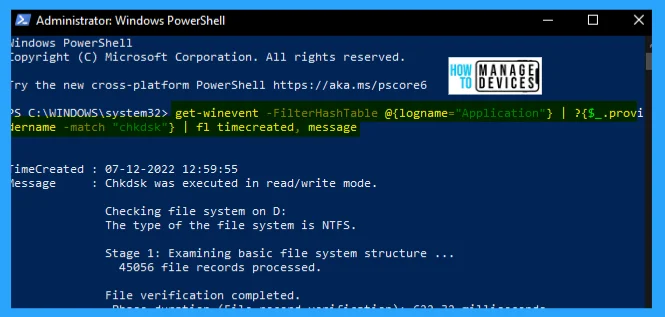
For Chkdsk enter the powershell script: get-winevent -FilterHashTable @{logname=”Application”} | ?{$_.providername -match “chkdsk”} | fl timecreated, message
For wininit enter the powershell script: get-winevent -FilterHashTable @{logname=”Application”} | ?{$_.providername -match “wininit”} | fl timecreated, message
The following image shows an example of executing the chkdsk PowerShell script in Administrator: Windows PowerShell.
To export the log to a specific location, the following can be added to the end of the command | out-file “$env:userprofile\location\filename.txt”. The script is provided below, and an example of chkdsk log export is provided.
For Chkdsk, enter the PowerShell script to export log: get-winevent -FilterHashTable @{logname=”Application”} | ?{$_.providername -match “chkdsk”} | fl timecreated, message | out-file “$env:userprofile\location\filename.txt.“
For wininit, enter the PowerShell script to export log: get-winevent -FilterHashTable @{logname=”Application”} | ?{$_.providername -match “wininit”} | fl timecreated, message | out-file “$env:userprofile\location\filename.txt.”
The information shared above regarding Repair Hard Drive Using CHKDSK in Windows 11 is helpful. Please follow us on HTMD Community and visit our website HTMD Forum if you like our content.
Author
Alok is a Master of Computer Applications (MCA) graduate. He loves writing on Windows 11 and related technologies. He likes to share his knowledge, quick tips, and tricks with Windows 11 or Windows 10 with the community.

Where do I find Win 10 and chkdsk?