In this post, let’s learn about the Audit Policies for Windows 11 and their configuration using GPO or Intune. The Audit policies provide better security for your device. Configuring policy settings in this category can help you document attempts to authenticate account data on a domain controller or a local Security Accounts Manager (SAM).
This policy setting allows you to audit events generated by validation tests on user account login credentials. Events in this subcategory occur only on the authoritative computer for those credentials. Intune Settings Catalog policies and Group Policy settings can help you here to configure audit policies.
There are 10 different categories in Group Policy Settings, and those ten categories have their subcategories to make some effective configuration in your device on in a domain. Also, in the Security Settings, there are 9 policies to configure Audit Policies in Windows 11.
In this post, I would like to discuss detailed information about the Audit Policies Settings in Windows 11. This post consists of Group Policy Settings, Security Settings, and Intune Policy Setting to modify the Audit Policies. Also, the command line to check the audit policy.
- Windows 11 Account Lockout Policy Settings Group Policy and Intune options
- Best Set of Updated Windows 11 Password Policies
- 4 Best Methods Enable Windows Sandbox | Configure Policies for Windows 11
Group Policy Settings for Audit Policies for Windows 11
You can, as an admin, change the Audit Policies in windows 11 by using the local or Domain group policy. The policy path navigates toward the account lockout policy settings. Some of the audit policies listed below do NOT apply to Windows 11 or the client operating system.
Open the Local Group Policy Editor and follow the path “Computer Configuration/Windows Settings/Security Settings/Advanced Audit Policy Configuration/System Audit Policies – Local Group Policy Object” to reach the proper location to perform the desired task.

You can open Run, type gpedit.msc, and press OK; the Local Group Policy Editor Opens. However, to open the Domain policy, open Run, type gpmc.msc and press OK. More detailed domain-level group policy settings using ADMX are explained -> Microsoft Edge ADMX Group Policy Templates.
Advance Audit Policy Configuration settings can provide detailed control over audit policies, identify attempted or successful attacks on your network and resources, and verify compliance with rules governing the management of critical organizational assets.
In the Audit Policy, the Group Policy Editor has 10 categories for its security settings are listed below:
- Account Logon
- Account Management
- Detailed Tracking
- DS Access
- Logon/Logoff
- Object Access
- Policy Change
- Privilege Use
- System
- Global Object Access Auditing
The detailed summary is presented in the table as well in the image below:
| Categories | Default Configurations |
|---|---|
| Account Logon | Not Configured |
| Account Management | Not Configured |
| Detailed Tracking | Not Configured |
| DS Access | Not Configured |
| Logon/Logoff | Not Configured |
| Object Access | Not Configured |
| Policy Change | Not Configured |
| Privilege Use | Not Configured |
| System | Not Configured |
| Global Object Access Auditing | Not Configured |
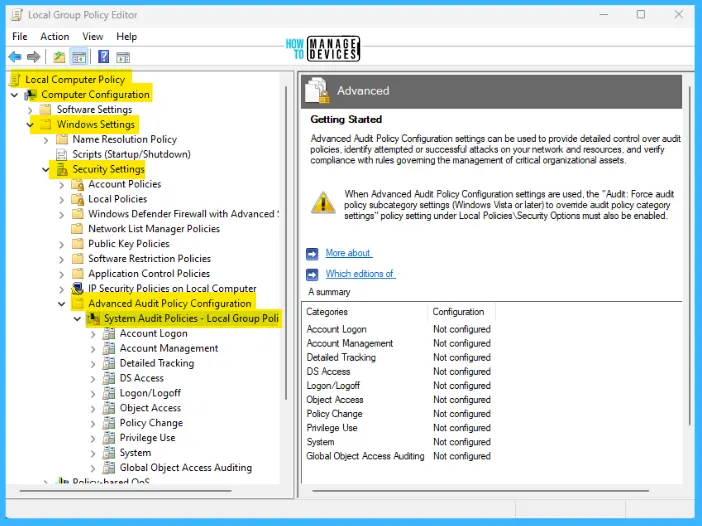
NOTE! When Advance Audit Policy Configuration settings are used, the “Audit: Force audit policy subcategory settings (Windows Vista or later) to override audit policy category settings” policy settings under Local Policies\Security Options must also be enabled.
The above categories have their subcategories for policy settings; the details are presented in this post.
Account Logon Audit Policy
Configuring policy settings in this category can help you document attempts to authenticate account data on a domain controller or on a local Security Accounts Manager (SAM).
Unlike Logon and Logoff policy settings and events, Account Logon settings and events focus on the account database that is used. This category includes the following subcategories:
- Audit Credential Validation
- Audit Kerberos Authentication Service
- Audit Kerberos Service Ticket Operations
- Audit Other Account Logon Events
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit Credential Validation | Not Configured |
| Audit Kerberos Authentication Service | Not Configured |
| Audit Kerberos Service Ticket Operations | Not Configured |
| Audit Other Account Logon Events | Not Configured |
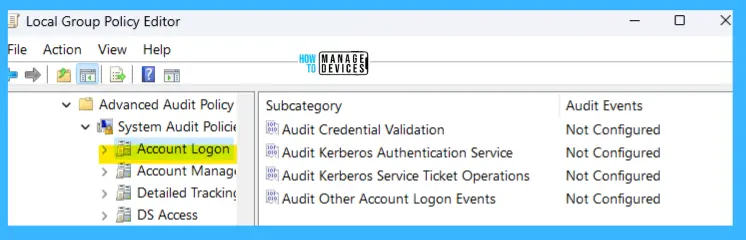
Account Management – Windows Audit Policy
The security audit policy settings in this category can be used to monitor changes to user and computer accounts and groups. This category includes the following subcategories:
- Audit Application Group Management
- Audit Computer Account Management
- Audit Distribution Group Management
- Audit Other Account Management Events
- Audit Security Group Management
- Audit User Account Management
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit Application Group Management | Not Configured |
| Audit Computer Account Management | Not Configured |
| Audit Distribution Group Management | Not Configured |
| Audit Other Account Management Events | Not Configured |
| Audit Security Group Management | Not Configured |
| Audit User Account Management | Not Configured |
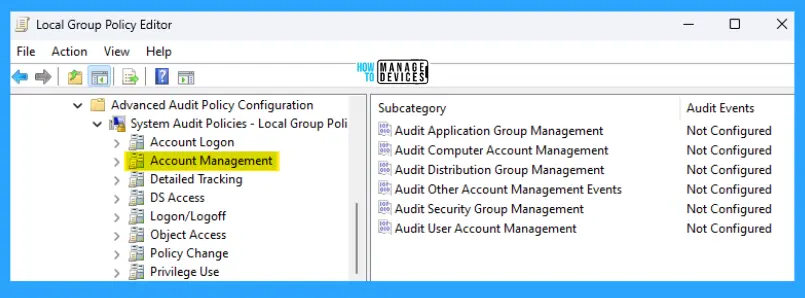
Detailed Tracking
Detailed Tracking security policy settings and audit events can be used for the following purposes:
- To monitor the activities of individual applications and users on that computer
- To understand how a computer is being used.
This category includes the following subcategories:
- Audit DPAPI Activity
- Audit PNP activity
- Audit Process Creation
- Audit Process Termination
- Audit RPC Events
- Audit Token Right Adjusted
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit DPAPI Activity | Not Configured |
| Audit PNP activity | Not Configured |
| Audit Process Creation | Not Configured |
| Audit Process Termination | Not Configured |
| Audit RPC Events | Not Configured |
| Audit Token Right Adjusted | Not Configured |
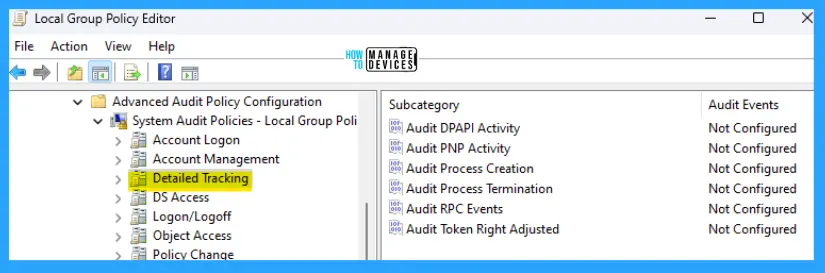
DS Access – Active Directory Domain Services Audit Policies
DS Access security audit policy settings provide a detailed audit trail of attempts to access and modify objects in Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). These audit events are logged only on domain controllers. This category includes the following subcategories:
- Audit Detailed Directory Service Replication
- Audit Directory Service Access
- Audit Directory Service Changes
- Audit Directory Service Replication
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit Detailed Directory Service Replication | Not Configured |
| Audit Directory Service Access | Not Configured |
| Audit Directory Service Changes | Not Configured |
| Audit Directory Service Replication | Not Configured |
Logon/Logoff – Windows 11 Audit Policies
Logon/Logoff security policy settings and audit events allow you to track attempts to log on to a computer interactively or over a network. These events are particularly useful for tracking user activity and identifying potential attacks on network resources. This category includes the following subcategories:
- Audit Account Lockout
- Audit User/Device Claims
- Audit IPsec Extended Mode
- Audit Group Membership
- Audit IPsec Main Mode
- Audit IPsec Quick Mode
- Audit Logoff
- Audit Logon
- Audit Network Policy Server
- Audit Other Logon/Logoff Events
- Audit Special Logon
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit Account Lockout | Not Configured |
| Audit User/Device Claims | Not Configured |
| Audit IPsec Extended Mode | Not Configured |
| Audit Group Membership | Not Configured |
| Audit IPsec Main Mode | Not Configured |
| Audit IPsec Quick Mode | Not Configured |
| Audit Logoff | Not Configured |
| Audit Logon | Not Configured |
| Audit Network Policy Server | Not Configured |
| Audit Other Logon/Logoff Events | Not Configured |
| Audit Other Logon/Logoff Events | Not Configured |
| Audit Special Logon | Not Configured |
Object Access Audit Policies
Object Access policy settings and audit events allow you to track attempts to access specific objects or types of objects on a network or computer. To audit attempts to access a file, directory, registry key, or any other object, enable the appropriate Object Access auditing subcategory for success and/or failure events.
For example, the file system subcategory needs to be enabled to audit file operations; the Registry subcategory needs to be enabled to audit registry accesses. This category includes the following subcategories:
Proving that these audit policies are in effect for an external auditor is more difficult. There is no easy way to verify that the proper SACLs are set on all inherited objects. To address this issue, see Global Object Access Auditing.
- Audit Application Generated
- Audit Certification Services
- Audit Detailed File Share
- Audit File Share
- Audit File System
- Audit Filtering Platform Connection
- Audit Filtering Platform Packet Drop
- Audit Handle Manipulation
- Audit Kernel Object
- Audit Other Object Access Events
- Audit Registry
- Audit Removable Storage
- Audit SAM
- Audit Central Access Policy Staging
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit Application Generated | Not Configured |
| Audit Certification Services | Not Configured |
| Audit Detailed File Share | Not Configured |
| Audit File System | Not Configured |
| Audit Filtering Platform Connection | Not Configured |
| Audit Filtering Platform Packet Drop | Not Configured |
| Audit Handle Manipulation | Not Configured |
| Audit Kernel Object | Not Configured |
| Audit Other Object Access Events | Not Configured |
| Audit Registry | Not Configured |
| Audit Removable Storage | Not Configured |
| Audit SAM | Not Configured |
| Audit Central Access Policy Staging | Not Configured |
Policy Change
Policy Change audit events allow you to track changes to important security policies on a local system or network. Because administrators typically establish guidelines to help secure network resources, tracking changes (or attempts) to these policies is an important aspect of security management for a network.
This category includes the following subcategories:
- Audit Policy Change
- Audit Authentication Policy Change
- Audit Authorization Policy Change
- Audit Filtering Platform Policy Change
- Audit MPSSVC Rule-Level Policy Change
- Audit Other Policy Change Events
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit Application Generated | Not Configured |
| Audit Authentication Policy Change | Not Configured |
| Audit Authorization Policy Change | Not Configured |
| Audit Filtering Platform Policy Change | Not Configured |
| Audit MPSSVC Rule-Level Policy Change | Not Configured |
| Audit Other Policy Change Events | Not Configured |
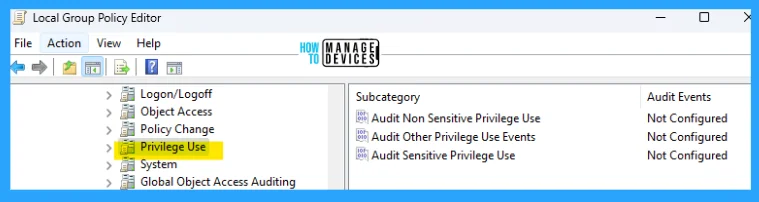
Windows Privilege Use Audit Policies
Permissions on a network are granted for users or computers to complete defined tasks. Privilege Use security policy settings and audit events allow you to track the use of certain permissions on one or more systems. This category includes the following subcategories:
- Audit Non-Sensitive Privilege Use
- Audit Other Privilege Use Events
- Audit Sensitive Privilege Use
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit Non-Sensitive Privilege Use | Not Configured |
| Audit Other Privilege Use Events | Not Configured |
| Audit Sensitive Privilege Use | Not Configured |
Windows Security System Audit Logs
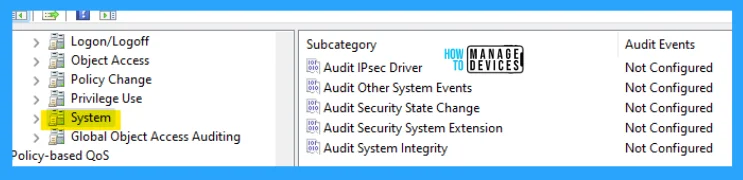
System security policy settings and audit events allow you to track the following types of system-level changes to a computer:
- Not included in other categories
- Have potential security implications.
This category includes the following subcategories:
- Audit IPsec Driver
- Audit Other System Events
- Audit Security State Change
- Audit Security System Extension
- Audit System Integrity
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit IPsec Driver | Not Configured |
| Audit Other System Events | Not Configured |
| Audit Security State Change | Not Configured |
| Audit Security System Extension | Not Configured |
| Audit System Integrity | Not Configured |
Global Object Access Auditing
Global Object Access Auditing policy settings allow administrators to define computer system access control lists (SACLs) per object type for the file system or the registry.
The specified SACL is then automatically applied to every object of that type. Auditors can prove that an audit policy protects every resource in the system. They can do this task by viewing the contents of the Global Object Access Auditing policy settings.
For example, if auditors see a policy setting called “Track all changes made by group administrators,” they know that this policy is in effect.
Resource SACLs are also useful for diagnostic scenarios. For example, administrators quickly identify which object in a system is denying a user access by:
- Setting the Global Object Access Auditing policy to log all the activities for a specific user
- Enabling the policy to track “Access denied” events for the file system or registry can help
NOTE! If a file or folder SACL and a Global Object Access Auditing policy setting (or a single registry setting SACL and a Global Object Access Auditing policy setting) are configured on a computer, the effective SACL is derived from combining the file or folder SACL and the Global Object Access Auditing policy. This means that an audit event is generated if an activity matches the file or folder SACL or the Global Object Access Auditing policy.
This category includes the following subcategories:
- File System (Global Object Access Auditing)
- Registry (Global Object Access Auditing)
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| File System (Global Object Access Auditing) | Not Configured |
| Registry (Global Object Access Auditing) | Not Configured |

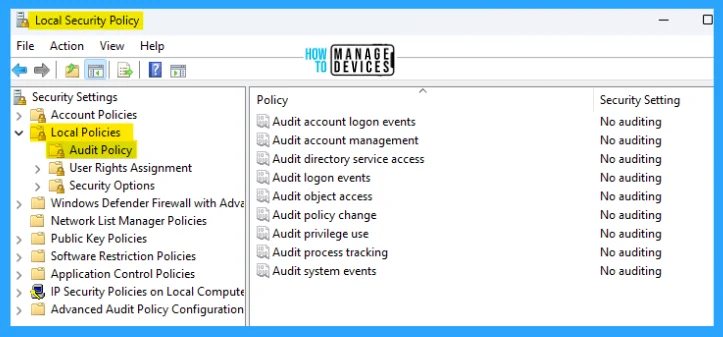
Security Policy Settings for Audit Policies in Windows 11
To open the Local Security Policy, open the Run command and type secpol.msc, press OK. The Local Security Policy window opens. There are 9 policies to configure Audit Policies in Windows 11 listed below:
- Audit Account Logon Events
- Audit Account Management
- Audit Directory Service Access
- Audit Logon Events
- Audit Object Access
- Audit Policy Change
- Audit Privilege Use
- Audit Process Tracking
- Audit System Events
The details are reflected in the table below and also seen in the image below for reference.
| Subcategory | Default Configuration of Audit Events |
|---|---|
| Audit Account Logon Events | No Auditing |
| Audit Account Management | No Auditing |
| Audit Directory Service Access | No Auditing |
| Audit Logon Events | No Auditing |
| Audit Object Access | No Auditing |
| Audit Policy Change | No Auditing |
| Audit Privilege Use | No Auditing |
| Audit Process Tracking | No Auditing |
| Audit System Events | No Auditing |
Intune Settings for Audit Policies in Windows 11
Let’s look at Intune policy options to check the settings of the Audit Policies. We have already seen 2 methods to do this in this post and the Intune settings catalog method to implement the same.
Go through Intune Settings Catalog Guide (linked below) to create the policy in detail. Search with the following keyboard for this context: Audit Policies—the detailed explanation is presented below.
NOTE! – More details on Intune settings catalog guide – Create Intune Settings Catalog Policy.
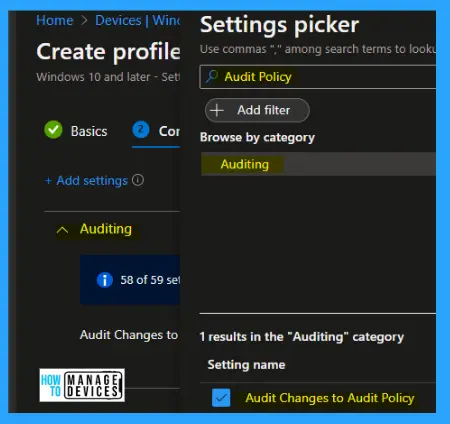
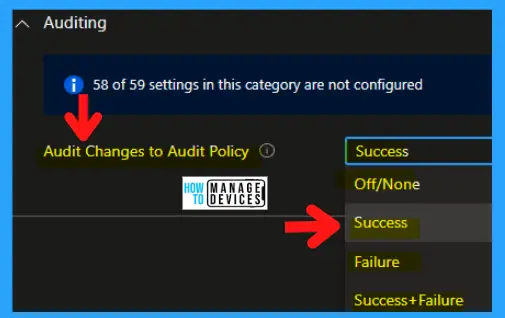
This policy setting allows you to audit changes in the security audit policy settings, such as the following:
- Settings permissions and audit settings on the Audit Policy object.
- Changes to the system audit policy.
- Registration of security event sources.
- De-registration of security event sources.
- Changes to the per-user audit settings.
- Changes to the value of CrashOnAuditFail.
- Changes to the system access control list on a file system or registry object.
- Changes to the Special Groups list.
NOTE! System access control list (SACL) change auditing is done when a SACL for an object changes and the policy change category is enabled. Discretionary access control list (DACL) and ownership changes are audited when object access auditing is enabled, and the object’s SACL is configured for auditing of DACL/Owner change.
The following are the drop-down options:
- Off/None
- Success
- Failure
- Success + Failure
I hope the information about Audit Policies Settings of Windows 11 using Intune and Group Policy is helpful. Please follow us on HTMD Community and visit our website HTMD Forum if you like our content.
Author
Alok is a Master of Computer Applications (MCA) graduate. He loves writing on Windows 11 and related technologies. He likes to share his knowledge, quick tips, and tricks with Windows 11 or Windows 10 with the community.
