This article will discuss how to Enable Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection Mode with Microsoft Intune. LSA Protection Mode is a security feature in Windows operating systems designed to protect against credential theft and other security threats.
When LSA Protection Mode is enabled, it restricts access to the memory and resources associated with the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS), which manages the system’s authentication and security policies. LSA Protection Mode operates in “Restricted Mode” and “Full Mode.”
Restricted Mode: In Restricted Mode, LSA Protection restricts access to sensitive data within the LSASS process, such as credentials and tokens. This helps prevent attacks that attempt to extract sensitive information from memory, such as Pass-the-Hash attacks.
Full Mode: Full Mode goes a step further by applying additional protections to the LSASS process, making it more resilient to advanced attacks such as Mimikatz. It utilizes virtualization-based security (VBS) features to isolate LSASS in a secure container, further reducing the risk of credential theft.
Enabling LSA Protection Mode helps strengthen the security posture of Windows systems by reducing the attack surface and mitigating the risk of credential theft and other security vulnerabilities. It is recommended to enable LSA Protection Mode, particularly in environments where security is a top priority, such as enterprise networks or systems handling sensitive data.
It’s important to note that enabling LSA Protection Mode may require compatible hardware and software support and careful planning and testing to ensure compatibility with existing applications and configurations. Additionally, proper monitoring and management practices should be implemented to ensure the continued effectiveness of LSA Protection Mode and to detect and respond to any security incidents or anomalies.

- Windows 11 New LSA Local Security Authority Policies
- Quick and Easy way to Turn on PowerShell Audit using Intune Policy
- How to Easily Disable Local Drive Redirection with Intune
- Best Guide to Enable WinSCP Win32 App Supersedence and Auto-Update with Intune
What are the Advantages of Enable Local Security Authority Protection Mode?
Enabling Local Security Authority (LSA) Protection Mode offers several advantages for enhancing the security of Windows systems:
Overall, enabling LSA Protection Mode helps organizations reduce the risk of credential theft and other security vulnerabilities, enhance their security posture, and better protect sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access and exploitation.
| Category | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Credential Theft Prevention | LSA Protection Mode helps prevent various credential theft techniques, including Pass-the-Hash and Pass-the-Ticket attacks, by restricting access to sensitive data stored within the LSASS process. |
| Mitigation of Credential Dumping Tools | LSA Protection Mode reduces the effectiveness of credential dumping tools such as Mimikatz by limiting their ability to extract sensitive information from memory. |
| Enhanced Security Posture | By safeguarding the LSASS process, which manages authentication and security policies, LSA Protection Mode strengthens the overall security posture of Windows systems. |
| Protection Against Credential-based Attacks | Enabling LSA Protection Mode mitigates the risk of credential-based attacks, which are commonly exploited by adversaries to escalate privileges and gain unauthorized access to systems. |
| Isolation of LSASS Process | In Full Mode, LSA Protection Mode utilizes virtualization-based security (VBS) features to isolate the LSASS process in a secure container, further reducing the risk of compromise. |
| Compliance Requirements | Enabling LSA Protection Mode may help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements by implementing additional security controls to protect sensitive data and systems. |
| Defense-in-Depth Strategy | LSA Protection Mode serves as an additional layer of defence in a defence-in-depth security strategy, complementing other security measures such as endpoint protection, access controls, and network security. |
| Resilience to Advanced Threats | By applying additional protections to the LSASS process, LSA Protection Mode enhances the resilience of Windows systems against advanced threats and sophisticated attack techniques. |
Create Configuration Profile to Enable Local Security Authority LSA Protection Mode
Follow the steps below to create a configuration policy to Enable Local Security Authority LSA Protection Mode with Intune. Sign in to the Microsoft Intune Admin Center using your administrator credentials.
- Navigate to Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles
- Click on +Create > +New Policy
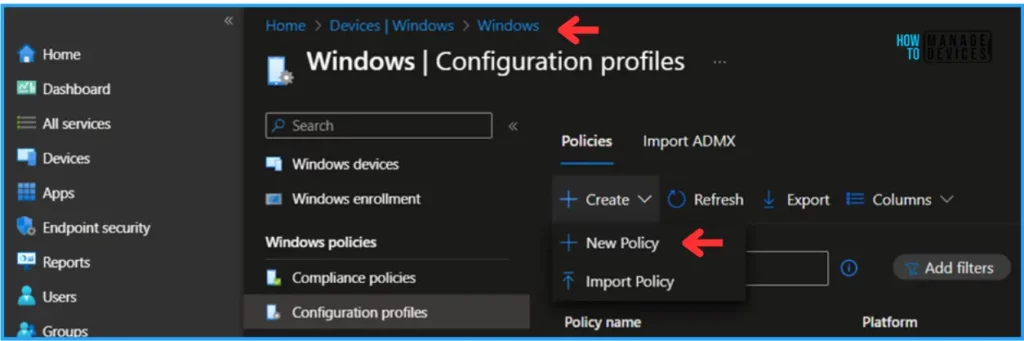
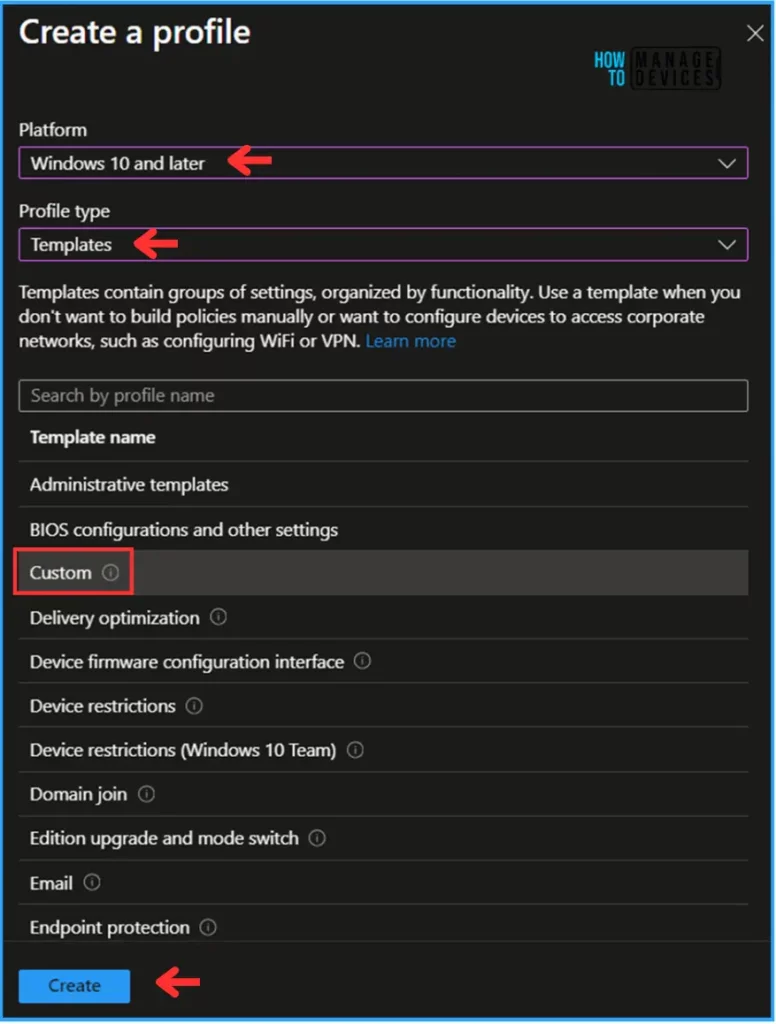
We can now create a profile using a Custom Windows template. To do that, specify the following details under the Create a profile option.
- Platform: Windows 10 and later
- Profile type: Templates
- Template name: Custom
Note! Microsoft Intune includes many built-in settings to control different features on a device. You can also create custom profiles, which are created similar to built-in profiles. Custom profiles are great when you want to use device settings and features that aren’t built into Intune. These profiles include features and settings for you to control on devices in your organization. For example, you can create a custom profile that sets the same feature for every Windows device.
Note! Did you know? Consider creating a Settings catalog profile instead. The Intune Settings catalog contains many settings and values previously only available through a custom profile in a native, easy-to-search experience. More settings are continually being added.
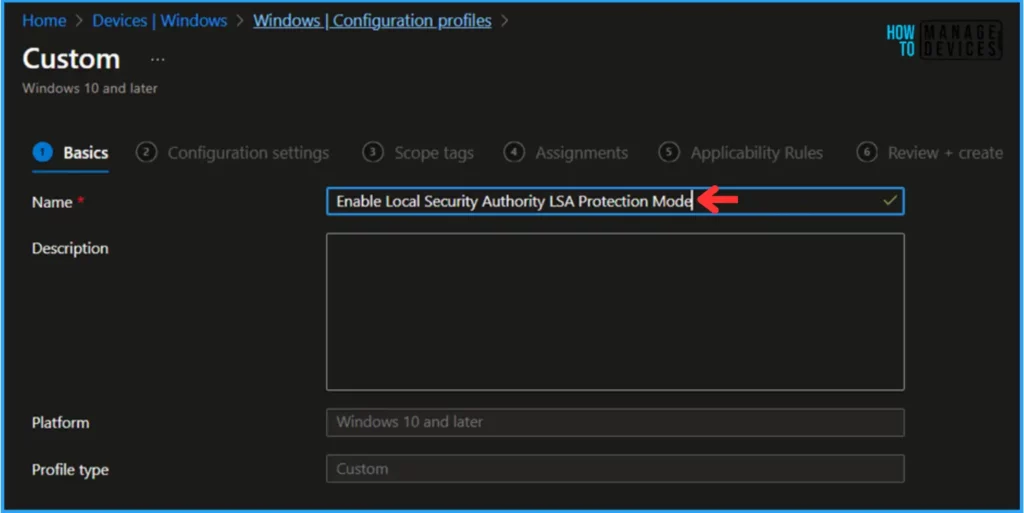
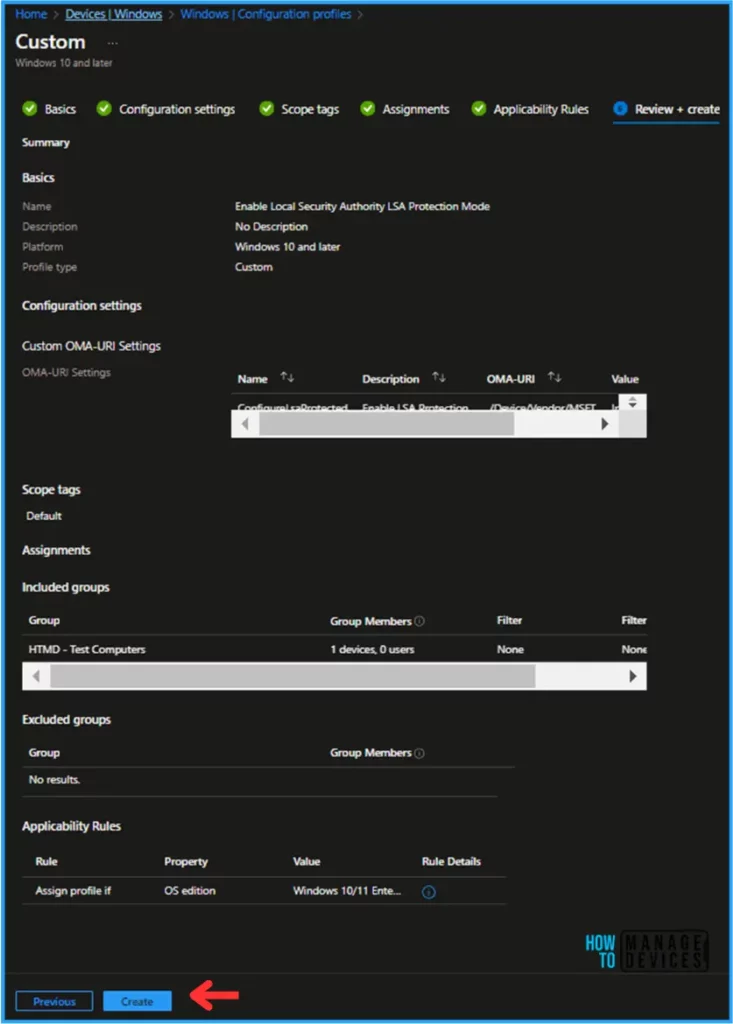
In the Basics section, enter the Custom policy name as “Enable Local Security Authority LSA Protection Mode” and click Next.
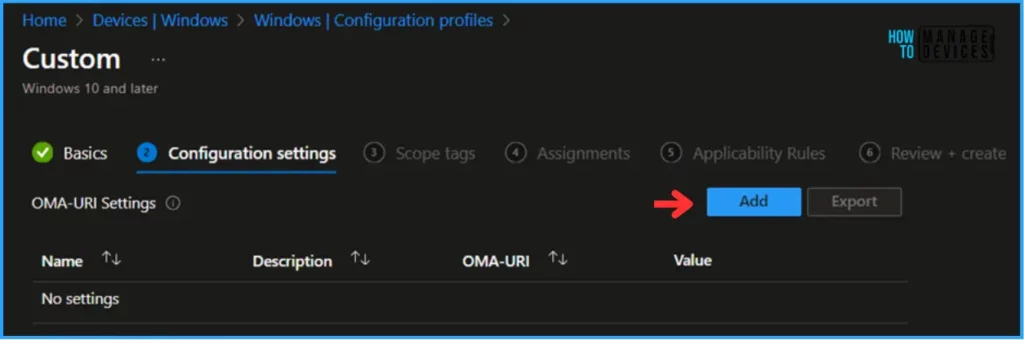
This is a Custom policy, so we must manually add OMA-URI Settings under the Configuration Settings pane. For that, click on Add.
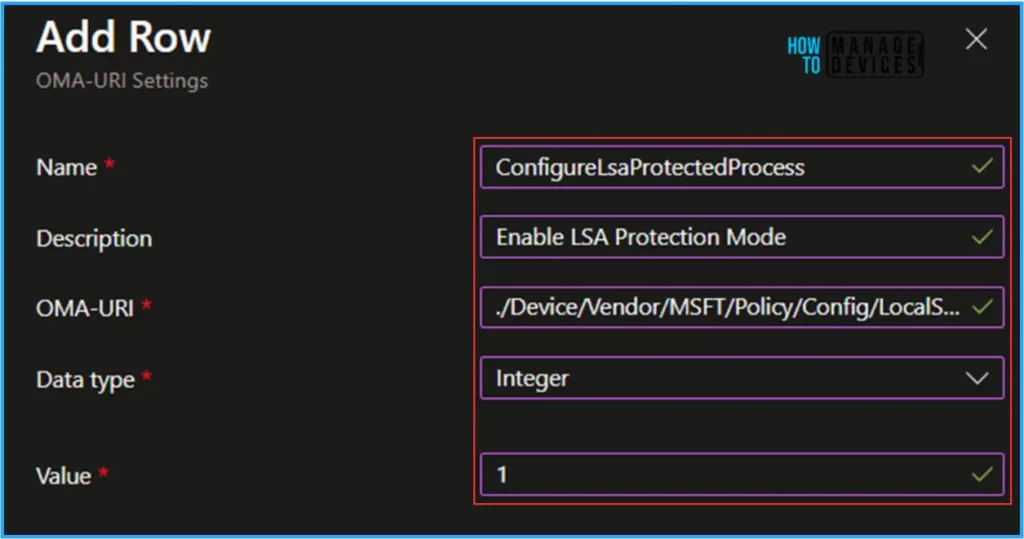
Policy CSP – LocalSecurityAuthority details are available on Microsoft’s Official site. We can find the ConfigureLsaProtectedProcess OMA-URI Settings on the same page.
- ./Device/Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config/LocalSecurityAuthority/ConfigureLsaProtectedProcess
| Scope | Editions | Applicable OS |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ Device ❌ User | ✅ Pro ✅ Enterprise ✅ Education ✅ Windows SE ✅ IoT Enterprise / IoT Enterprise LTSC | ✅ Windows 11, version 22H2 [10.0.22621] and later |
To configure the policy for our current requirements, you must provide the details below on the OMA-URI Settings Add Row pane. Once you have added all the details, click on the Save option.
On the next page, leave the Scope tags as Default. Alternatively, you can select any custom scope tags available in the tenant.
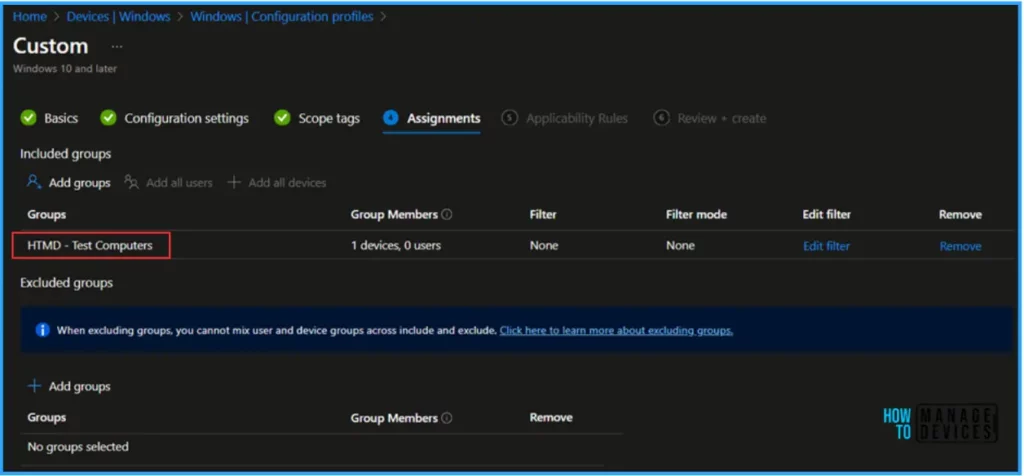
Click on Next and assign the policy to HTMD – Test Computers. In the Included Groups option, click on Add Groups and select the required device group. As discussed earlier, this policy is only supported for Devices, not for Users.
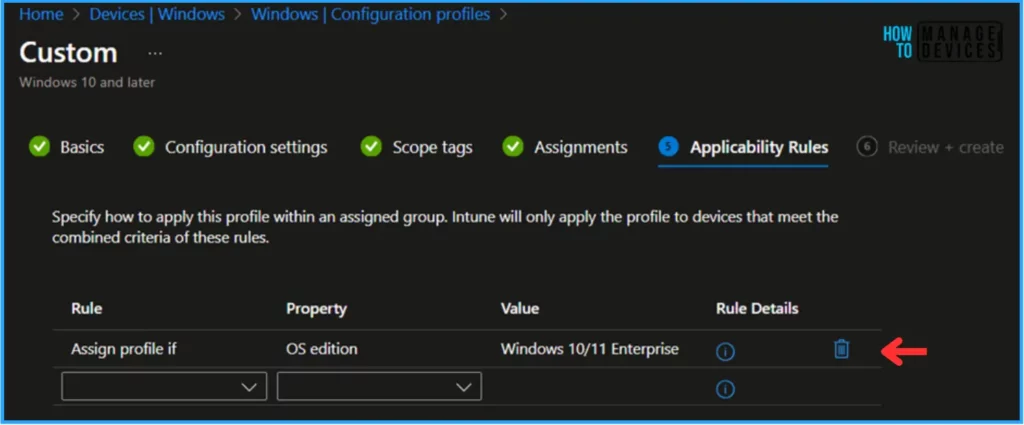
In the Applicability Rules pane, you can set the rule according to your requirements. My test device runs Windows 11 23H2 Enterprise Edition, and I have set the OS edition value to Windows 10/11 Enterprise. Therefore, the policy will only apply in production scenarios when the rule is satisfied; otherwise, it will show as “Not applicable” on the monitoring page.
Please take a moment to carefully review all the settings you’ve defined for the “Enable Local Security Authority LSA Protection Mode” policy on the “Review + Create” page. When you’re ready, select “Create” to implement the changes.
Monitor Enable LSA Protection Mode Policy in Intune
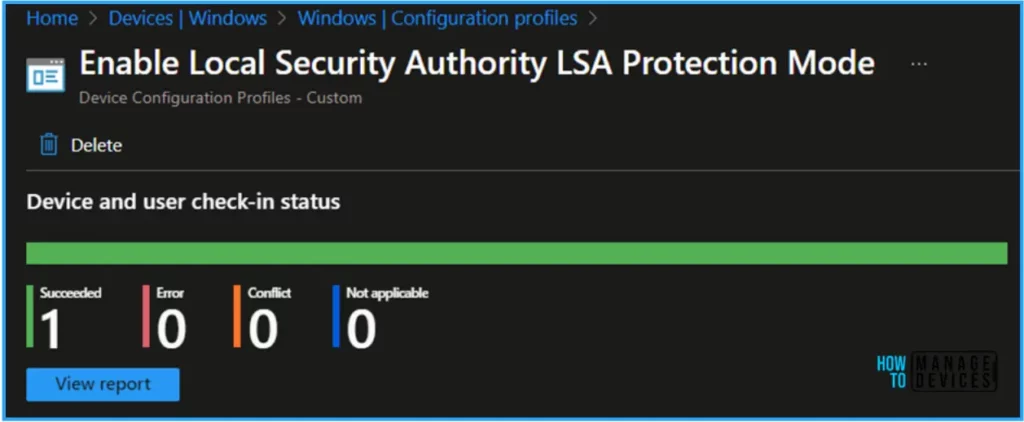
The policy has been deployed to the Microsoft Entra ID groups. So once the targeted devices are synced, it will take effect as soon as possible. To monitor the policy deployment status from the Microsoft Intune Portal, follow the steps below.
Navigate to Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles > Search for the “Enable Local Security Authority LSA Protection Mode” policy. The deployment status will appear under the Device and User check-in status.
End User Experience – Enable LSA Protection Mode Policy
Log in to your targeted device, and here I am, trying to test whether the “Enable Local Security Authority LSA Protection Mode” policy is working as expected.
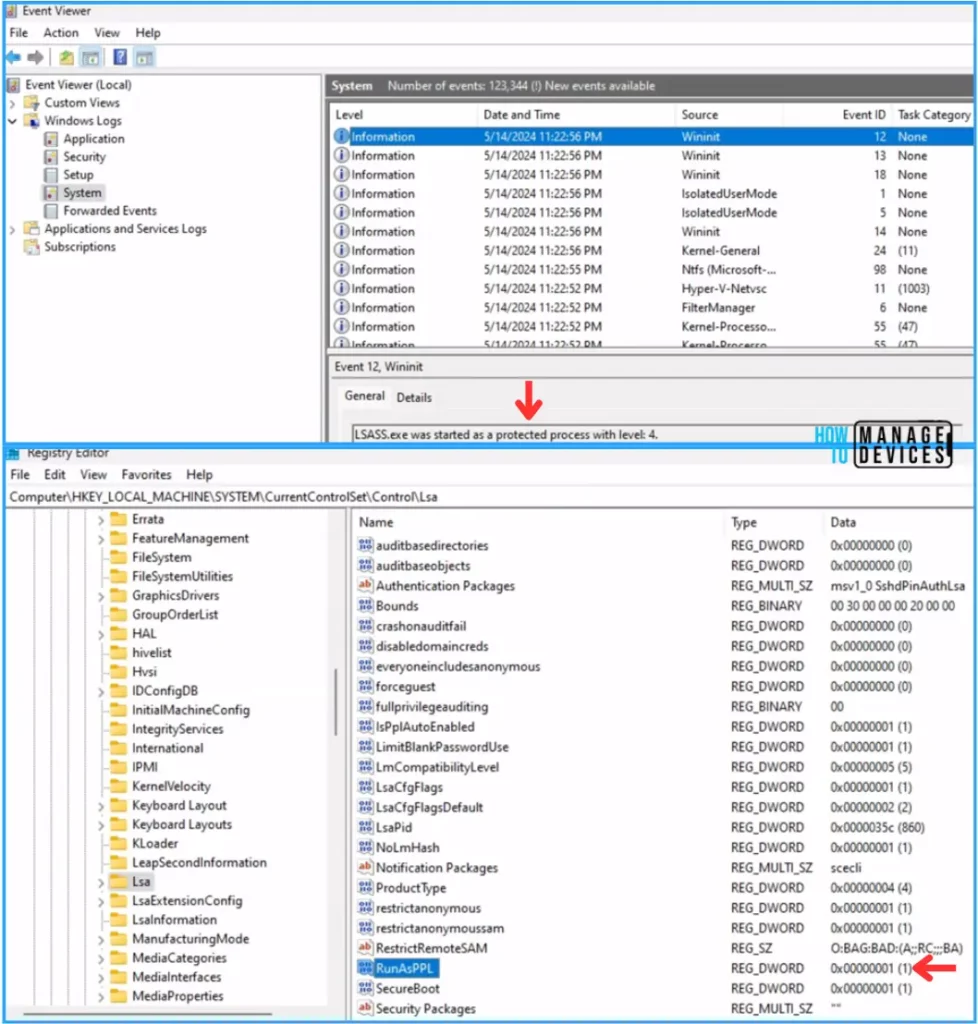
Open Event Viewer. Navigate to Windows Logs > System and search for Log Source Wininit. You can see Event ID 12, and it states that LSASS.exe was started as protected process with level:4
You can also confirm the successful Policy deployment with the Systems Registry for that open Registry Editor. Navigate to Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa path. You will find the new registry entry, ie. RunAsPPL, and the value is (1).
I appreciate you taking the time to read my article. I’m excited to see you in the upcoming post. Continue to support the HTMD Community.
We are on WhatsApp now. To get the latest step-by-step guides, news, and updates, Join our Channel. Click here. HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
Vaishnav K has over 10+ years of experience in SCCM, Device Management, and Automation Solutions. He writes and imparts his knowledge about Microsoft Intune, Azure, PowerShell scripting, and automation. Check out his profile on LinkedIn.

Don’t forget to mention this only works for windows 11 (Windows 11, version 22H2 [10.0.22621] and later), most companies still run win 10.
Hi Luis, ConfigureLsaProtectedProcess official MS page (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/client-management/mdm/policy-csp-lsa#configurelsaprotectedprocess) Applicable OS mentioned as Windows 11, version 22H2 [10.0.22621]. Since it supported to Windows 10 also. Raised a feedback concern with Microsoft.