Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to manage Windows Subsystem for Linux using Intune Policy. Microsoft Intune Settings Catalog added settings to the Windows settings catalog for Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
These Intune settings enable Intune integration with WSL so admins can manage deployments of WSL and control Linux instances themselves. Administrators should ensure that necessary settings are configured to enable access.
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) lets developers run a GNU/Linux environment, including most command-line tools, utilities, and applications directly on Windows, unmodified, without the overhead of a traditional virtual machine or dual-boot setup.
WSL 2 is a new version of the Windows Subsystem for Linux architecture that powers the Windows Subsystem for Linux to run ELF64 Linux binaries on Windows. Its primary goals are to increase file system performance, as well as add full system call compatibility.
Windows Subsystem for Linux and Windows Subsystem for Android also help IT Admins and Developers to test and run the programs/applications compatible with those operating systems. The Windows Sandbox feature also helps IT Admins perform the application packaging process with Cloud PC.
- How To Install And Use Linux On Windows 11 With WSL
- Windows 11 Cloud PC Enable Windows Subsystem For Linux Android Sandbox And Hyper-V
Manage Windows Subsystem for Linux using Intune Policy
By following these steps, you can effectively manage Windows Subsystem for Linux using Intune. This allows you to control the process on Intune-managed devices, Starting with the Intune 2310 October Update, You can now able to Import and Export Settings Catalog Policy from the Intune Admin Center.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune Admin portal https://intune.microsoft.com/.
- Select Devices > Configuration profiles > Create profile.
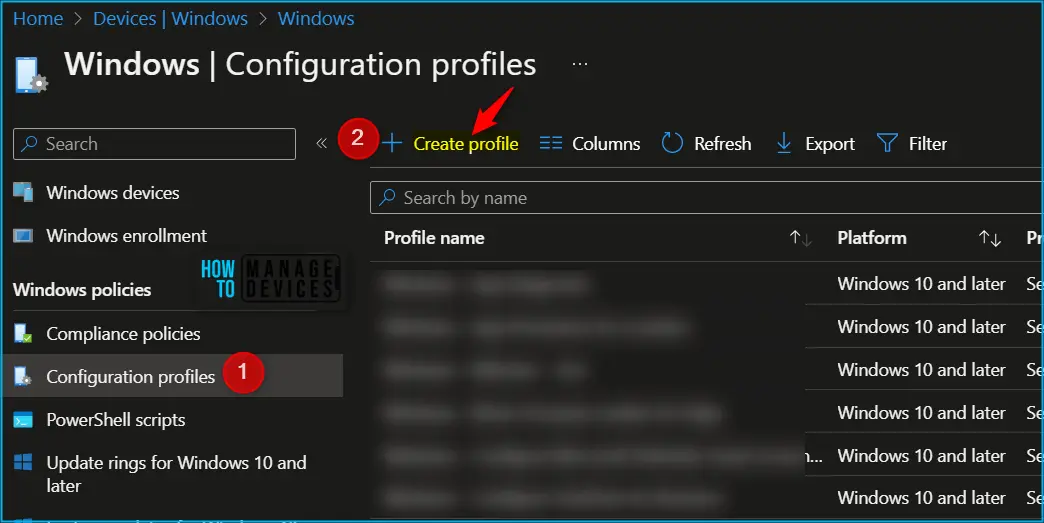
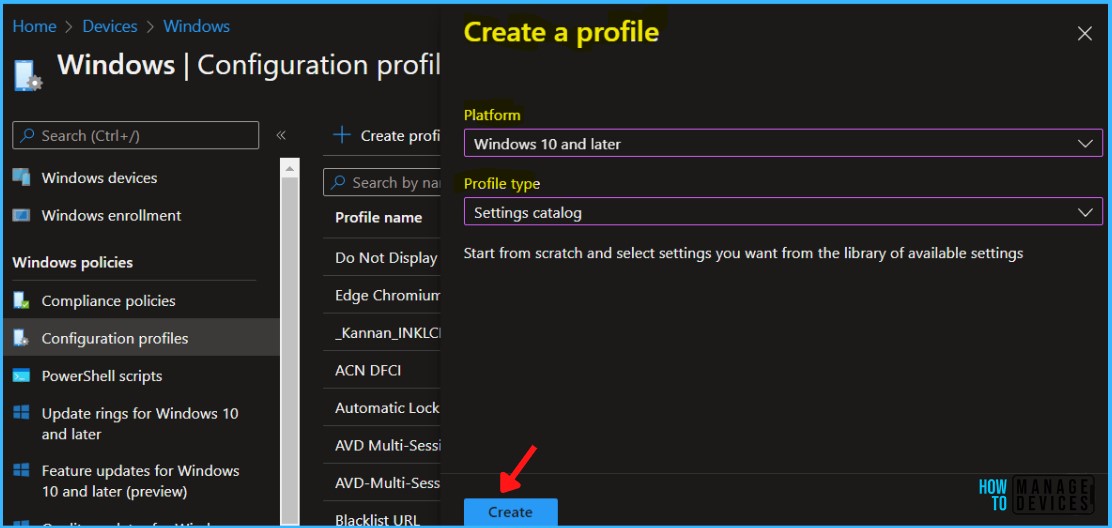
In Create Profile, Select Windows 10 and later in Platform, Select Profile Type as Settings Catalog. Click on Create button.
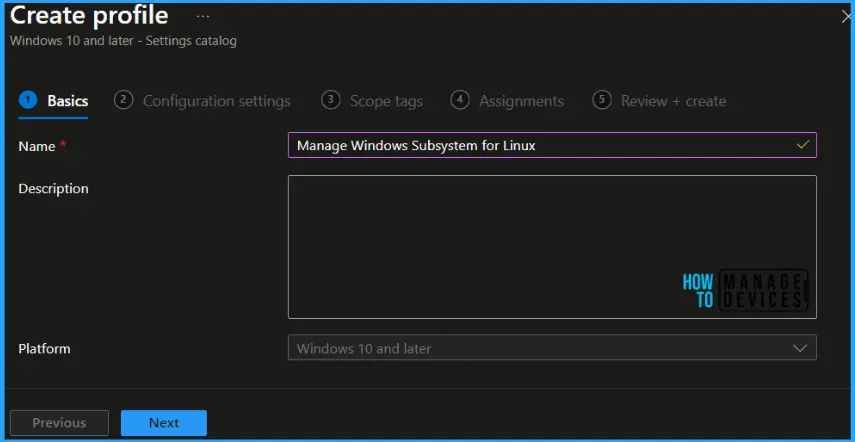
In Basics, enter the descriptive name for the new profile. For example, Manage Windows Subsystem for Linux, add a description for the profile to understand the policy usage and Select Next.
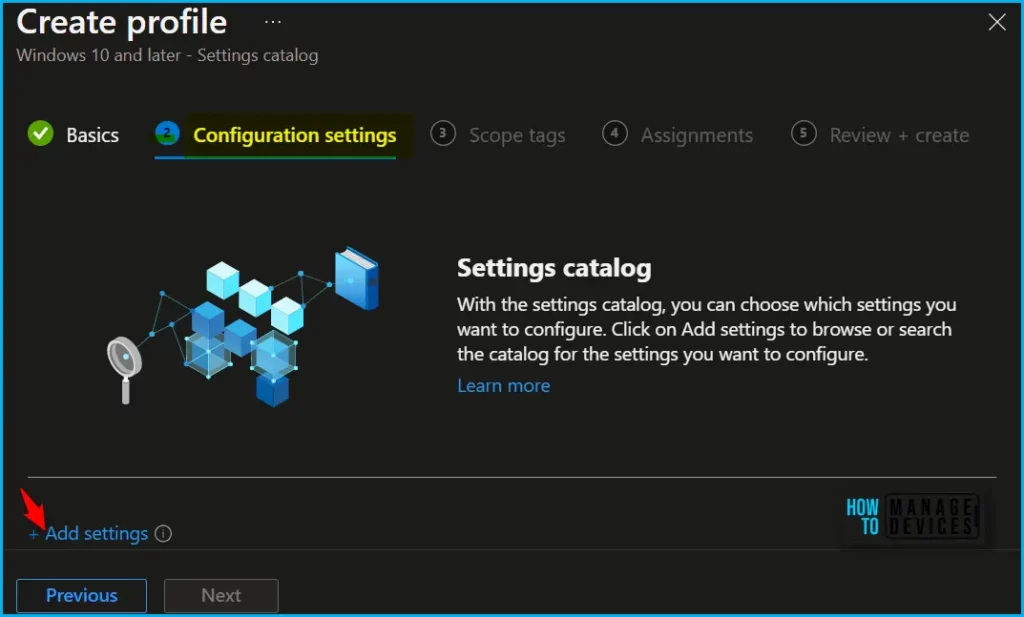
On the Configuration settings tab, With the settings catalog, you can choose which settings you want to configure. Click on Add Settings to browse or search the catalog for the settings you want to configure.
Search for “Windows Subsystem for Linux”. Select the “Windows Subsystem for Linux” from the search result. Select the settings list, here, you will find 12 settings in the “Windows System For Linux” category.
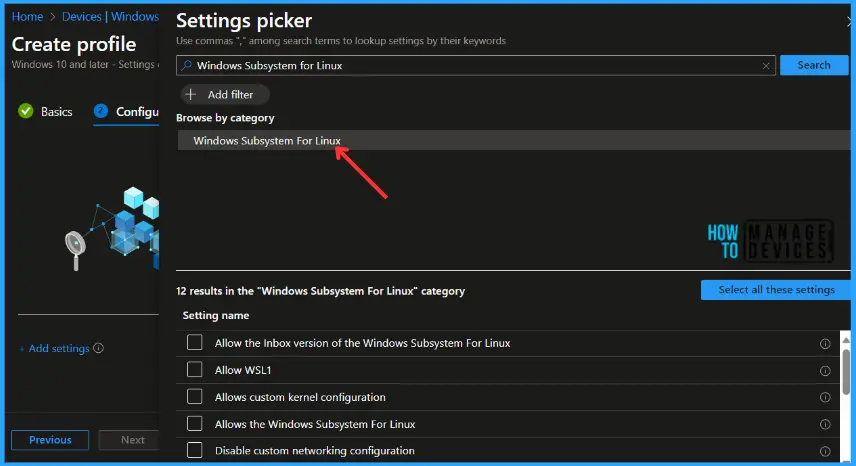
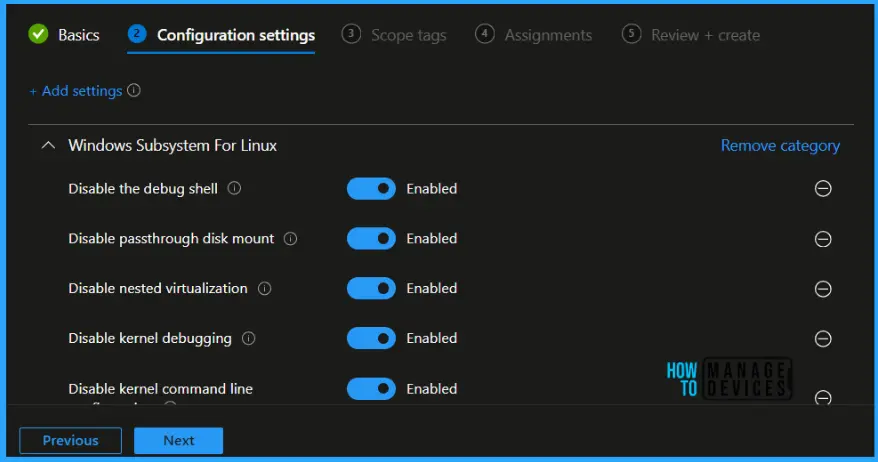
The next step is to toggle the switch to Enabled. Once you enable the option, the selected setting will appear, and click on Next.
- Disable the debug shell – When set to disabled, this policy disables the debug shell (wsl.exe –debug-shell). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Disable passthrough disk mount – When set to disabled, this policy disables passthrough disk mounting in WSL2 (wsl.exe –mount). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Disable nested virtualization – When set to disabled, this policy disables nested virtualization configuration via .wslconfig (wsl2.nestedVirtualization). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Disable kernel debugging – When set to disabled, this policy disables kernel kernel debugging configuration via .wslconfig (wsl2.kernelDebugPort). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Disable kernel command line configuration – When set to disabled, this policy disables kernel command line configuration via .wslconfig (wsl2.kernelCommandLine). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Disable firewall configuration – When set to disabled, this policy disables firewall configuration via .wslconfig (wsl2.firewall). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Disable custom system distribution configuration – When set to disabled, this policy disables custom system distribution configuration via .wslconfig (wsl2.systemDistro). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Disable custom networking configuration – When set to disabled, this policy disables custom networking configuration via .wslconfig (wsl2.networkingmode). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Allows the Windows Subsystem For Linux – When set to disabled, this policy disables access to the Windows Subsystem For Linux for all users on the machine.
- Allows custom kernel configuration – When set to disabled, this policy disables custom kernel configuration via .wslconfig (wsl2.kernel). This policy only applies to Store WSL.
- Allow WSL1 – When set to disabled, this policy disables WSL1. When disabled, only WSL2 distributions can be used.
- Allow the Inbox version of the Windows Subsystem For Linux – When set to disabled, this policy disables the inbox version (optional component) of the Windows Subsystem For Linux. If this policy is disabled, only the store version of WSL can be used.
Using Scope tags, you can assign a tag to filter the profile to specific IT groups. One can add scope tags (if required) and click Next to continue.
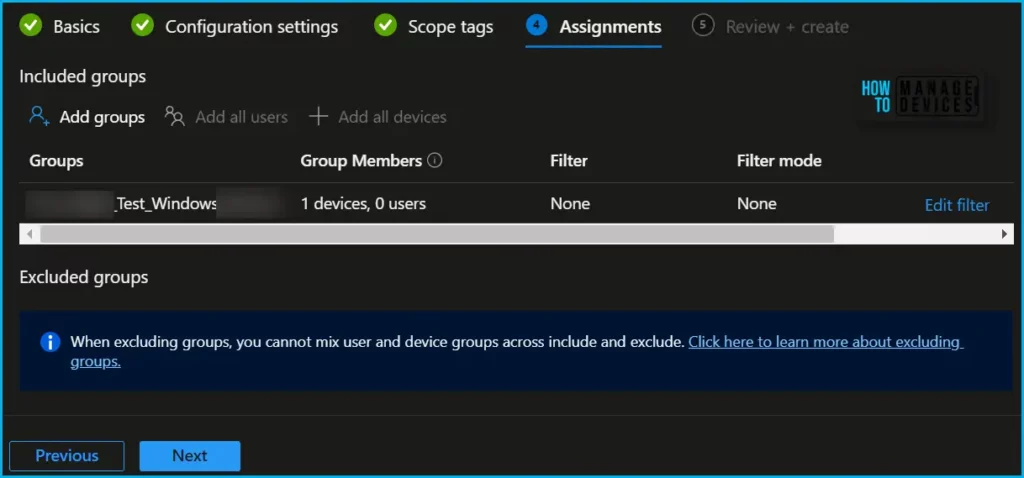
Now in Assignments, in Included Groups, you need to click on Add Groups, choose Select Groups to include one or more groups, and click Next to continue.
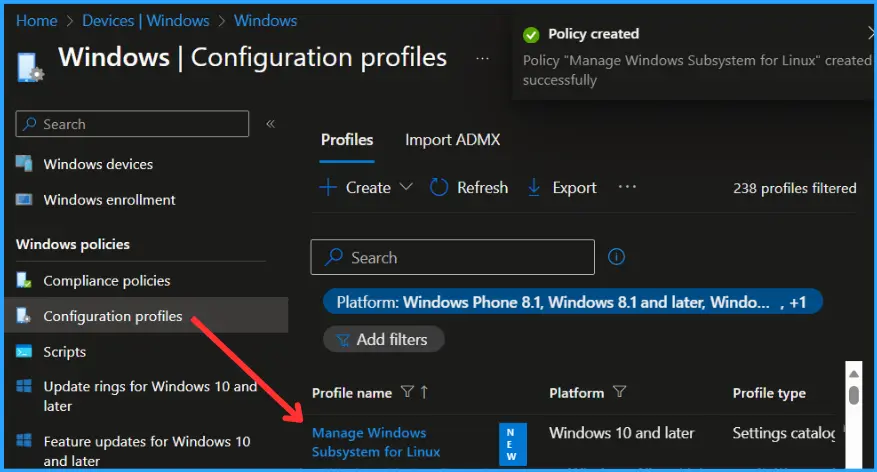
In the Review + Create tab, you need to review your settings. After clicking Create, your changes are saved, and the profile will be assigned to the added devices group.
A notification will appear automatically if you see it in the top right-hand corner. You can easily see that the Policy “Manage Windows Subsystem for Linux” was created successfully. Also, if you check the Configuration Profiles list, the Policy is visible there with the tag NEW.
Monitor Windows Subsystem for Linux Policy Deployment
Intune provides several features to monitor and manage device configuration profiles. Once the device groups will receive your profile settings when the devices check in with the Intune service. The Policy applies to the device.
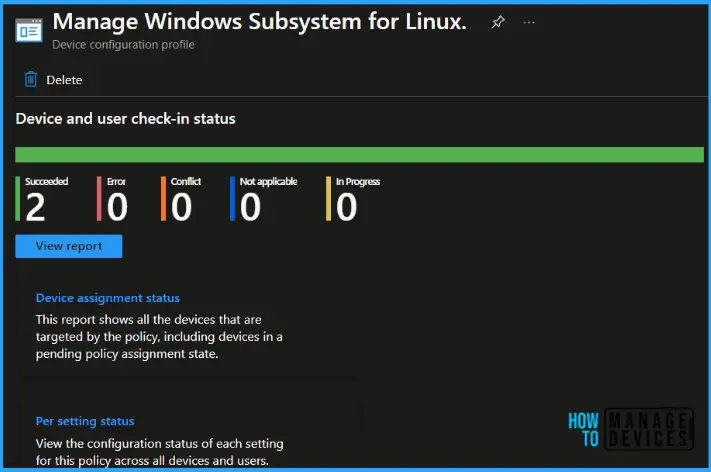
To monitor Intune policy assignment, from the list of Configuration Profiles, select the policy you targeted, and here you can check the device and user check-in status. If you click View Report, additional details are displayed. Additionally, you can quickly check the update as Device and user check-in status reports.
Monitor Event Log for Windows Subsystem for Linux
Once you target the Windows Subsystem for Linux using Intune. The event IDs 813 or 814 can indicate that a string policy has been applied to Windows 10 or 11 devices. These event IDs can provide valuable information about the policy that has been applied, including the exact value of the policy enforced on those devices.
In the case of the policy mentioned earlier, which is for Windows Subsystem for Linux, event ID 814 would be used to indicate that the string policy has been applied, and you can view the specific value of the policy.
To confirm this, check the Event log path – Applications and Services Logs – Microsoft – Windows – Devicemanagement-Enterprise-Diagnostics-Provider – Admin.
If you found any issue while deploying the policy to Windows devices, there are several checks and steps you may follow to troubleshoot security policy deployment issues with Intune.
We are on WhatsApp. To get the latest step-by-step guides and news updates, Join our Channel. Click here –HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
About Author – Jitesh, Microsoft MVP, has over six years of working experience in the IT Industry. He writes and shares his experiences related to Microsoft device management technologies and IT Infrastructure management. His primary focus is Windows 10/11 Deployment solution with Configuration Manager, Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT), and Microsoft Intune.
