Let’s discuss the topic Reboot the VM from Azure Portal Vs Operating System. Another point that I want to discuss is Turn OFF the VM from Azure Portal Vs Turning OFF the VM from Operating System. More details on Soft reboot and hard reboot of Azure VMs.
Let’s check and confirm whether the Restart of Azure VM from the portal initiates the deallocation of resources for a fraction of a second. This deallocation of resources might create issues if you are doing it for thousands of AVD (aka Azure Virtual Desktop) VMs.
The deallocation of hardware resources could cause a bigger problem for your VDI infra if the Microsoft region or Availability Zone is having hardware availability issues. In that scenario, you can’t get the AVD VMs back online!
This could create priority 1 tickets because thousands of users might not be able to log in and work. In this post, let us understand the basic difference between Turning OFF or rebooting the Azure VM from the Azure portal and Turn OFF or rebooting the VM from the operating system.
- Availability Set for Azure VMs Step by Step Guide
- Use Managed Identities for Azure Resources | How to Guide
Reboot the VM from Azure Portal Vs Operating System | Differences
Let’s analyze the differences between Reboot from the Azure portal and the Operating system. Here we will discuss what happened in the background and what impact it will do when we Turn OFF or reboot the Azure VM from the portal Vs Turn OFF or reboot the VM from the operating system.
Basically, there is not much difference in the billing perspective when we reboot the VMs from the Azure portal or operating system, the only difference we can see is on the logging part.
If we reboot the VM from Azure Portal, we can see its log of who initiated this reboot in the Activity Log option which we get on the Azure Portal Virtual Machine page.
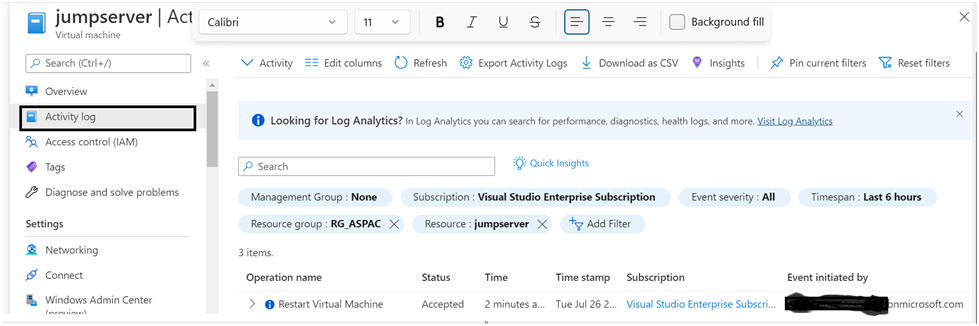
Reboot the VM from Azure Portal – Rebooted by the user (Customer Initiated)
Let’s check the VM reboot initiated from the Azure Portal scenario first. I have navigated to the VM page and initiated the reboot from the VM Overview page command menu. You can check more details in the below screenshot.
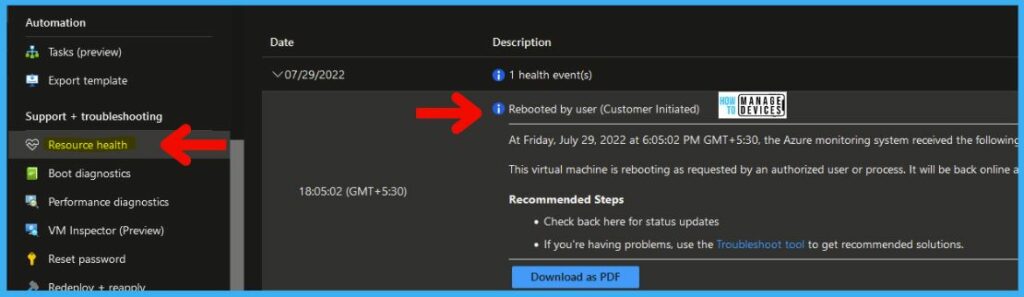
You can check and confirm the activities from Azure Portal Activity logs as mentioned in the above section. You can also check the Resource Health tab from the Azure Virtual Machine page in the post as shown below.
- On Friday, July 29, 2022, at 6:05:02 PM GMT+5:30, the Azure monitoring system received the following information regarding your Virtual machine:
- This virtual machine is rebooting as requested by an authorized user or process. It will be back online after the reboot completes.
NOTE! – I don’t see any deallocation of resources (hardware) during the reboot that is initiated from the Azure portal.
- Improve VM Network Performance Using Azure Proximity Placement Groups
- Step by Step Guide to Configure Azure Bastion Host
Reboot the VM from Windows Operating System
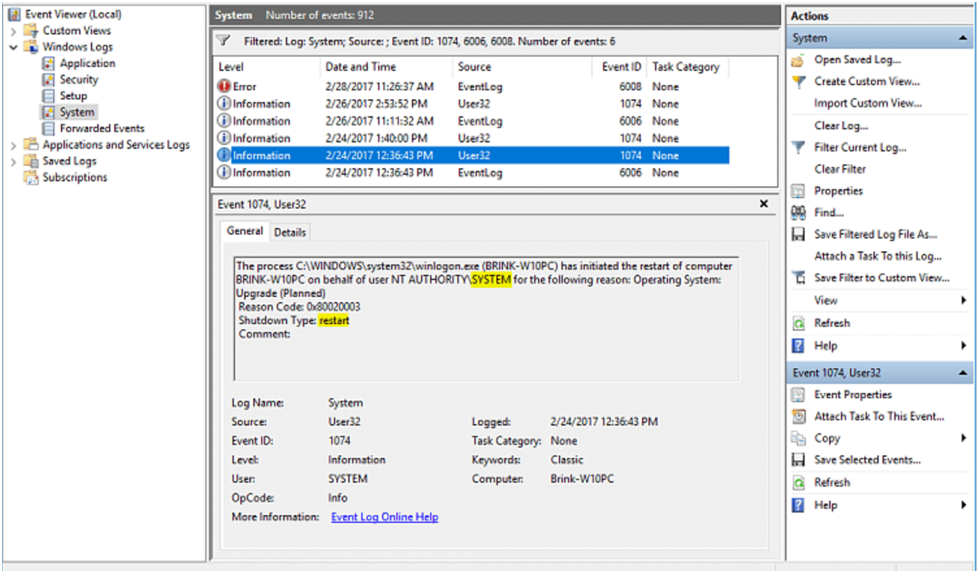
Let’s check the reboot of the VM from the Windows Operating System. If we reboot the VM from Operating System we can find the event in the system logs. The event ID is 1074.
NOTE! – You won’t see any activity on Azure portal for the reboot initiated from the operating system.
Soft Vs. Hard Reboot
Software reboot of a computer is the action that uses to restart a PC or Server properly without switching it off abruptly. A soft reboot always gives the operating system a chance to follow a standard stop or restart process as per the best practices whereas a hard reboot of a PC/Laptop/Server is just the opposite of a soft reboot.
A hard reboot is an action that abruptly stops pc/laptop/server by removing power or any other component such as disk or memory while the operating system is running. A hard reboot can cause a severe impact on the operating system and the entire PC/laptop/server can get crashed.
A hard reboot is helpful only in some extreme situations, not all situations. You must avoid all the hard reboot situations.
Azure VM Soft Reboot Vs. Hard Reboot
As per the test conducted by Azure portal based reboot and Operating System based reboot, both types of Azure VM reboots are Soft reboots.
I don’t think there is any hard reboot option available from the Azure portal or inside the VM’s operating system. If you initiate the Restart from the Azure portal, this Restart action gives instruction to the operating system to initiate a normal restart of the VM.
NOTE! – If that reboot instruction to the operating system is failed the backup plan might be to force a reboot (Hard reboot) of the VM. I have not tested this scenario. Have you seen a hard reboot in Azure VM context ever?
From Azure VM Windows OS perspective, both STOP and RESTART call from the outside operating system (from Portal or PowerShell). The event ID is 1074 for the restart and or stop from the Azure portal.
I get the same event for force STOP or Restart from Azure ports. So from an OS perspective, both are the same. It’s a soft reboot.
The process C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe (Prod-Win20) has initiated the shutdown of computer Prod-Win20 on behalf of user NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM for the following reason: Other (Planned)
Reason Code: 0x80000000
Shutdown Type: shutdown
Comment: Calling CleanShutdown by wvchelper
Reason for shutdown: Stop callTurn OFF or Stop the VM from Azure Portal Vs Operating System
There is a difference in the billing perspective when we Turn OFF/STOP the VMs from the Azure portal and Turn OFF the Azure VMs from the operating system.
When we Turn OFF the Azure VMs from Operating System it goes into a “Stopped” state at this time it does not release any Azure VM compute resources (aka hardware allocation).
This is the reason why we still are paying for these resources even if VMs are in a stopped state. If you turn off the VM from Operating System, then it won’t get the deallocation state. Hence, you end up paying for all the resources.
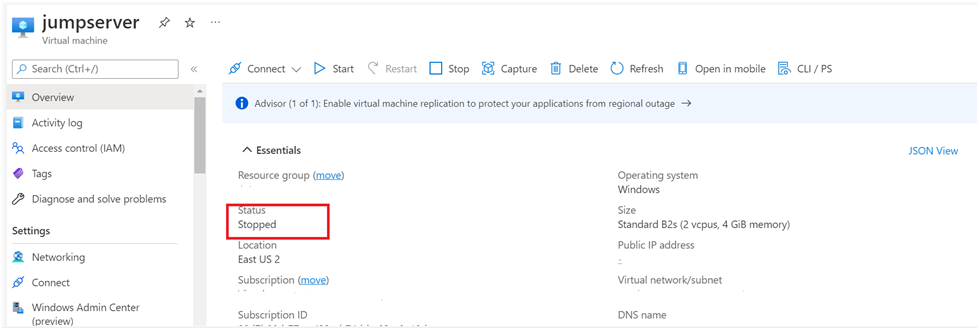
When you Stop the Azure VM by going into Azure Portal (or use the Azure CLI or Azure PowerShell), it will release the Azure VM compute resources (aka hardware allocation). Check out the Windows event log entry (Event ID = 1074) related to the Azure portal STOP action.
The process C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe (Prod-Win20) has initiated the shutdown of computer Prod-Win20 on behalf of user NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM for the following reason: Other (Planned)
Reason Code: 0x80000000
Shutdown Type: shutdown
Comment: Calling CleanShutdown by wvchelper
Reason for shutdown: Stop call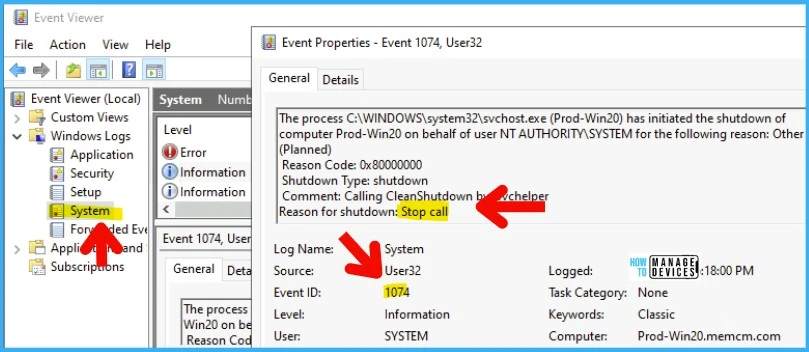
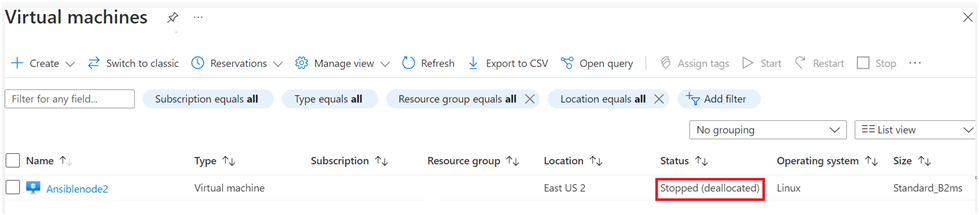
The Turn Off action from Azure Portal deallocate the hardware resource (compute related) hence you will not have to pay for all the resources. The recommendation is to STOP the Azure VM from the Azure portal rather than shutting it down from the operating system.
NOTE! – You will still get charges for storage and some other resource that are associated with the VM unless you use an ephemeral disk etc for Azure VMs.
- VM goes in a Stopped (deallocated) state.
Resource -> Understand a system reboot for an Azure VM – Virtual Machines | Microsoft Docs
Author
Abhinash has over 5 years of working experience in the IT Industry. His primary focus area is Azure IAAS, PAAS & SAAS, and Azure DevOps. He writes and shares his experiences related to Cloud Computing, mainly Azure.

Does rebooting or shutting down from Azure portal is soft or hard reboot?
Both are soft reboot I think…
It’s always a soft reboot from an OS perspective. I have updated the post with one example.