Microsoft Connected Cache in Azure (Microsoft’s answer to bandwidth issues with DO?) is the topic I will cover in this post.
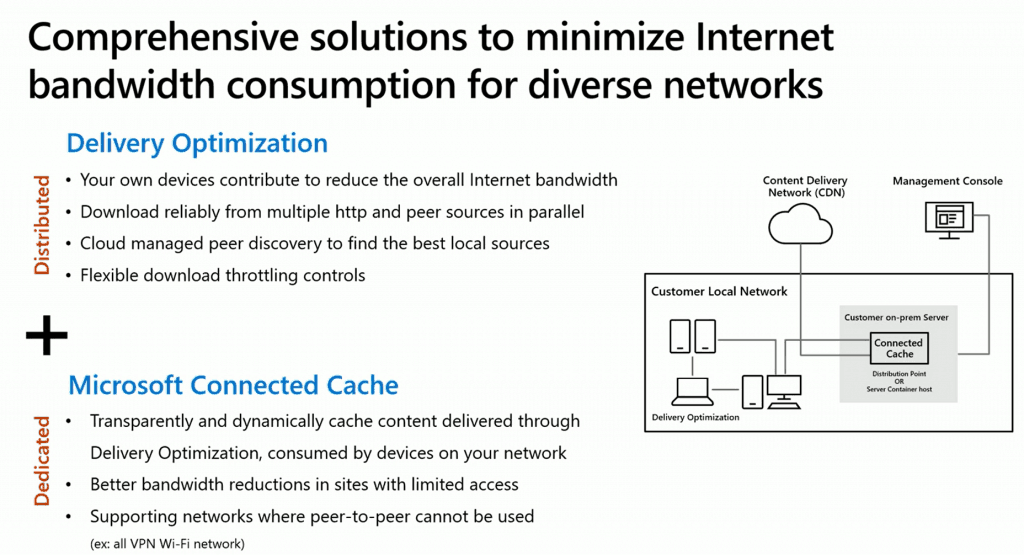
The cache server operates as an on-demand transparent cache that stores content downloaded by Delivery Optimization. By configuring client settings, you can restrict access to this server so that it is only available to members of the local Configuration Manager boundary group.
It’s important to note that this cache is separate from Configuration Manager’s distribution point content, providing an added layer of versatility for content management within your network.
All the screenshots are taken from Andy Rivas’s and Narkis Engler’s Ignite session demo. More details about the session and recording are below this post.
Ignite 2019 Coverage
- Microsoft Endpoint Management SCCM Intune Windows Updates
- Microsoft Endpoint Manager is the future of SCCM Intune MEMMI MEMCM
- iOS Android macOS Mobile Enrollment Options with Intune
- Basics of Windows Dynamic Update Explained Update Management
- WVD End User Experience Availability Updates
- MSIX Updates from Ignite Reliability Network Disk-space
- Microsoft Learning Certification Exams Updates
- Intune Reporting Strategies Advanced Reporting
- Intune Endpoint Security Policies Enhancements
- Intune Policy Sets Collection of Workflows
- Windows Autopilot Updates Timelines
- Microsoft Connected Cache Container Instances in Azure via Intune
- SCCM and Microsoft Connected Cache Integration
- Windows 10 Bandwidth Management DO Delivery Optimization with LEDBAT in LAN
Microsoft Connected Cache Container Instances in Azure
Microsoft Connected Cache is now in the private preview stage. The post below provides more details about the private preview and roadmap. The connected cache node instances will be on a server in your on-prem data center.
Connected Cache Container is a Linux container, and you can run it on:
- Connected Cache Container Host
- Windows Server 2019
- Connected Cache Container
- Linux Server Ubuntu Server 16.04
- Connected Cache Container
- Windows Server 2019
NOTE 1 – You might need Azure tools (like Azure IOT Edge runtime) to securely deploy provision and manage these Microsoft-connected cache instances.
NOTE 2—Microsoft E3 and EMS A3 licenses (more details coming soon) are enabled to use Microsoft Connected cache managed in Azure.
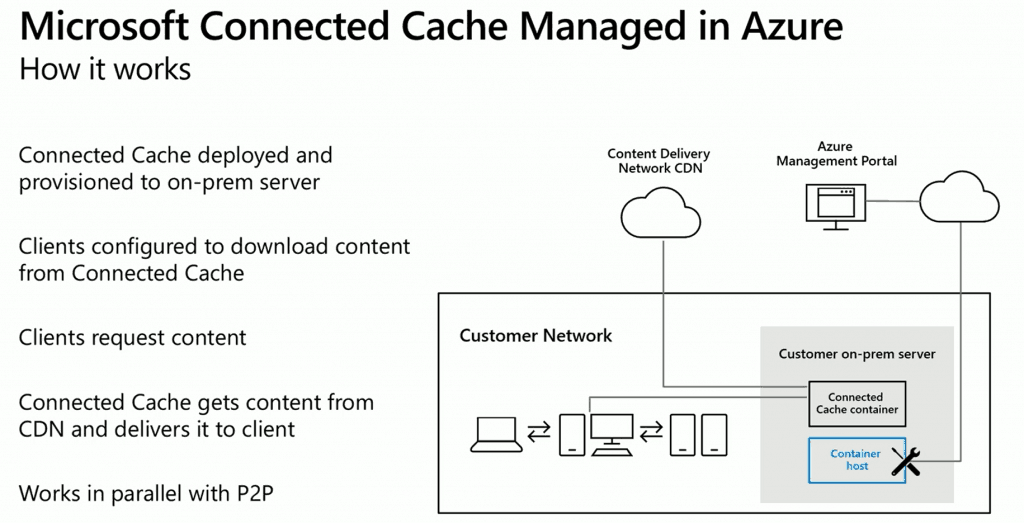
How Microsoft Connected Cache in Azure Works?
- Connected Cache Container Host
- Connected Cache Container Instances (Linux container) deployed onto your Windows 2019 or Ubuntu 16.04
- Clients configured to download the content from Connected Cache
- Configure the policies through Intune/Airwatch/Mobileiron (MDM solutions)
- Group Policy
- DHCP options (coming in the 2020 H1 timeline)
- Windows Clients request the content from the Connected Cache Container.
- Connected Cache Container gets the content from CDN and delivers it to the client.
- Once the content is available on the client’s devices, the DO peer-to-peer can be used to transfer the content between clients
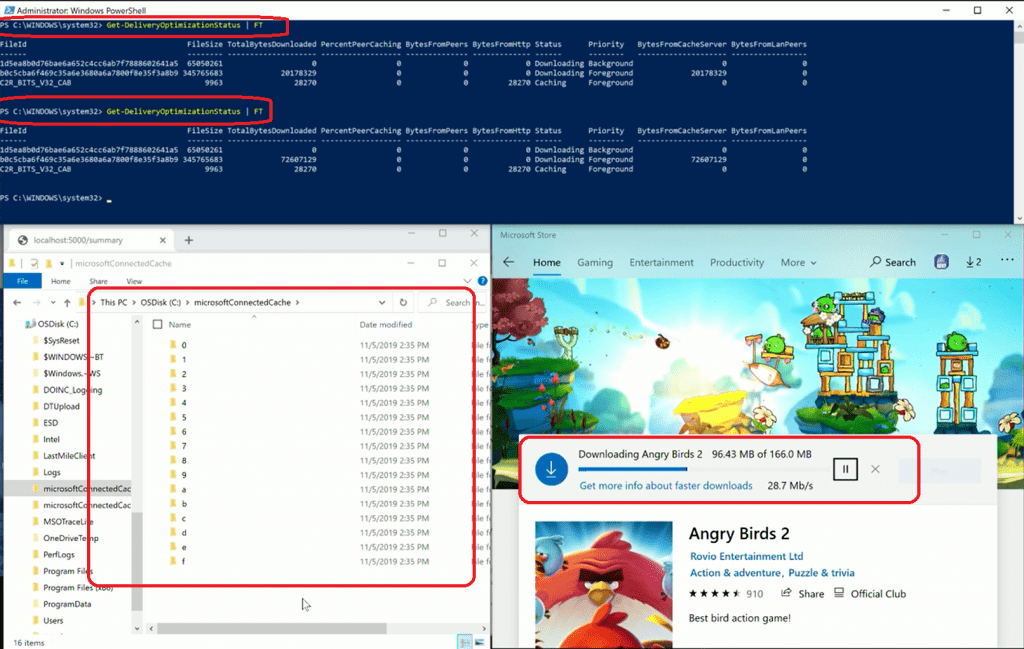
IT Admin Testing Experience with Connected Cache in Azure
- You can download an app from the Microsoft store
- You can see the files getting stored in the Connected Cache container
- You can use the following PowerShell commands to get more details
- Get-DeliveryOptimizationStatus | FT
PS C:\Users\Anoop C Nair> Get-DeliveryOptimizationStatus | FT
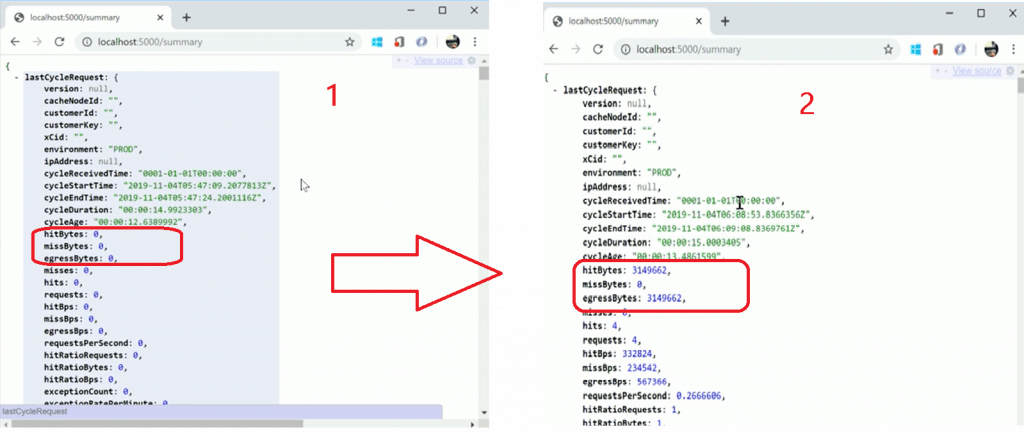
hitBytes missBytes egressBytes Summary
NOTE! – Microsoft Connected Cache Summary Report (shown below) refreshes every 15 secs.
- Hitters – what are Bytes coming from the cache server
- Miss bites – what are the Bytes not there in Cache Servers that the Cache server had to go out and retrieve from the Internet?
- egressBytes – What are the Bytes coming OUT from the cache server?
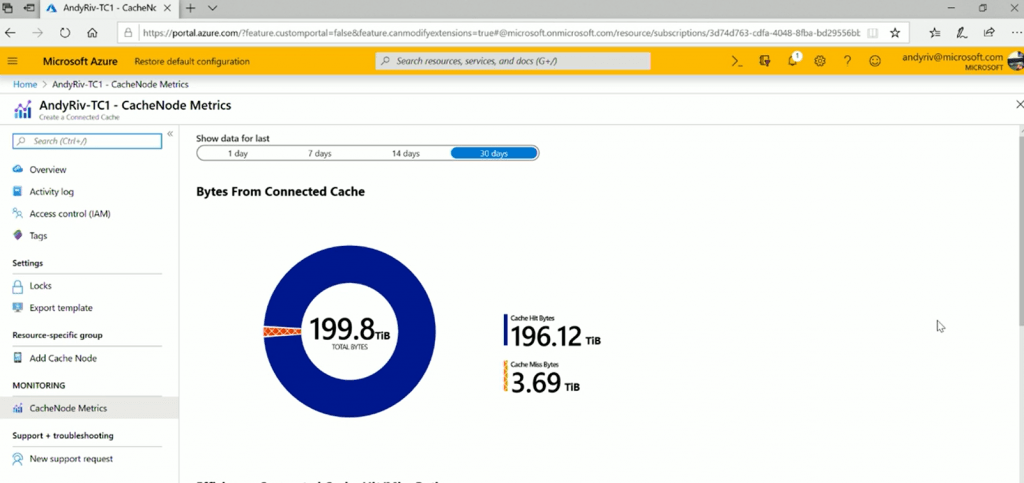
Reporting Options – Microsoft Connected Cache
You can get all the reports in the Azure portal directly from your on-prem Microsoft-connected cache instance via container host connectivity.
- Efficiency: Connected Cache Hit/Miss Ratio
- Bytes from the connected cache
- Connected Cache Hit/Miss Counts
- Connected Cache Hit/Miss Bytes
Connected Cache in Azure Roadmap
- Private preview – Reach out to msconnectedcache at microsoft com
- Blog post details – https://aka.ms/PreviewConnectedCache
Microsoft Solutions to Endpoint Bandwidth Network Issues
Session
Stay current while minimizing network traffic: The power of Delivery Optimization. Session Recording by Andy Rivas & Narkis Engler.
Resources
- Introducing Microsoft Connected Cache: Microsoft’s cloud-managed cache solution
- How to Handle SCCM Bandwidth Issues with Branch Cache Vs. Peer Cache
We are on WhatsApp. To get the latest step-by-step guides and news updates, Join our Channel. Click here –HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
Anoop C Nair is Microsoft MVP! He is a Device Management Admin with more than 20 years of experience (calculation done in 2021) in IT. He is a Blogger, Speaker, and Local User Group HTMD Community leader. His main focus is on Device Management technologies like SCCM 2012, Current Branch, and Intune. He writes about ConfigMgr, Windows 11, Windows 10, Azure AD, Microsoft Intune, Windows 365, AVD, etc.
