Let’s learn how to upgrade the SCUP Environment SCCM System Center Updates Publisher. The new version of SCUP was released a few weeks ago. This post answers the following questions about SCUP Upgrade.
I have also created a video tutorial to help us understand how to upgrade the SCUP version to the latest one. Download the latest version of SCUP 6.0.278.0.
Do we need to uninstall the existing version of SCUP to install the new version? Do we lose all the configurations and data as part of the upgrade?
System Center Updates Publisher (SCUP) is a stand-alone tool that enables independent software vendors (third-party -3rd – applications) or line-of-business application developers to manage custom updates.
Table of Contents
What is Microsoft SCUP?
Let’s discuss the Microsoft SCUP. The section below will help you to see more details.
| What is Microsoft SCUP? |
|---|
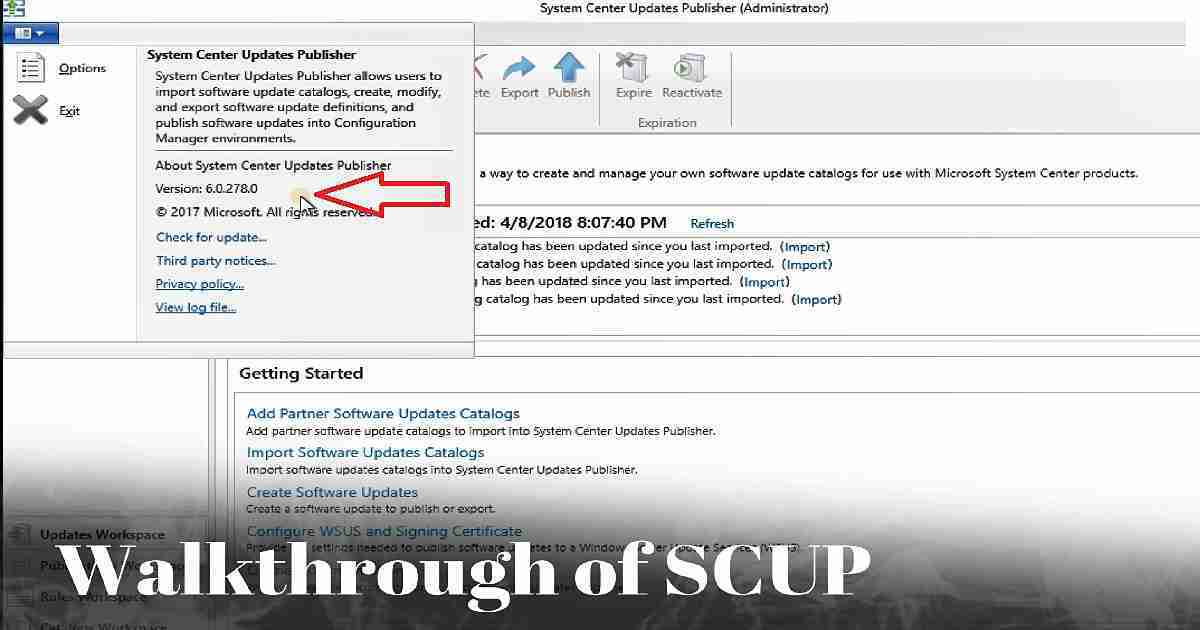
| Version: 6.0.278.0 |
| File Name:- UpdatesPublisher.msi |
SCUP Related Posts
You wanted to learn more about SCUP and its functionality through video tutorials. I recommend reading the previous SCUP posts for more details on this topic.
- SCUP 2017 Preview Installation and Configuration Video Guide
- SCCM SCUP 2017 How to Publish 3rd Party App Patches
- How to Deploy Dell Bios Firmware Updates Via SCUP and SCCM CB
- How Tedious for SCCM Admins to Patch 3rd Party Applications via SCUP
Features of SCUP?
SCUP is a tool for importing updates from external catalogs (non-Microsoft update catalogs). It also enables the modification of updated definitions, including applicability and deployment metadata.
SCUP Upgrade Experience
SCUP is the tool used to export updates to external catalogs. Using SCUP, we can publish updates to a WSUS server.
As I showed in the SCUP Upgrade video tutorial, the SCUP upgrade process is straightforward and smooth. You won’t lose any of your existing configuration.
In my experience, everything configured in the existing version of SCUP will remain the same. The following is the high-level process that I followed to upgrade the SCUP environment.
Download the latest version of SCUP from Microsoft Download Center. The size of the MSI file is not big. It’s only ~5 MB.
The old version of SCUP is installed and configured on the server. There is no need to remove the previous version of SCUP before installing the new one; the latest version will upgrade the previous version.
Once SCUP is successfully installed on the server, we can launch it from the start menu. It will take time for you to launch SCUP for the first time.
This is because all the configuration options will happen in the background once we launch SCUP for the first time.
I will share my detailed review of SCUP in a different post. I’m interested to see the changes Microsoft promised in their SCUP release blog post.
SCUP Prerequisites or Requirements
The following are the prerequisites for the new version of SCUP.
Supported Operating System
- Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016
- A supported Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) console. On Windows Server, install the default Administration Console to meet this requirement.
- For Windows 10, install the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows operating systems.
SCCM Dependency
SCCM 2012 R2 SP2
SCCM 2012 R2 SP1
A supported version of SCCM CB.
SCCM LTSB version 1606
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sNn77zOSiBo
Resources
- System Center Updates Publisher (SCUP) adds support for new OSes
- System Center Updates Publisher (SCUP) Documentation
We are on WhatsApp now. To get the latest step-by-step guides, news, and updates, Join our Channel. Click here. HTMD WhatsApp.
Author
Anoop C Nair is Microsoft MVP from 2015 onwards for consecutive 10 years! He is a Workplace Solution Architect with more than 22+ years of experience in Workplace technologies. He is a Blogger, Speaker, and Local User Group Community leader. His main focus is on Device Management technologies like SCCM and Intune. He writes about technologies like Intune, SCCM, Windows, Cloud PC, Windows, Entra, Microsoft Security, Career etc…